Federalism in India | Political Science - Meaning of Federalism | 12th Political Science : Chapter 5 : Federalism in India
Chapter: 12th Political Science : Chapter 5 : Federalism in India
Meaning of Federalism
Federalism in India
Meaning of Federalism
Federalism refers to a political system that
possess Constitutionally provided and guaranteed distribution of powers between
a national government and several regional governments. The fundamental
attribute of a federal Constitution is the Constitutionally created and
protected State or regional governments. If regions in a country are distinct
in terms of ethnicity, language, religion etc., the ideal form of government
will be the federal system. Democratic federalism is the best instrument to ensure
‘Unity in diversity’. The constituent States retain and safeguard their distinct
linguistic, religious or cultural identity, without compromising the unity of
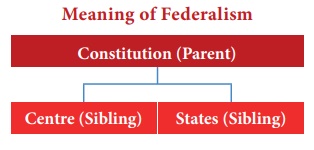
the federated nation. The federal system is based on distribution of powers
between the federal or central or Union Government and the constituent States.
This distribution is determined by the Constitution, in clear written terms.
Hence in any federal system, the Constitution becomes the supreme authority.
Evolution of Federalism
In the modern world, the United States of America
became the first federal State. Thereafter British colonies in Australia and
Canada were also granted self government and they too adopted federal forms of
government. The trilingual Switzerland similarly adopted a federal form of
government. The European Union today another example of federal formation on a
voluntary basis.
Rise of Federalism in India
The beginnings of federalism in modern India could
be traced in the Regulating Act of 1773, which brought the three regions in
India under East India Company’s authority (Madras, Calcutta and Bombay). The
Indian National Movement recognized the plural character of colonial India. The
Government of India Act 1919, introduced partial autonomy (Dyarchy) in the
Presidencies, while the Government of India Act 1935, granted provincial
autonomy to the presidencies and proposed a Dyarchical form of government at
the Centre. The Nehru Committee Report in 1928 and Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru’s
first proposals of a Constitution favoured a federal structure with more powers
for the constituent States. The Seventh Schedule of the Constitution contains
the three lists relating to the distribution of powers between the Centre and
States.
Related Topics