Chapter: Electric Energy Generation and Utilisation and Conservation : Industrial Heating and Welding
Laser Beam Welding
Laser Beam Welding
The “laser welding process” is the focusing of a monochromatic light into extremely con-centrated beams. It employs a carefully focused bem of light that concentrates tremendous amount of energy on a small area to produce fusion.
Refer to Fig. The laser welding system comprises the ollowing:
1. Electrical storage unit
2. Capacitor bank
3. Triggering device
4. Flash tube that is wrapped with a wire
5. Lasing material
6. Focusing lens mechanism
7. Work-table (operatable in three axes X Y and Z)
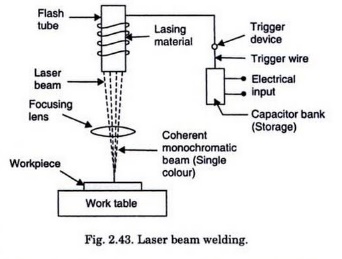
When capacitor bank is triggered energy is injected into the wire that surrounds the lash tube. This wire establishes an imbalance in the material inside the flash tube. Thick xenon often is used in the material for the flash tube, producing high power levels for very short period of time. The flash tubes or lamps are designed for operation at a rate of thousands of flashes per second. By operating in this manner, the lamps become an efficient device for converting electrical energy into light energy, the process of pumping the laser. The laser is then activated. The beam is emitted through the coated end of the lasing material. TI goes through a ocussing device where it is pin-pointed on the workpiece. Fusion takes place and the weld is accomplished.
Advantages:
i. This process can be used to weld dissimilar metals with widely varying physical properties.
ii. Metals with relatively high electrical resistance and parts of considerably different sizes and mass can be welded.
iii. Because the laser is simply a beam, no electrode is required, so that any part in a particular position can be welded if there is a direct line of sight rom beam to the workpiece.
iv. Welds can be made with a high degree of precision and on material that is only a few thousands of a centimetre thick.
v. Laser welding holds thermal distortion and shrinkage to a minimum.
Related Topics