Chapter: Principles of Compiler Design : Lexical Analysis
Analysis of the source program
ANALYSIS OF THE SOURCE PROGRAM
In Compiling, analysis consists of three phases:
1.
Lexical Analysis
2.
Syntax Analysis
3.
Semantic Analysis
1.Lexical analysis:
In a compiler linear
analysis is called lexical analysis or scanning. The lexical analysis phase
reads the characters in the source program and grouped into them tokens that
are sequence of characters having a collective meaning.
Example :
position : = initial + rate * 60
Identifiers – position,
initial, rate.
Operators - + , *
Assignment symbol - : =
Number - 60
Blanks – eliminated.
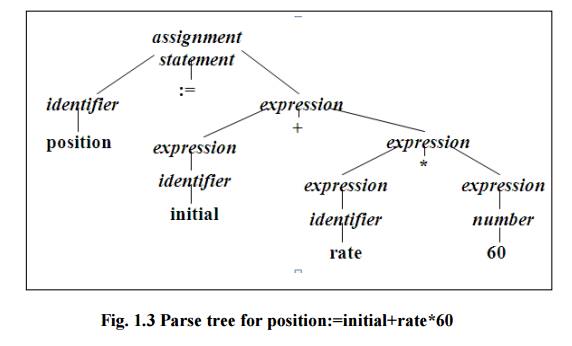
Fig.
1.3 Parse tree for position:=initial+rate*60
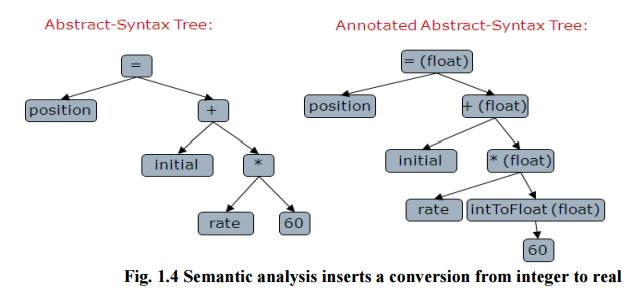
Fig.
1.4 Semantic analysis inserts a conversion from integer to real
2.Syntax analysis:
Hierarchical Analysis
is called parsing or syntax analysis. It involves grouping the tokens of the
source program into grammatical phrases that are used by the complier to
synthesize output. They are represented using a syntax tree as shown in Fig.
1.3
·
A syntax tree is the tree
generated as a result of syntax analysis in which the interior nodes are the
operators and the exterior nodes are the operands.
·
This analysis shows an error when the
syntax is incorrect.
Example :
position : = initial +
rate * 60
3.Semantic analysis :
This phase checks the source program for semantic errors and gathers type information for subsequent code generation phase. An important component of semantic analysis is type checking. Here the compiler checks that each operator has operands that are permitted by the source language specification.
Related Topics