Chapter: Ophthalmology: Uveal Tract (Vascular pigmented layer)
Malignant Tumors (Uveal Melanoma)
Malignant Tumors (Uveal Melanoma)
With an incidence of one per ten thousand,
malignant uveal melanoma is the most common primary intraocular tumor. It
usually occurs as a choroidal melanoma, and is almost always unilateral. Tumors in the iris are detected earlier
than tumors located in the ciliary body
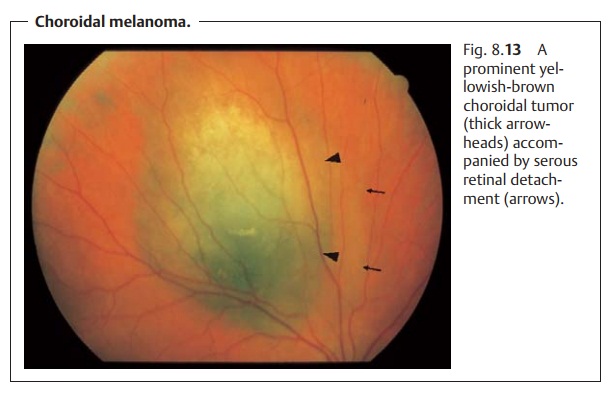
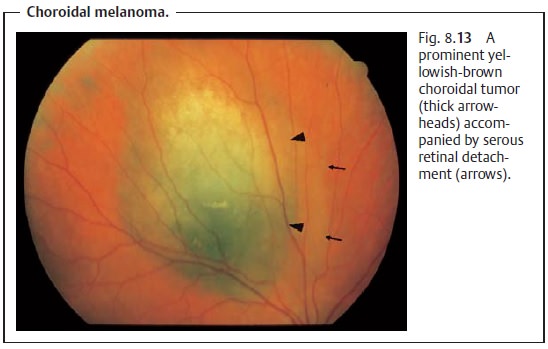
and choroid (Fig. 8.13).
❖ Iris melanomas: These tumors areoften initially asymptomatic.However,metastatic melanoma cells in the angle of the anterior chamber can lead to secondary glaucoma. Circumscribed iris melanomas are removed by seg-mental iridectomy.
❖ Ciliary body melanomas: Symptoms include changes in accommodationand refraction
resulting from displacement of the lens. Ciliary body melanomas are resected en bloc.
❖ Choroidal melanomas: These tumors become clinically symptomaticwhen involvement of
the macula reduces visual acuity or
the patient notices a shadow in his or her field of vision as a result of the
tumor and the accompanying retinal
detachment. The diagnosis is confirmed with the aid of transillumination,
ultrasound, and fluorescein angiography. Choroidal tumors are treated with
radioactive isotopes delivered by plaques of radioactive material (brachytherapy). Enucleation is indicated for tumors whose diameter exceeds 8 mm and
whose prominence exceeds 5 mm.
❖ Uveal metastases most frequently develop from carcinomas of the breastor lung.
They are usually flat with little pigmentation.
Related Topics