Federalism in India | Political Science - Federal features of Indian Constitution | 12th Political Science : Chapter 5 : Federalism in India
Chapter: 12th Political Science : Chapter 5 : Federalism in India
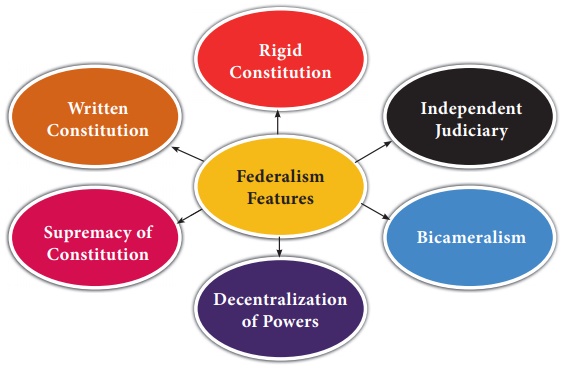
Federal features of Indian Constitution
Federal features of Indian Constitution
Indian Constitution possesses several federal features
1. Written Constitution
Federalism requires a written Constitution. There
are many governments in any federal system and for their smooth and friction
free functioning their powers must be stated in crystal clear terms. There are
Twenty Eight State Governments and One national government at present operating
in Indian federalism and therefore their powers and functions must be clearly
defined.
2. Supremacy of the Constitution
The Constitution must be the supreme legal document
in the country. All governments must follow the terms and conditions,
procedures contained in the Constitution. NO government can claim powers above
the Constitution.
3. Distribution of Powers
The distribution of powers between Centre and
States is the cardinal principle of any federal system. Indian Constitution
distributes powers between the two levels of governments in a comprehensive
scheme. There are three lists of power distribution unlike in the classical
federalism of American Constitution where there is only a single mode of
distribution.
4. Bicameralism
The federal Constitutions provide for bicameralism.
It refers to parliament having two houses. Indian Parliament is bicameral as it
consists of two houses. The upper house is called RajyaSabha or Council of States
while the lower house is known as LokSabha or House of the People. The Council
of States is the guardian of States’ rights and it consists of the
representatives of the States. All over the world the upper house is deemed to be
the protector of States’ rights and interests.
5. Rigidity of Constitution
A Constitution will be called a rigid Constitution
if its provisions can be amended only through a special process of
Constitutional amendment or through a separate amendment body and not through
ordinary legislative process. Federal Constitutions do not permit
Constitutional changes through ordinary legislative process. They prescribe a
tougher, rigid process of amendment like greater majority. The rationale behind
this rigidity is the desire to protect States’ rights. The article 368 in Part
XX Indian Constitution provides a separate amendment procedure for amending
Constitutional provisions and therefore our Constitution is rigid one and to some
extent protects the States.
6. Supreme Court
Indian Supreme Court acts as the umpire of the
federal system and protector of the Constitution. It possesses the powers of
interpretation and adjudication. If any disagreement or contradiction arises
among the Central and State Governments the Supreme Court resolves them. The
Constitution endows the Supreme Court with Original Jurisdiction. It means that
the Supreme Court alone possesses the exclusive powers to resolve any federal
dispute between Union Government and State governments or among State
governments. If a problem arises between Tamil Nadu and Union Government or
between Tamil Nadu and any other State only Supreme Court has powers to resolve
it.
Indian Constitution is described to be a federal one on the grounds of the aforementioned factors
Territory of India
There are important
differences between Union of States and Territory of India. Union of State
refers to the twenty eight states and Central Government. Territory of India
means:
1. Twenty Eight
States
2. Nine Union
Territories
3. Acquired
Territory (Any territory acquired by India like Pondicherry, Daman Diu after
they became part of India and before they were made Union Territories)
Related Topics