Chapter: Civil : Remote Sensing Techniques and GIS : EMR and Its Interaction With Atmosphere and Earth Material
Important Questions and Answers - EMR And Its Interaction With Atmophere And Earth Material
EMR And Its Interaction With Atmophere And
Earth Material
1.What is
Remote Sensing?
Remote
sensing is the science and art of
obtaining information about object,
area, or phenomena through the analysis of data
acquired by a device that is not in
contact with the object, area, or
phenomena under investigation.
2.What
are all the applications of remote sensing?
In
many respects, remote
sensing can be thought of as
a reading process. Using various
sensors, we remotely collect data that may be analyzed to obtain
information about the objects,
areas,or phenomena
beinginvestigated.
The
remotely collected data can be of many
forms, including Variations in force distributions, acoustic wave
distributions, or electromagnetic energy distributions.
3.Write
the physics of remote sensing ?
Visible light is only one of many
forms of Electromagnetic energy. Radio waves, heat, ultraviolet rays,
and X-rays are other familiar forms.
All this energy is inherently similar and radiates in accordance with basic
wave theory. This theory describes electromagnetic energy as traveling in
harmonic, sinusoidal fashion
at the 'velocity
of light' c.
The distance from one wave peak
to the next is the wave
length ?, and the number of peaks passing a fixed point in space
per unit time is the wave frequency V.
From basic physics, wave obey the general equation
C = v y
4.What
are the Components of Remote Sensing ?
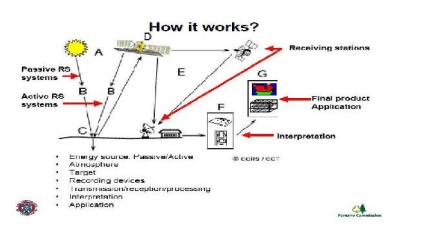
5.What is
Electromagnetic radiation?
Electromagnetic (EM)
radiation is a self-propagating wave in space or through matter.
EM radiation has
an electric and magnetic
field component which oscillate in phase perpendicular to each
other and to the direction of energy propagation.
6.Write
the type of Electromagnetic radiation?
Electromagnetic
radiation is classified into types
according to the frequency of the wave, these types include (in order of increasing frequency): radio waves,
microwaves, terahertz radiation,
infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation,
X-rays and gamma rays.
7.Draw
the quantum theory interaction?
A quantum
theory of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter
such as electrons
is described by the theory of quantum electrodynamics.
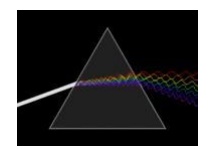
8.Write
about refraction?
In refraction, a wave crossing from
one medium to another of different density alters its
speed and direction upon entering
the new
medium.
The ratio of
the refractive indices of the
media determines the degree of refraction, and is summarized by
Snell's law. Light disperses into a visible spectrum as light is shone through
a prism because of refraction.
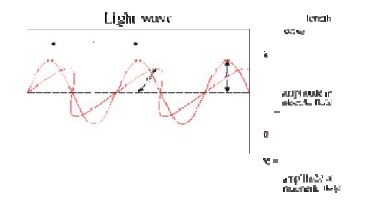
9.Draw
the Wave model?
10.Write
Planck's equation?
The frequency of the wave is proportional to the magnitude of the particle's energy. Moreover, because photons are emitted and absorbed by charged particles, they act as transporters of energy.
The energy per
photon can be calculated by Planck's equation:
where E
is the energy, h is Planck's constant, and f is frequency.
11.What
is Black body ?
By
definition a black body is a material that absorbs all the radiant energy that
strikes it. A black body also radiates the maximum amount of energy, which is
dependent on the kinetic temperature.
12.Write
Stefan Boltzman law?
According
to the Stefan-Boltzman law the radiant flux of a black body, Fb, at a kinetic
temperature, Tkin, is Fb = s* Tkin 4 where s is the Stefan- Boltzman constant,
5.67*10-12 W*cm-2* o K-4.
13.What
is emissivity?
Emissivity
is a measure of the ability of a material to both radiate and absorb energy.
Materials with a high emissivity absorb and radiate large proportions of
incident and kinetic energy, respectively (and vice-versa).
14.Write
Wein's Displacement law?
For an
object at a constant temperature the radiant power peak refers to the
wavelength at which the maximum amount of energy is radiated, which is
expressed as lmax. The sun, with a surface temperature of almost 6000 o K, has
its peak at 0.48mm (wavelength of yellow). The average surface temperature of
the earth is 290 o K (17 o C), which is also called the ambient temperature; the
peak concentration of energy emitted from the earth is at 9.7mm.This shift to
longer wavelengths with decreasing temperature is described by Wien's
displacement law, which states:
lmax =
2,897mm o K /Trad o K
15.Write
Planck's Law?
The
primary law governing blackbody radiation is the Planck Radiation Law, which
governs the intensity of radiation emitted by unit surface area into a fixed
direction (solid angle) from the blackbody as a function of wavelength for a
fixed temperature. The Planck Law can be expressed through the following
equation.
16.What
is Scattering?
Scattering
occurs when particles or large gas molecules present in the atmosphere interact
with and cause the electromagnetic radiation to be redirected from its original
path. How much scattering takes place depends on several factors including the
wavelength of the radiation, the abundance of particles or gases, and the
distance the radiation travels through the atmosphere. There are three (3)
types of scattering which take place.
17.What
are the types of scattering?
(i)
Rayleigh scattering occurs when particles are very small compared to the
wavelength of the radiation.
(ii) Mie
scattering It occurs when the particles are just about the same size as the
wavelength of the radiation.
(iii) Non
Selective Scattering
The final
scattering mechanism of importance is called nonselective scattering. This
occurs when the particles are much larger than the wavelength of the radiation.
18.What
is Atmospheric Windows?
The areas
of the spectrum which are not severely influenced by atmospheric absorption and
thus, are useful to remote sensors, are called atmospheric windows.
Related Topics