Chapter: Modern Pharmacology with Clinical Applications: Drug Absorption and Distribution
Human Available Distribution Volume
AVAILABLE
DISTRIBUTION VOLUME
The total volume of the fluid
compartments of the body into which drugs may be distributed is approximately
40 L in a 70-kg adult. These compartments include plasma water (approximately
10 L), interstitial fluid (10 L), and the intracellular fluid (20 L). Total
extracellular water is the sum of the plasma and the interstitial water.
Factors such as sex, age, edema, pregnancy, and body fat can in-fluence the
volume of these various compartments.
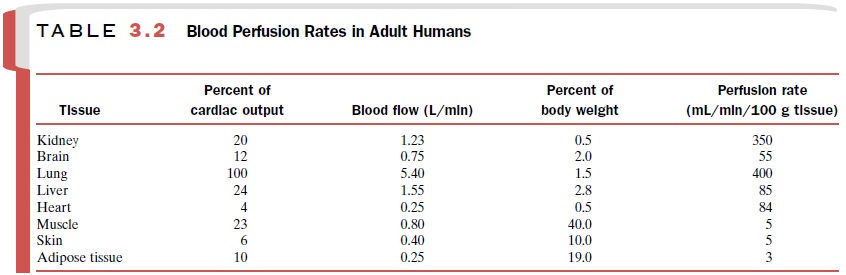
The rate at which an
equilibrium concentration of a drug is reached in the extracellular fluid of a
particular tissue will depend on the tissue’s perfusion rate; the greater the
blood flow the more rapid the distribution of the drug from the plasma into the
interstitial fluid. Thus, a drug will appear in the interstitial fluid of
liver, kidney, and brain more rapidly than it will in muscle and skin (Table
3.2).
Related Topics