Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Human eye : Errors of refraction
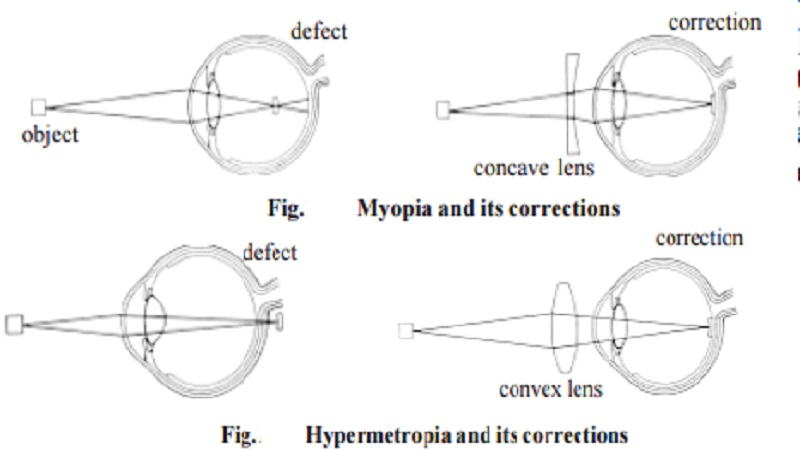
Human eye : Errors of refraction
In a normal eye focused for distant objects, parallel rays of light come to a sharp focus exactly on the retina. It can accommodate for clear vision of objects from infinity (far point) down to 25 cm (near point). This ideal refractive state is calledemmetropia. A deviation from emmetropia is called ametropia . The important forms of ametropia are myopia , hypermetropia,astigmatism, presbiopia. Ametropia results from an imbalance between the length of the eye ball and its refractive power.
(a) Myopia (Short Sightedness)
Myopia results if the lens curvature is too great or the entire eyeball becomes elongated. Light rays entering the eye are refracted more than is necessary. Consequently light is focused in front of the retina. The image perceived is thus blurred. The condition is called short-sightedness as objects near the eye are clearer than those further away. Myopia can be corrected by placing a concave lens in front of the eye. The surface of the concave lens refracts light rays in such a way that the rays diverge slightly from their original path. The lens of the myopic eye now refracts the diverged light rays in to focus on the retina.
(b). Hypermetropia (Long Sightedness)
Hypermetropia results when the curvature of the eye lens is not great enough. Light rays are not refracted enough and would thus be focused behind the retina. The condition is called long-sightedness because distant objects are clearer than near ones. This happens because light rays from distant objects require less refraction than rays from near objects. Correction of hypermetropia requires placing a convex lens in front of the eye. The lens converges light rays before they enter the eye so that the eye's focuses the light correctly on the retina.
(c). Astigmatism
Astigmatism occurs if either the cornea or lens is distorted. One part of the focusing mechanism then refracts light rays too much, or too less. Usually most of the images perceived is out of focus. Light rays from part of the object are focused in front of the retina, as in myopia. Rays from other parts would be focused behind the retina, as in hypermetropia. Astigmatism can be corrected by placing a lens in front of the eye. The curvature of this lens varies from one part to another to compensate for the eye's deficiencies.
(d). Presbiopia
This is the result of a reduction in the amplitude of accommodation with age due to hardening and loss of plasticity of the lens. Hence it becomes less capable of being moulded into a more complex form. Presbiopia begins at about 40 years of age. The remedy is convex lenses for reading. Any defect in the eye should be consulted immediately with the optometrist.
Optometry
The practice of assessing vision and establishing whether glasses or contact lenses are needed to correct any visual defect is known as
optometry. The eyes are examined by a qualified optometrist who will as-sess the errors of refraction, prescribe and supply glasses or contact lenses to correct it. Optometrists are not qualified to diagnose or treat disorders of the eye but will refer patients requiring further to an ophthalmologist.
Related Topics