Chapter: Computer Architecture : Memory and I/O Systems
I/O Processors
I/O PROCESSORS.
IO processor is
• A
specialized processor
• Not only loads and stores into memory but also can execute instructions, which are among a set of I/O instructions
• The
IOP interfaces to the system and devices
• The sequence of events involved in I/O transfers to move or operate the results of an I/O operation into the main memory (using a program for IOP, which is also in main memory)
• Used
to address the problem of direct transfer after executing the necessary format
conversion or other instructions
• In
an IOP-based system, I/O devices can directly access the memory without
intervention by the processor
IOP instructions
• Instructions help in format conversions─ byte from
memory as packed decimals to the output
device for line-printer
• The I/O device data in different format can be
transferred to main memory using an IOP
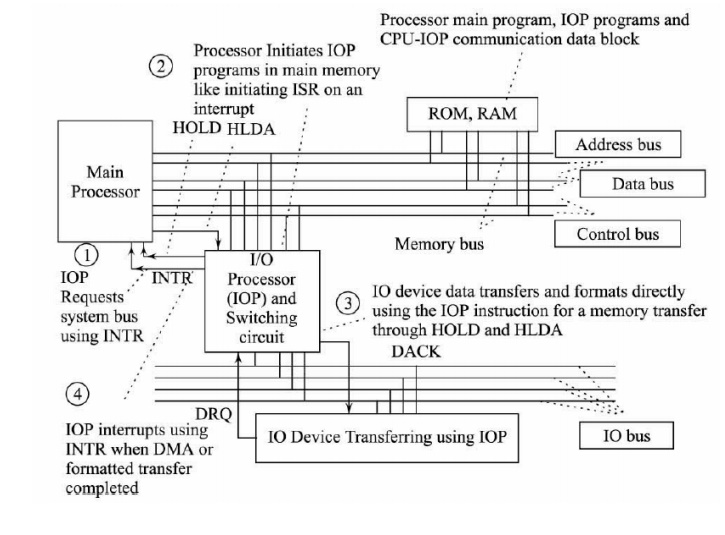
Sequence of events when using an I/O
Processor
Sequence 1:
A DRQ (for IOP request)
signal from an IOP device starts the IOP sequence, the IOP signals an interrupt
on INTR line this requests attention from the processor
Sequence 2:
The processor responds
by checking the device’s status via the memory-mapped control registers and
issues a command telling the IOP to execute IOP instructions for the transfer
to move the formatted data into the memory.
Sequence 3:
During each successive
formatted byte(s) transfer, the device DMAC (DMA controller) logic inside the
IOP uses a processor bushold request line, HOLD, distinct from INTR device
interrupt request line
• The main processor sends to the device a signal
from the processor called DACK (distinct from
INTA device-interrupt request-acknowledge line)
• The I/O device bus
has access to the address and data buses of the memory bus when DACK is
activated
• It
has no access when DACK is not activated when a HOLD request is not accepted by
the processor when the processor is using the memory bus
• Once
the DMA logic start command has been issued to IOP, the main processor begins
working on something else while the I/O device transfers the data into the
memory
Sequence 4:
When the IOP’s DMA transfer as per instructions is complete, the I/O device signals another interrupt (using DRQ) . Lets the main processor know that the DMA is done and it may access the data
Related Topics