Chapter: Web or internet Programming : JAVA
JAVA - Data Types
DATA
TYPES:
Java defines eight primitive types of data: byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, and boolean. The primitive types are also commonly referred to as simple
types. These can be put in four
groups:
•
Integers This group includes byte, short, int, and long, which are for whole-valued signed
numbers.
• Floating-point numbers This group includes float and double, which
represent numbers with fractional precision
• Characters This group includes char,
which represents symbols in a character set, like letters and numbers.
• Boolean This group includes boolean,
which is a special type for representing true/false values.
INTEGER :
Java defines four integer types: byte, short, int, and long. All of these are signed,
positiveand negative values. Java does not support unsigned, positive-only
integers.
Byte: The smallest integer type is byte.
This is a signed 8-bit type that has a range from –128 to
127.
Short:
short is a signed 16-bit type. It has a
range from –32,768 to 32,767.
Int: The most commonly used integer type is int. It is a signed 32-bit type that has a range from
–2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647.
Long: long is a signed 64-bit type and is useful for those occasions where an int type is not large enough to hold the desired value. The
range of a long is quite large
Floating-Point
Types
Floating-point numbers, also
known as real numbers, are used when
evaluating expressions that require fractional precision.
Float: The type float specifies a single-precision value that uses 32 bits of storage
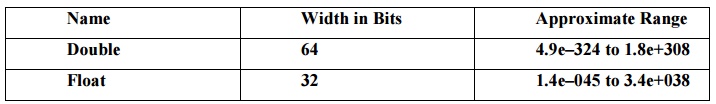
Double: Double precision, as denoted by the double keyword, uses 64 bits to store a value.
Characters
In Java, the data type used to
store characters is char. Java char is a 16-bit type. The range of a char is 0 to 65,536. There are no
negative chars.
Booleans
Java has a primitive type, called
boolean, for logical values. It can
have only one of two possible values, true
or false.
Type
Conversion and Casting
it is fairly common to assign a
value of one type to a variable of another type which is known as casting.
Java’s
Automatic Conversions
When one type of data is assigned
to another type of variable, an automatic
type conversion will take place
if the following two conditions are met:
• The two types are compatible.
• The destination type is larger than the source type.
When these two conditions are
met, a widening conversion takes
place. For example, the int type is
always large enough to hold all valid
byte values, so no explicit cast statement is required.
if you want to assign an int value to a byte variable. This conversion will not be performed automatically,
because a byte is smaller than an int. This kind of conversion is
sometimes called a narrowing conversion,
since you are explicitly making the value narrower so that it will fit into the
target type. To create a conversion between two incompatible types, you must
use a cast. A cast is simply an
explicit type conversion. It has this general form:
(target-type) value int a;
byte b;
// ...
b = (byte) a;
Arrays: An array is a group of
like-typed variables that are referred to by a common name. Arrays of any type can be created and may have one or more
dimensions. Aspecific element in an array is accessed by its index. type var-name[ ];
An Example for
Multidimensional Array.
While we define an multidimensional array it is necessary to
define the number of row but not the column values.
public class arrayl {
public static void main(String args[]){
int twoD[][]= new int[4][];
// Multidimensional array each row has variable
column values. twoD[0]=new int[1];
twoD[1]=new int[2]; twoD[2]=new int[3]; twoD[3]=new int[4];
int i,j,k=0;
for(i=0;i<4;i++) for(j=0;j<i+1;j++){
twoD[i][j]=k; k++;
}
for(i=0;i<4;i++){ for(j=0;j<i+1;j++)
System.out.print(twoD[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
System.out.printf("the value of k is %d",k);
}
}
Related Topics