Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Nursing Health Care Hospital Hygiene Higher secondary school College Notes
Methods of Disinfections and Sterilisation
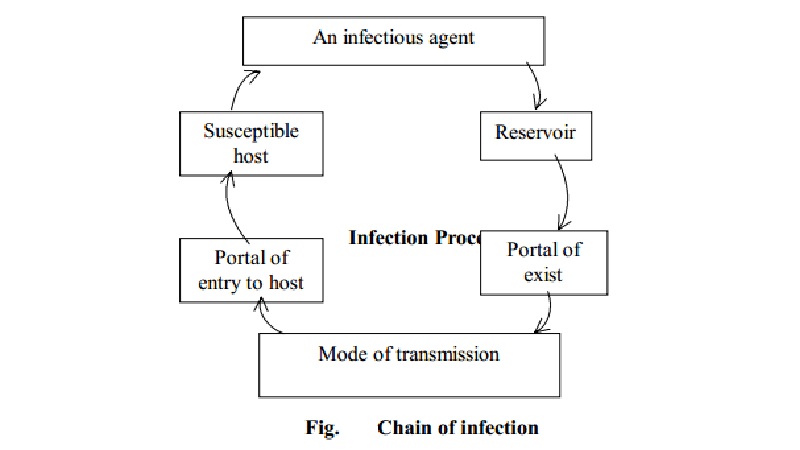
METHODS OF DISINFECTIONS AND
STERILISATION:
1.
Mechanical
a.
Scrubbing
b. Filtration
c.
Sedimentation.
2.
Physical
a.
Moist heat
i.
boiling
ii.
steam under pressure
iii.
pasteurization.
b.
Dry heat. Baking. Incineration
Flaming. Sunlight.
c.
Low temperature.
3.
Chemical. - use of disinfectants
such as Phenol lysol etc.
MECHANICAL:
1. Scrubbing: Hand washing is one of the important procedures of a nurse in order to control and prevent
self-infection as well as cross infection. Scrubbing and washing the hands with
soap and water removes the organisms mechanically.
2.
Filtration: In
laboratories fluids are sterilized by filtration.
The process of filtration aids in retaining certain bacteria.
3.
Sedimentation: It
is used in the purification of water. By
this method the suspending materials together with bacteria settles down in the
bottom of liquid.
PHYSICAL METHODS:
1.Moist
heat:
Boiling - Boiling at 100º C for 3 to 5 minutes kills microorganisms except spore bearing
organisms such as bacillus tetani. There are certain rules to be observed while
boiling.
Scrub and clean the articles to remove organic matter, which
will coagulate around the organisms and protect them.
Articles except the glass should be put at the boiling point
of water (great care should be taken for glass articles, and they should be
wrapped with cloth and put in cold water and then brought to boil).
Articles should be well covered by the water and boiled for
the required length of time.
Steam
under pressure:
Spore bearing organisms are killed by steam under pressure. Autoclave
is an apparatus used for sterilization of articles by steam under pressure.
In this, the steam is allowed to circulate in a closed
container and it is compressed and thereby raises the temperature above the
boiling point of water (121º C).
In this method the articles are sterilized under 15 pounds
pressure of steam for 15 to 20 minutes. Materials sterilized by autoclaving
method are dressings, gloves, linen, syringes, certain instruments and culture
medias.
Pasteurization:
Pasteurization is a method of sterilizing milk. Milk is
heated to a temperature of 60º C for half an hour and rapidly cooled to 13º C.
This aids in destroying all pathogenic organisms and reduces acid-producing
organisms and thus prevents souring of milk.
2). Dry
Heat:
Baking:
This method of sterilization is used in sterilizing
glassware, syringes, needles, culture tubes and medias. Most of the vegetative
forms of bacteria are killed. Spores need to be heated for 1 to 2 hours. The
apparatus used for baking is known as 'hot
air oven'.
Incineration:
In order to destroy all organisms, infected wound dressings,
contaminated materials, garbage and other hospital wastages etc are burnt by
incineration. The apparatus used for this complete burning is incinerator.
Flaming:
This is used in sterilizing platinum loops in laboratory and
also in sterilizing needles and instruments. This aids in killing organisms.
Sunlight:
The ultra-violet rays from sunlight have the effect of
destroying a large number of bacteria. Blankets, pillows, mattress are
disinfected by sunlight. Care should be taken to turn the articles often to
kill the microorganisms on both surfaces.
3). Low
temperature:
Cold has the effect of decreasing or completely stopping the
growth of bacteria. Constant freezing will destroy bacteria.
CHEMICAL METHODS:
Certain chemicals are used in
disinfection of articles like thermometer and also the disinfection of floor
and decontamination of infected linen etc.
Principles to be observed:
1. All articles contaminated with blood, faeces, pus, sputum,
or other substances must be rinsed with cold water to prevent coagulation of
protein material.
2. Use soap and water for cleaning the instruments and use a
brush whenever necessary.
3. Allow sufficient time for articles to be disinfected or sterilized
by physical or chemical agents.
4. It is important to select the right disinfectant, the right
strength and the right time.
5.
Use the right procedure to render
instruments and other articles safe for further use in order to prevent the
spread of infection.
Chemical substances, which are
commonly used.
Dettol:This is widely used chemical for sterilization of instruments, thermometer etc. It is non-poisonous
and non-irritant to the skin. 5 to 50% solution is used for dressings and wound
irrigation.
Savlon:
1:30
savlon solution is used to destroy or kill vegetative bacteria.
Chloride of lime(Bleaching powder): This
is used for disinfection of drinking water, stools, urine, sputum. As it
decomposes quickly when exposed to air. Solutions must be made fresh for each
use.
Formalin: A 40 percent
solution is used to disinfect faeces, urine and sputum. It is not used for the
skin and tissues, as it is an irritant.
Tincture
of Iodine:
1-2 percent iodine is used for cleaning skin and treating injuries to the skin.
Hydrogen peroxide: 1-5 percent of
solution is used in cleaning wounds and to remove pus from infected ears.
Hydrogen peroxide is also used to clean the mouth. It is an oxidizing agent.
Potassium permanganate: It is an
oxidizing agent used for cleaning the mouth 1:1000 strength. It is also used
for irrigation of wounds.
Carbolic
acid (Phenol): It
is a good disinfectant for faeces, pus, blood and sputum. It is a skin irritant
and a poison. Dissolves easily in hot water. For thermometers 1:20 solution for
a duration of 10 minutes.
Lysol:
This
is a phenol or chlorasol preparation mixed with soap. It is less poisonous than
a carbolic acid but has a greater bacteriocidal action. 2 % solution for 6-8
hours is used for disinfecting linen.
Ethyl alcohol 70% is effective for skin
disinfection. Certain gases like formaldehyde and gluteraldehyde are used in
disinfection of rooms
Related Topics