Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Principles and practice of medicine and surgery
Hyperkalaemia - Fluid and electrolyte balance
Hyperkalaemia
Definition
A serum potassium level of >5.5 mmol/L is defined as hyperkalaemia. Hyperkalaemia of >6.0 mmol/L can cause cardiac arrhythmias and sudden death without warning.
Incidence
This is a common problem, affecting as many as 1 in 10 inpatients.
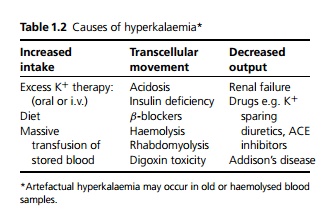
Aetiology
The causes are given in Table 1.2.
Pathophysiology
Hyperkalaemia lowers the resting potential, shortens the cardiac action potential and speeds up repolarisation, therefore predisposing to cardiac arrhythmias. The rapidity of onset of hyperkalaemia often influences the risk of cardiac arrhythmias, such that patients with a chronically high potassium level are asymptomatic at much greater levels.
Clinical features
Hyperkalaemia is almost always asymptomatic and only diagnosed on blood testing. There may be a history of conditions that predispose to hyperkalaemia and it is important to take a careful drug history. Foods high in potassium include bananas, citrus fruits, tomatoes and salt substitutes. The first indication of hyperkalaemia
Investigations
U&Es, calcium, magnesium to look for evidence of renal impairment and any associated abnormality in sodium, calcium and magnesium. Low calcium can increase the risk of arrhythmia. An arterial blood gas to look for acidosis may be indicated and diabetics should have their glucose checked.
An ECG should be performed immediately in all cases. Abnormalities occur in the following order: tall, tented T-waves, small P-wave and a widened, abnormal QRS complex. Patients may develop bradycardia or complete heart block, and if left untreated may die from ventricular standstill or fibrillation. Continuous ECG monitoring should occur until the hyperkalaemia is treated and ECG abnormalities resolve.
Management
Ideally hyperkalaemia should be prevented in at-risk patients by regular monitoring of serum levels and care with medication and intravenous supplements. Once hyper-kalaemia is diagnosed, withdraw any potassium supplements or causative drugs.
If the hyperkalaemia is mild (<6.0 mmol/L) and the ECG is normal, withdrawal of causative drugs or treatment of the underlying cause may be sufficient. Moderate asymptomatic hyperkalaemia (6.0–6.9 mmol/L) needs early specific treatment. If there are ECG changes, severe muscle weakness or the potassium level is >7 mmol/L, it is a medical emergency:
· Calcium gluconate is given intravenously. The calcium provides some immediate cardio-protection by reducing myocardial excitability, even in a patient with normal serum calcium levels. It can be repeated after a few minutes if the abnormalities on ECG persist.
· Until treatment of the underlying cause can take place, a glucose and insulin infusion promotes intracellular K+ uptake. Salbutamol nebulisers have a similar effect through β receptor stimulation. These can be repeated whilst the underlying cause is addressed, but have only a temporary effect.
· Diuretics, e.g. loop diuretics can be used to increase renal excretion. Oral ion-exchange resins or enemas may be used to increase gastrointestinal elimination of potassium. Oral resins can cause severe constipation, so these should be given with laxatives and are not a long-term solution.
· Any acidosis should be corrected.
· Refer to a renal physician or intensive care unit for haemofiltration or haemodialysis if the hyperkalaemia is refractory to treatment or if there is severe renal failure.
Related Topics