Chapter: VLSI Design : Circuit Characterization and Simulation
Logical Effort
LOGICAL EFFORT
Logical
effort is a gate delay model that takes transistor sizes into account. Allows
us to optimize transistor sizes over combinational networks. Isn’t as accurate
for circuits with reconvergentfanout.
1. Logical effort gate
delay model
Express
delays in process-independent unit
Gate
delay is measured in units of minimum-size
Inverter
delay τ
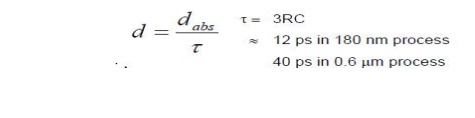
Gate
delay formula:
d = f +
p.
Effort
delay f is related to gate’s load. Parasitic delay p depends on gate’s
structure. Represents delay of gate driving no load set by internal parasitic
capacitance
2. Effort delay
Effort
delay has two components: f = gh.
Electrical
effort h is determined by gate’s load: h
= Cout/Cin Sometimes called fanout
Logical
effort g is determined by gate’s structure. Measures relative ability of gate
to deliver
current g
≡ 1 for inverter
3. Delay plots
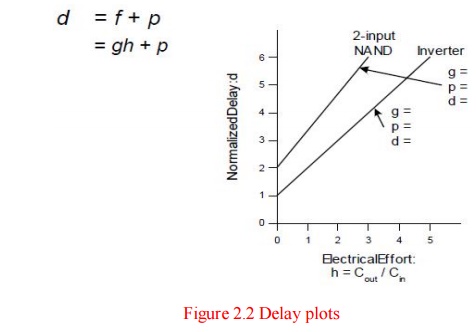
4. Computing Logical
Effort
Logical
effort is the ratio of the input capacitance of a gate to the input capacitance
of an inverter delivering the same output current. Measure from delay vs.
fanout plots Or estimate by counting transistor widths
Related Topics