Chapter: Satellite Communication : Satellite Orbits
Important Questions and Answers: Satellite Orbits
SATELLITE ORBITS
1. What is Satellite?
An
artificial body that is projected from earth to orbit either earth (or) another
body of solar systems.
Types:
Information satellites and Communication Satellites
2. Define Satellite Communication.
It
is defined as the use of orbiting satellites to receive, amplify and retransmit
data to earth stations.
3. State KeplerŌĆÖs first law.
It
states that the path followed by the satellite around the primary will be an
ellipse.
An
ellipse has two focal points F1 and F2. The center of mass of the two body
system, termed the barycenter is always centered on one of the foci.
e
= [square root of (a2ŌĆō b2) ] / a
4. State KeplerŌĆÖs second law.
It
states that for equal time intervals, the satellite will sweep out equal areas
in its orbital plane, focused at the barycenter
5. State KeplerŌĆÖs third law.
It
states that the square of the periodic time of orbit is perpendicular to the
cube of the mean distance between the two bodies.
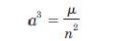
Where,
n
= Mean motion of the satellite in rad/sec.
┬Ą=
EarthŌĆÖs geocentric gravitational constant. With the n in radians per sec. the
orbital period in second is given by,
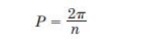
6. Define apogee.
The
point farthest from the earth.
7. Define Perigee.
The
point closest from the earth.
8. What is line of apsides?
The
line joining the perigee and apogee through the center of the earth.
9. Define ascending node.
The
point where the orbit crosses the equatorial plane going from south to north.
10. Define descending node.
The
point where the orbit crosses the equatorial plane going from north to south.
11. Define Inclination.
The
angle between the orbital plane and the earthŌĆÖs equatorial plane. It is
measured at the ascending node from the equator to the orbit going from east to
north.
12. Define mean anomaly.
It
gives an average bvalue of the angular position of the satellite with reference
to the perigee.
13. Define true anomaly.
It
is the angle from perigee to the satellite position, measured at the earthŌĆÖs
center.
15. What is meant by azimuth angle?
It
is defined as the angle produced by intersection of local horizontal plane and
the plane passing through the earth station, the satellite and center of earth.
16. Give the 3 different types of
applications with respect to satellite systems.
ŌĆó
The largest international system (Intelsat)
ŌĆó
The domestic satellite system (Dom sat) in U.S.
ŌĆó
U.S. National oceanographic and atmospheric administrations (NOAA)
17. Mention the 3 regions to
allocate the frequency for satellite services.
ŌĆó
Region1: It covers Europe, Africa and Mangolia
ŌĆó
Region2: It covers North & South Ameriaca and Greenland.
ŌĆó
Region3: It covers Asia, Australia and South West Pacific.
18. Give the types of satellite
services.
ŌĆó
Fixed satellite service
ŌĆó
Broadcasting satellite service
ŌĆó
Mobile satellite service
ŌĆó
Navigational satellite services
ŌĆó
Meteorological satellite services
19. What is mean by Dom sat?
Domestic
Satellites. These are used for voice, data and video transmissions within the
country.
20. What is mean by INTELSAT &
SARSAT ?
’éĘ
International Telecommunication Satellite.
’éĘ
Search and rescue satellite.
21. Define polar-orbiting
satellites.
Polar
orbiting satellites orbit the earth in such a way as to cover the north and
south polar regions.
22. Give the advantage of
geostationary orbit.
There
is no necessity for tracking antennas to find the satellite positions.
23. Define look angles.
The
azimuth and elevation angles of the ground station antenna are termed as look
angles.
24. Write short notes on station
keeping.
It
is the process of maintenance of satelliteŌĆÖs attitude against different factors
that can cause drift with time. Satellites need to have their orbits adjusted
from time to time, because the satellite is initially placed in the correct
orbit, natural forces induce a progressive drift.
25. What are the geostationary
satellites?
The
satellites present in the geostationary orbit are called geostationary
satellite. The geostationary orbit is one in which the satellite appears
stationary relative to the earth. It lies in equatorial plane and inclination
is ŌĆś0ŌĆÖ. The satellite must orbit the earth in the same direction as the earth
spin. The orbit is circular.
26. What is sun transit outage.
The
sun transit is nothing but the sun comes within the beam width of the earth
station antenna. During this period the sun behaves like an extremely noisy
source and it blanks out all the signal from the satellite. This effect is
termed as sun transit outage.
Related Topics