Chapter: Principles of Compiler Design : Lexical Analysis
Important Short Questions and Answers : Principles of Compiler Design - Lexical Analysis
1.
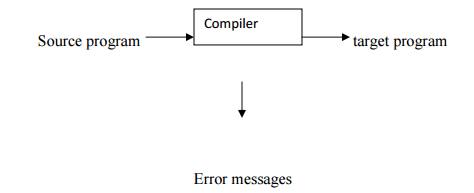
What is a Complier?
A Complier is a program
that reads a program written in one language-the source language-and translates
it in to an equivalent program in another language-the target language . As an
important part of this translation process, the compiler reports to its user
the presence of errors in the source program
2. State
some software tools that manipulate source program?
i. Structure
editors
ii. Pretty
printers
iii. Static
checkers
iv. Interpreters.
3. What
are the cousins of compiler?
The following are the cousins of compilers
i. Preprocessors
ii. Assemblers
iii. Loaders
iv. Link
editors.
4. What
are the main two parts of compilation? What are they performingThe
two main parts are
Analysis part breaks up the
source program into constituent pieces and creates an intermediate
representation of the source program.
·
Synthesis part
constructs the desired target program from the intermediate representation
5. What
is a Structure editor?
A structure editor
takes as input a sequence of commands to build a source program .The structure
editor not only performs the text creation and modification functions of an
ordinary text editor but it also analyzes the program text putting an
appropriate hierarchical structure on the source program.
6. What
are a Pretty Printer and Static Checker?
·
A Pretty printer analyses a program and
prints it in such a way that the structure of the program becomes clearly
visible.
·
A static checker reads a program, analyses
it and attempts to discover potential bugs with out running the program.
7. How
many phases does analysis consists?
Analysis
consists of three phases
i
.Linear analysis
ii
.Hierarchical analysis
iii. Semantic
analysis
8. What
happens in linear analysis?
This is the phase in
which the stream of characters making up the source program is read from left
to right and grouped in to tokens that are sequences of characters having
collective meaning.
9. What happens in Hierarchical
analysis?
This is the phase in
which characters or tokens are grouped hierarchically in to nested collections
with collective meaning.
10. What happens in Semantic analysis?
This is the phase in
which certain checks are performed to ensure that the components of a program
fit together meaningfully.
11.State some compiler construction
tools?
i.Parse Scanner generators
ii.
Syntax-directed translation engines
iii.Automatic code
generator
v. Data
flow engines.
12. What is a Loader? What does the
loading process do?
A
Loader is a program that performs the two functions
i.
Loading
ii
.Link editing
The process of loading
consists of taking relocatable machine code, altering the relocatable address
and placing the altered instructions and data in memory at the proper
locations.
13. What does the Link Editing does?
Link editing: This
allows us to make a single program from several files of relocatable machine
code. These files may have been the result of several compilations, and one or
more may be library files of routines provided by the system and available to
any program that needs them.
14. What is a preprocessor? Nov/Dev 2004
A preprocessor is one,
which produces input to compilers. A source program may be divided into modules
stored in separate files. The task of collecting the source program is
sometimes entrusted to a distinct program called a preprocessor.
The
preprocessor may also expand macros into source language statements.
15.
State some functions of
Preprocessors
i)
Macro processing
ii)
File inclusion
iii)
Relational Preprocessors
iv)
Language extensions
16.
What is a Symbol table?
A Symbol table is a
data structure containing a record for each identifier, with fields for the
attributes of the identifier. The data structure allows us to find the record
for each identifier quickly and to store or retrieve data from that record
quickly.
17.
State the general phases of a
compiler
i)
Lexical analysis
ii)
Syntax analysis
iii)
Semantic analysis
iv)
Intermediate code generation
v)
Code optimization
vi)
Code generation
18.
What is an assembler?
Assembler
is a program, which converts the source language in to assembly language.
19.
What is the need for separating the
analysis phase into lexical analysis and parsing? (Or) What are the issues of
lexical analyzer?
·
Simpler design is perhaps the most
important consideration. The separation of lexical analysis from syntax
analysis often allows us to simplify one or the other of these phases.
·
Compiler efficiency is improved.
·
Compiler portability is enhanced.
20.
What is Lexical Analysis?
The first phase of
compiler is Lexical Analysis. This is also known as linear analysis in which
the stream of characters making up the source program is read from
left-to-right and grouped into tokens that are sequences of characters having a
collective meaning.
21.
What is a lexeme? Define a regular
set.
·
A Lexeme is a sequence of characters in
the source program that is matched by the pattern for a token.
·
A language denoted by a regular
expression is said to be a regular set
22.
What is a sentinel? What is its
usage?
A Sentinel is a special
character that cannot be part of the source program. Normally we use ‘eof’ as
the sentinel. This is used for speeding-up the lexical analyzer.
23. What is a regular expression? State
the rules, which define regular expression?
Regular
expression is a method to describe regular language
Rules:
1) ɛ-is
a regular expression that denotes { ɛ } that is the set containing the empty
string
2) If
a is a symbol in ∑,then a is a regular expression that denotes {a}
3)
Suppose r and s are regular expressions
denoting the languages L(r ) and L(s) Then,
a)
(r )/(s) is a regular expression
denoting L(r) U L(s).
b)
(r )(s) is a regular expression denoting
L(r )L(s)
c)
(r )* is a regular expression denoting
L(r)*.
d)
(r) is a regular expression denoting L(r
).
24.
What are the Error-recovery actions
in a lexical analyzer?
1. Deleting
an extraneous character
2. Inserting
a missing character
3. Replacing
an incorrect character by a correct character
4. Transposing
two adjacent characters
25.
Construct Regular expression for
the language
L= {w E{a,b}/w ends in abb} Ans:
{a/b}*abb.
26. What is recognizer?
Recognizers are
machines. These are the machines which accept the strings belonging to certain
language. If the valid strings of such language are accepted by the machine
then it is said that the corresponding language is accepted by that machine,
otherwise it is rejected.
Related Topics