Chapter: Medical Physiology: Membrane Physiology, Nerve, and Muscle : Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
Molecular Mechanism of Muscle Contraction
Molecular Mechanism of Muscle Contraction
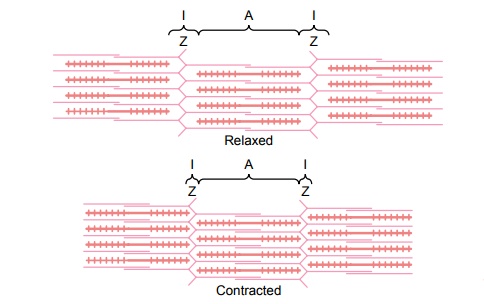
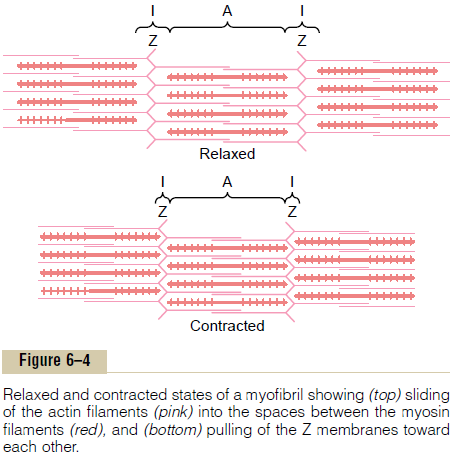
Sliding Filament Mechanism of Muscle Contraction. Figure 6–4 demonstrates the basic mechanism of muscle contraction. It shows the relaxed state of a sarcomere (top) and the contracted state (bottom). In the relaxed state, the ends of the actin filaments extending from two successive Z discs barely begin to overlap one another. Conversely, in the contracted state, these actin filaments have been pulled inward among the myosin filaments, so that their ends overlap one another to their maximum extent. Also, the Z discs have been pulled by the actin filaments up to the ends of the myosin filaments. Thus, muscle contraction occurs by a sliding filament mechanism.
But what causes the actin filaments to slide inward among the myosin filaments? This is caused by forces generated by interaction of the cross-bridges from the myosin filaments with the actin filaments. Under resting conditions, these forces are inactive, but when an action potential travels along the muscle fiber, this causes the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release large quantities of calcium ions that rapidly surround the myofibrils. The calcium ions in turn activate the forces between the myosin and actin filaments, and contrac-tion begins. But energy is needed for the contractile process to proceed. This energy comes from high-energy bonds in the ATP molecule, which is degraded to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to liberate the energy. In the next few sections, we describe what is known about the details of these molecular processes of contraction.
Related Topics