Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Modern Welded Railway Track
Modern Welded Railway Track
Modern Welded Railway Track
Introduction
As mentioned earlier, a rail
joint is the weakest link in the railway track. The ill effects of the rail
joint are well known, including the fact that a track with joints requires
about 30% extra maintenance work as compared to a plain track. The best remedy
for the problems caused by rail joints lies in welding the rails and reducing
the number of joints to the extent possible. The modern welded railway track
incorporates systematic welding of rails, which provides it the potential to
carry trains at faster speeds, provide better riding conditions, and reduce
maintenance costs. The following terms are commonly used with respect to welded
tracks.
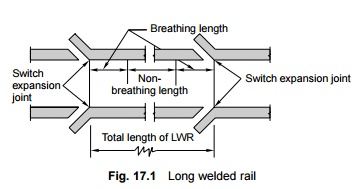
Long
welded rail The long welded rail (LWR) is a welded rail in which
the central portion does not undergo any longitudinal contraction or
expansion due to temperature variations (thermal expansion). Normally, a rail
with a length greater than 250 m on BG and 500 m on MG functions as an LWR
(Fig. 17.1). In the Indian setting, the maximum length of the LWR is normally
restricted to one block section.
Continuous welded rail The
continuous welded rail (CWR) is a type of LWR that continues through
station yards, including points and crossings.
Short welded rail The short
welded rail (SWR) is a welded rail that contracts and expands throughout
its length.
Breathing
length Breathing length is the length at each end of an LWR that is
subjected to expansion or contraction on account of variations in temperature.
Anchor length (la)
The anchor length is the length of the track that is required to resist
the pull exerted by the rail tensor on the rails.
Switch expansion joint The
switch expansion joint (SEJ) is an expansion joint installed at each end
of an LWR to permit the expansion or contraction of the adjoining breathing
lengths due to temperature variations.
Buffer rails Buffer
rails are a set of rails provided at the ends of an LWR to allow the
expansion or contraction of the breathing lengths due to temperature
variations.
Destressing Destressing
is an operation undertaken with or without the use of rail tensors to
attain a stress-free LWR at a specified rail temperature.
Rail temperature This is
the temperature of the rail as recorded by an approved rail thermometer
at the site. This is different from the ambient temperature, which is the
atmospheric temperature as reported by the meteorological department.
Mean rail temperature (tm)
The
mean rail temperature for a section is the average of the maximum and
minimum rail temperatures recorded for the section.
Installation temperature (ti)
This
is the average rail temperature achieved when the rails are being
fastened to the sleepers at the time of installation of LWRs.
Standard installation temperature
(ts) This is the installation temperature at which
a standard gap of 6 mm is provided for fish-plated joints.
Prevailing rail temperature (tp)
This
is the prevailing temperature of the rail at the time of any operation
connected with destressing being carried out.
Stress free temperature (to)
This
is the rail temperature at which the rail is free of thermal stresses.
Destressing temperature (td)
This
is the average rail temperature at the time of the fastening of rails to
sleepers after destressing an LWR without the use of rail tensors.
Related Topics