Chapter: Web or internet Programming : JAVA
Java - The File Class
I/O Fundamentals
The Java language provides a
simple model for input and output (I/O). All I/O is performed by writing to and
reading from streams of data. The data may exist in a file or an array, be
piped from another stream, or even come from a port on another computer. The
flexibility of this model makes it a powerful abstraction of any required input
and output.
The File
Class
The File class is Java's representation of a file
or directory path name. Because file and directory names have different formats
on different platforms, a simple string is not adequate to name them. The File
class contains several methods for working with the path name, deleting and
renaming files, creating new directories, listing the contents of a directory,
and determining several common attributes of files and directories.
Creating a File Object
You create a File object by
passing in a String that represents the name of a file, and possibly a Stringor
another Fileobject. For example,
File a = new
File("/usr/local/bin/IPLAB");
defines an abstract file name for the smurf file in
directory /usr/local/bin. This is an absolute
abstract file name. It gives all path
information necessary to find the file.
You could also create a file object as follows:
File b = new File("bin/IPLAB");
This is a relative
abstract file name, because it leaves out some necessary path information,
which will be filled in by the VM. By default, the VM will use the directory in
which the application was executed as the "current path".
File
Attribute Methods
The File object has several methods that provide information on the
current state of the file.
boolean canRead() Returns
trueif the file is readable
Boolean canWrite() Returns
trueif the file is writeable
Boolean exists() Returns trueif
the file exists
boolean isAbsolute() Returns
trueif the file name is an absolute path name
boolean isDirectory() Returns
trueif the file name is a directory
boolean isFile() Returns trueif
the file name is a "normal" file (depends on OS)
boolean isHidden() Returns
trueif the file is marked "hidden"
long lastModified() Returns
a longindicating the last time the file was modified
long length() Returns the
length of the contents of the file
Text I/O
Versus Binary I/O
Java's I/O classes are divided
into two main groups, based on whether you want text or binary I/O. Readerand
Writerclasses handle text I/O. InputStreamand OutputStream classes handle
binary I/O.
Reader and InputStream
Java supplies Readers and InputStreams to read data; their use is
similar. The following table shows the most commonly used methods in these
classes. See the javadocs for the other methods available. Note that these two
classes are abstract; you won't ever
create an instance of either, but they provide the base implementation details
for all other input classes.
Reader Class Methods:

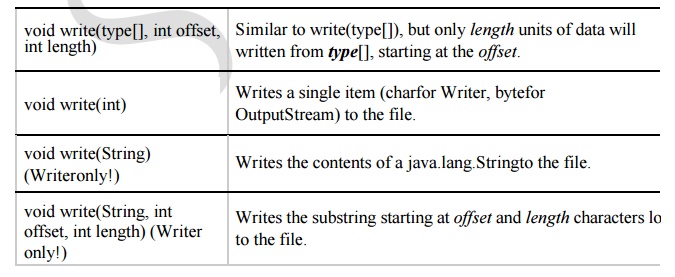
Writer
and OutputStream
Java supplies Writerand OutputStream to write data; their use is
similar. The following table shows the methods provided in these classes. Note
that these two classes are abstract;
you won't ever create an instance of either, but they provide the base
implementation details for all other output classes.
Reading and Writing Files
To read and write from files on a disk, use the following classes:
•
FileInputStream
•
FileOutputStream
•
FileReader
•
FileWriter
Each of these has a few constructors, where class is the name of one of the above
classes:
•class(File) - create an input
or output file based on the abstract path name passed in
•class(String)- create an
input or output file based on the String path name
•class(FileDescriptor)-
create an input or output file based on a FileDescriptor (you generally won't
use this and this class will not discuss it)
•class(String,
boolean)- [for output classes only]
create an input or output file based on the path name passed in, and if the
boolean parameter is true, append to
the file rather than overwrite it
For example, we could copy one file to another by
using: import java.io.*;
public class FileCopy {
public static void main(String args[]) { try {
// Create an input file
FileInputStream inFile = new FileInputStream(args[0]);
// Create an output file
FileOutputStream outFile = new FileOutputStream(args[1]);
// Copy each byte from the input
to output int byteRead;
while((byteRead = inFile.read()) != -1)
outFile.write(byteRead);
//
Close the files!!!
inFile.close(); outFile.close();
}
// If something went wrong, report it! catch(IOException e) {
System.err.println("Could not copy "+ args[0] + " to " +
args[1]); System.err.println("Reason:"); System.err.println(e);}
Related Topics