Chapter: Electric Energy Generation and Utilisation and Conservation : Solar Radiation and Solar Energy Collectors
Important Short Questions and Answers: Solar Radiation and Solar Energy Collectors
Solar Radiation
and Solar Energy Collectors
1. Define solar collector.
A
solar collector is a device for collecting solar radiation and transfer and the
energy to a fluid passing in contact with it. Utilization of solar energy
required solar collectors.
2. What are the different types of
solar collectors.
Solar
collectors are classified into two types. They are
i.
Non-concentrating or Flat plate type solar collector.
ii.
Concentrating (Focusing) type solar collector.
3. What is the advantages of
concentrating type solar collector over Non-concentrating type solar collector.
In
concentrating collector, the area intercepting the solar radiation is greater
sometimes hundred of times greater than absorber area.
By
means of concentrating collectors, much higher temperature can be obtained than
with non-concentrating type. Concentrating collectors may be used to generate
medium pressure steam.
They
use many different arrangement of mirrors and lenses to concentrate the sun ray’s
on the boiler. This type shows better efficiency than the flat plate type.
4. Define flat plate collectors
Solar
collectors for home heating usually called flat plate collectors, almost have
one or more glass covers, although various plastic and other transparent
materials are often used instead of glass.
5. State Wien’s Law
Wien’s
Law state that, the emission increases with temperature. The re-emitted light
if so progressively shorter wavelength and greater energy as the temperature of
blockbody increases. This is expressed by Wien’s Law, which can be written as,
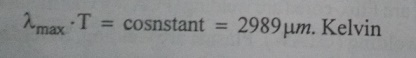
6. State Plank’s Law
Planck’s
Law state that the spectral emissive power of a black surface is give by,
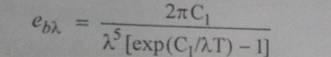
Where,
C1 and C2 are constants whose values are 0.596 x 10-16
W-m2 and 0.014387m-K respectively, l is the
wavelength and T is the temperature of the black surface in K.
7. State Stefan – Boltzmann Law.
The
Stefan – Boltzmann law is obtained by integrating Planck’s Law over all the
wavelength from 0 to µ and state that the emissive power of a
black surface is given by
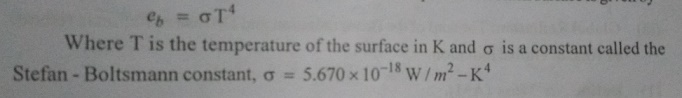
8. Define Solar Constant.
The
Solar Constant ISC is the rate at which energy is received from the
Sun on a unit area perpendicular to the rays of the Sun, at the mean distance o
the earth from the Sun. Based on experimental investigation and subsequent
measurement, the value of ISC is 1367 W/m2 has been
recommended.
9. Draw the spectral distribution
of extraterrestrial solar radiation.
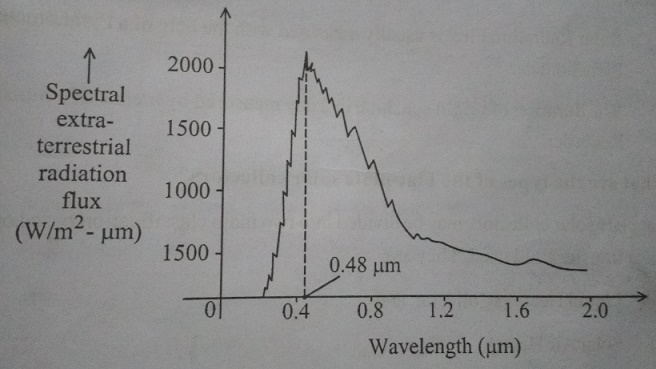
10. Define the following terms.
i.
Direct radiation
ii.
Diffuse radiation, and
iii.
Global radiation
i. Direct radiation: Solar
radiation received at the earth’s surface without change of direction, i.e., in
the with the Sun, is called Beam or Direct radiation.
ii. Diffuse radiation: The
radiation received of the Earth’s surface from all parts of the sky’s
hemisphere, after being subjected to scattering in the atmosphere is called
Diffuse radation.
iii. Global radiation: The
sum o the Beam radiation and Diffuse radiation is referred as Total or Global
radiation.
11. Define Air Mass(AM)
Air
Mass(AM) is often used as a measure of the distance travelling by beam
radiation through the atmosphere before it reaches a location on the earth
surface. It is defined as the ratio o the mass of the atmosphere through which
the beam radiation passes to the mass it would pass through if the Sun directly
overhead(i.e., at its zenith).
12. Name the instruments used to
measure the Solar Radiation and Sunshine hours.
Solar
Radiation Flux is usually measured with the help of a Pyranometer or
Pyrheliometer.
The
duration of bright sunshine in a day measured by means of a Sunshine Recorder.
13. What are types of the Flat-
plate solar collectors?
Flat
plate solar collectors may be divided into two main classification based on the
type of heat transfer fluid used. They are,
i.
Liquid Heating Collector
ii.
Solar Air Heater
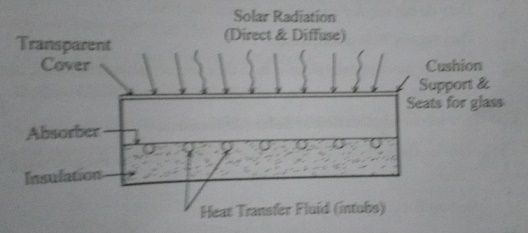
14. Give the main components of
Flat-Plate Collector.
The
majority of the Flat-Plate Collector have five main components as follows:
i.
A transparent cover.
ii.
Tubes, fins, passages or channels.
iii.
Absorber plates
iv.
Insulation
v.
Casing or Container.
15.
Draw the typical structure of Liquid Collector.
16. Draw the typical cross section
of typical Air Collector or Solar Air Heaters.

17. What are the different types of
Air Heaters?
Basically
air heaters are classified into the following two categories
i.
Non-porous type air heaters.
ii.
Porous type air heaters.
18.
What are the different losses occurs in Solar Collector?
i.
Conductive Loss
ii.
Convective Loss
iii.
Radiative Loss
19. Define Collector Efficiency
Collector
Efficiency (ÎĽc) is the collector performance and is defined as the
ratio of the useful gain over any time period to the incident solar energy over
the same time perioid.
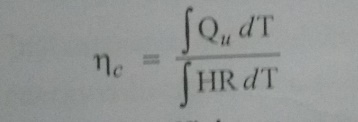
20. Define fin efficiency
Fin
efficiency is used to indicate the effectiveness of a fin in transferring a
given quantity of heat. In efficiency is defined as,
Fin
efficiency = Actual heat transferred / Heat which would transferred if entire
fin area were at base temperature.
21.What are the different types of
concentrating collectors?
As
per the number of concentrating collectors are
i.
Parabolic through collector
ii.
Mirror strip reflector
iii.
Fresnel lens collector
iv.
Flat plate collector with adjustable
mirrors.
v.
Compound parabolic concentrator(C.P.C)
22. What are the different types of
heat transfer mechanism?
Heat
transfer occurs by three basic mechanisms, they are
i.
Radiation
ii.
Conduction
iii.
Convection
23. Define concentration Ratio
It
is the ratio of the effective area of the aperture to the surface area of the
absorber.
24. What are the main advantage of
concentrator system over flat plate system.
i.
Concentration system can be used for electric power generation, because of high
temperature of working fluid obtained.
ii.
The heat storage cost will be less causes of the high temperature attainable
and high temperature storage made possible.
iii.
Solar heating and cooling applications system can attain higher efficiencies.
iv.
Anti-freeze and other liquid to protect the absorbers may not be required.
25. What are the properties of
materials used in Flat Plate Collector ?
The
following three properties considered for selecting material for Flat Plate
Collector:
i.
Thermo-physical properties
ii.
Physical properties
iii.
Environment properties
26. Define Transmissivity –
Absorptiviy Product.
The
efine Transmissivity – Absorptiviy Product is defined as the ratio o the flux
absorbed in the absorber plate to the flux incident on the cover system, and is
denoted by the symbol (ta), an appropriate subscript (b to d)
being added to indicate the type of incident radiation.
Related Topics