Chapter: Clinical Anesthesiology: Anesthetic Equipment & Monitors : Breathing Systems
Insufflation
INSUFFLATION
The term insufflation usually denotes
the blowing of anesthetic gases across a patient’s face. Although insufflation
is categorized as a breathing system, it is perhaps better considered a
technique that avoids direct connection between a breathing circuit and a
patient’s airway. Because children often resist the placement of a face mask
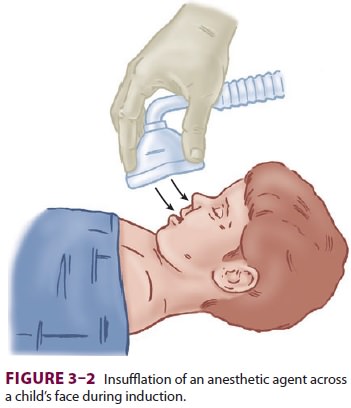
(or an intravenous line), insufflation is particularly valuable during
induc-tions with inhalation anesthetics in children (Figure 3–2). It is useful in
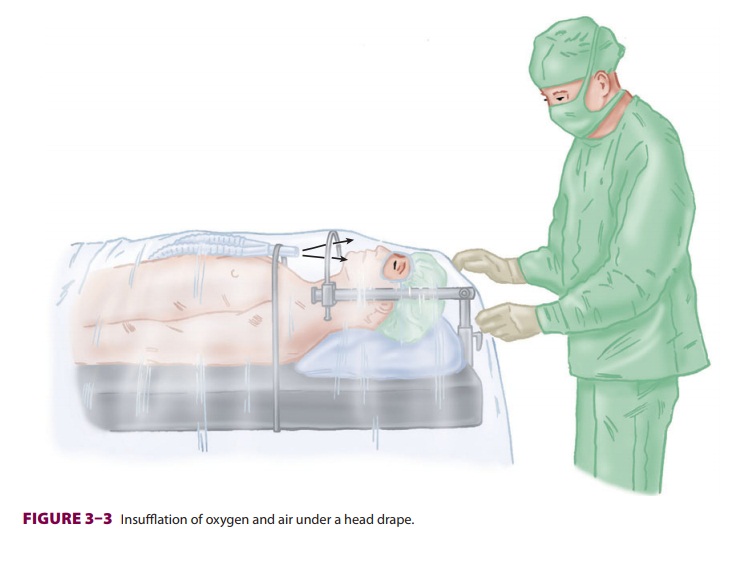
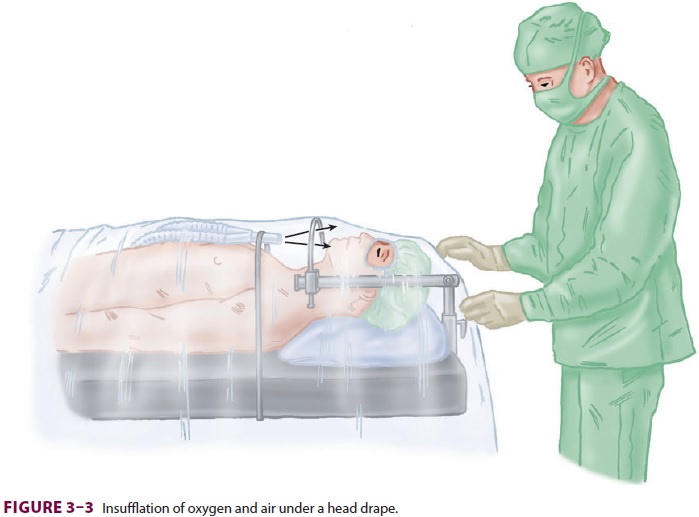
other situations as well. Carbon dioxide accumulation under head and neck
draping is a hazard of ophthalmic surgery per-formed with local anesthesia.
Insufflation of air across the patient’s face at a high flow rate (>10 L/min) avoids this problem, while not increas-ing
the risk of fire from accumulation of oxygen(Figure 3–3). Because
insufflation avoids any direct patient contact, there is no rebreathingof
exhaled gases if the flow is high enough. Ventilation cannot be controlled with
this technique, however, and the inspired gas contains unpredict-able amounts
of entrained atmospheric air.
Insufflation can also be used to
maintain arterial oxygenation during brief periods of apnea (eg, dur-ing
bronchoscopy). Instead of blowing gases across the face, oxygen is directed
into the lungs through a device placed in the trachea.
Related Topics