Chapter: Linear Integrated Ciruits : Application of Op-Amp
Log and Antilog Amplifier
Log and Antilog Amplifier:
There are
several applications of log and antilog amplifiers. Antilog computation may
require functions such as ln x, log x or Sinhx.
These can
be performed continusely with log amps, and also used for direct dB display on
a digital Voltmeter and Spectrum analyzer.
Log-amp
can also be used to compress the dynamic range of a signal.
Log Amplifier:
The
fundamental log amp circuit shown in fig
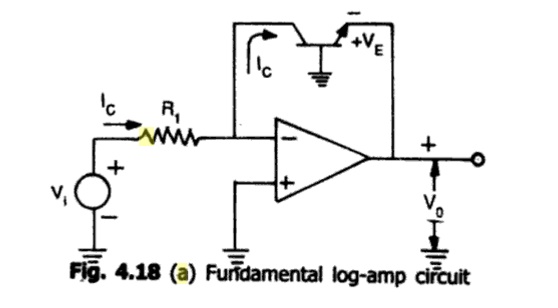
Fig a.
Fundamental log-amp Circuit

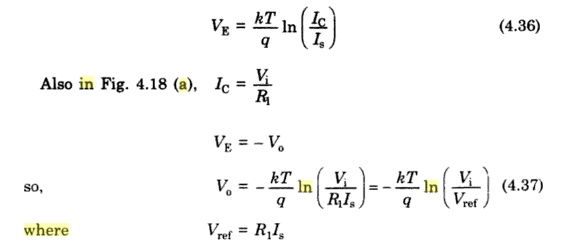
Where a
grounded base transistor is placed in the feedback path. Since the collector is
placed in the feedback path. The circuit have one problem.The emitter
saturation current Is varies from transistor to transistor and with
temperature. Thus a stable reference voltage V ref cannot be obtaine This is
eliminated by the circuit given in fig(b) The input is applied to one log-amp,
while a reference voltage is applied to one log- amp,while a reference voltage
is applied to another log-amp. The two transistors are integrated close
together in the same silicon wafer. This provides a close match of saturation
currents and ensures good thermal tracking. Fig(b)Log-amp with saturation
current and temperature compensation
Assume IS1=IS2=I
Antilog Amplifier
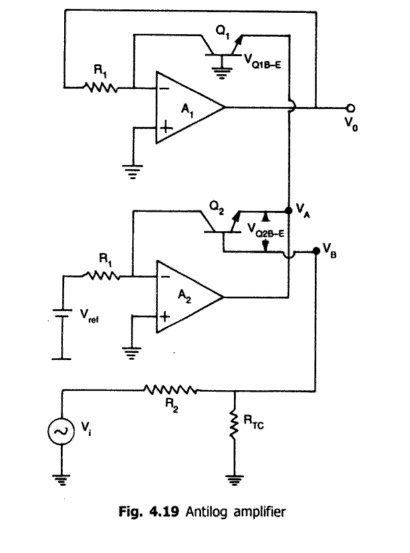
The
Circuit is shown in fig.The input Vi for the antilog-amp is fed into
the temperature compensating voltage divider R2 and RTC
and then to the base of Q2 . The output Vo of the
antilog- amp is fed back to the inverting input of A1 through the
resistor R1. The base to emitter
voltage
of transistors Q1 and Q2 can be written as
Since the
base of Q1 is tied to ground, we get
or kT R2 + RTC V ref
Changing
the natural log i.e., ln to log10 using eqn(6) we get Hence an increase of
input by one volt causes the output to decrease by a decade

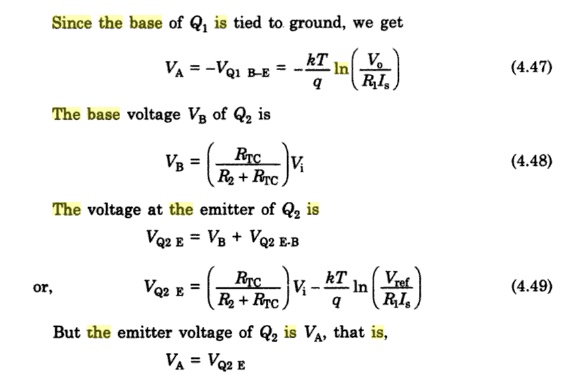
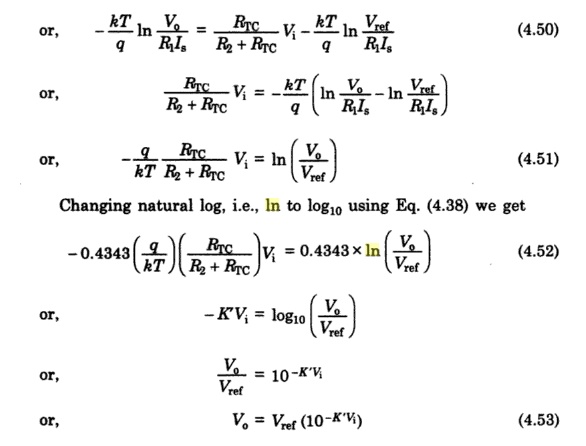
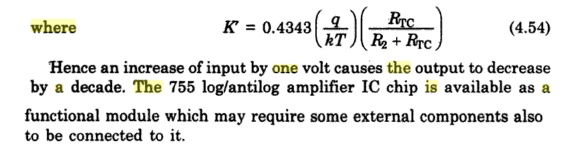
Related Topics