Chapter: Mechanical : Total Quality Management (TQM) : Quality Systems
ISO 9000 STANDARDS
QUALITY
SYSTEMS
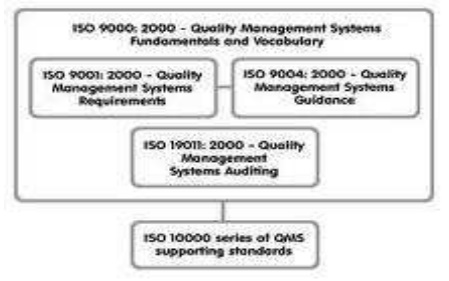
ISO 9000
STANDARDS

ISO 9000
1)ISO
9001
2)ISO
9002
3)ISO
9003
ISO 9001
Design, Development, Production, Installation & Servicing
ISO 9002
Production,
Installation & Servicing
ISO 9003
Inspection
& Testing
ISO 9004
Provides
guidelines on the technical, administrative and human factors affecting the
product or services.
BENEFITS
OF ISO 9000 STANDARDS :
Ă˜ Achievement
of international standard of quality.
Ă˜ Value for
money.
Ă˜ Customer satisfaction.
Ă˜ Higher
productivity.
Ă˜ Increased
profitability
Ă˜ Improved
corporate image
Ă˜ Access to
global market
Ă˜ Growth of
the organization
Ă˜ Higher
morale of employees

CLAUSES
(ELEMENTS) OF ISO 9000 (During the year 1987)
Management Responsibility
Ă˜ Adequate
resources for the verification activities
Ă˜ Need for
trained personnel
Ă˜ Work and
verification activities including audits
Ă˜ A
Management Representative to be identified
Ă˜ Review
the Quality System performance and customer complaints periodically
· Quality
System
· Contract
review
· Design
Control
· Documents
Control
· Purchasing
· Purchaser
– Supplied
Product
· Product
Identification and Traceability
· Process
Control
· Inspection
and Testing
· Inspection
Measuring and Test Equipment
· Inspection
and Test Status
·
Control of Non –
Conforming Product
· Corrective
Action
· Handling,
Storage, Packaging and Delivery
· Quality
Records
· Internal
Quality Audits
· Training
· Servicing
· Statistical
Techniques

CLAUSES
(ELEMENTS) OF ISO 9000 (During the year 2000)
1. Scope
2. Normative
Reference
3. Terms
and Definitions
4. Quality
Management System (QMS)
General Requirements
Documentation
5. Management
Responsibility
Management Commitment
Customer Focus
Quality Policy Planning
Responsibility, Authority and
Communication Management Review
6. Resource
Management
Provision of Resources Human Resources
Infrastructure
Work Environment
7. Product Realization Planning of Product
Realization Customer related processes Design and Development Purchasing
Production and Service Provision
Control of Monitoring and Measuring devices
8. Monitoring
and Measurement General
Monitoring and Measurement
Control of Non-Conforming Product
Analysis of Data
Improvement
IMPLEMENTATION
OF QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM :
1.
Top Management Commitment
2.
Appoint the Management Representative
3.
Awareness
4.
Appoint an Implementation Team
5.
Training
6.
Time Schedule
7.
Select Element Owners
8.
Review the Present System
9.
Write the Documents
10.
Install the New System
11.
Internal Audit
12.
Management Review
13.
Pre-assessment
14.
Registration
PITFALLS
OF SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION :
1.
Using a generic documentation program or
another organization’s documentation program
2.
Over-documentation or documentation that is too
complex
3.
Using External Consultants without involvement
4.
Neglecting to obtain top management’s
involvement
5.
Developing a system that does not represent what
actually occurs
DOCUMENTATION
In every organization, the
quality system must be documented properly. The documentation of the system can
be seen as a hierarchical format as shown.
QUALITY
AUDITING
The term Audit refers to a regular examination and checking of
accounts or financial records, settlement or adjustment of accounts.
It also
refers to checking, inspection and examination of Production Processes.
PURPOSE
OF QUALITY AUDIT :
Ă˜ To
establish the adequacy of the system.
Ă˜ To
determine the effectiveness of the system.
Ă˜ To afford
opportunities for system analysis.
Ă˜ To help
in problem solving.
Ă˜ To make decision
making easier etc.
TYPES OF
QUALITY AUDIT :
1.
First – Party
Audit.
3.
Third – Party
Audit.
Quality
audit can also be classified on the basis of the area taken into account for
the audit such as
Ă˜ System
Audit.
Ă˜ Process
Audit.
Ă˜ Product
Audit.
Ă˜ Adequacy
Audit.
Ă˜ Compliance
Audit.

Related Topics