Type A, B Hepatitis (HAV, HBV), Laboratory Diagnosis - Hepatitis Viruses | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 10 : Medical Virology
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 10 : Medical Virology
Hepatitis Viruses
Hepatitis Viruses
The term
viral hepatitis refers to a primary
infection of the liver, hepatitis viruses
consists of types A, B, C, D, E and G. Except for type B which is a DNA virus all the others are RNA viruses.
Two types
of viral hepatitis had been recognised. Type
one affects mainly children and young adults and transmitted by the
fecal-oral route called as infective
or infectious hepatitits or type A
hepatitis. Second type transmitted mainly by receiving serum inoculation or blood transfusion named as homologous serum jaundice, serum hepatitis transfusion hepatitis or type B hepatitis
Type A Hepatitis (HAV)
HAV is a
27nm non enveloped RNA virus belonging to the picorna virus family. It is designated as ‘entero virus 72’, HAV is recognised as new genus ‘Hepatovirus’. It can be grown in human
and simian cell cultures and is the only human hepatitis virus which can be
cultivated in vitro.
HAV
transmission is by the fecal oral route. Infection is by ingestion. The
virus multiplies in the intestinal
epithelium and reaches the liver by hematogenous
spread. Once jaundice develops, it
is rarely detectable in feces. The
incubation period is 2 - 6 weeks. The clinical disease consists of two stages
the prodromal and the icteric stage. The onset may be
acute with fever, malaise, anorexia,
nausea, vomiting and liver tenderness. These usually subside with the onset of
jaundice. Recovery is slow, over a period of 4–6 weeks. The disease
is milder in children. Type A
hepatitis caused by contaminated food, water or milk. Over crowding and poor sanitation favour its spread.
Laboratory Diagnosis
Diagnosis
of type A hepatitis may be made by demonstration
of the virus or its antibody.
Virus can be visualized by Immunelectron
Microscopy (IEM) in fecal
extracts during the late incubation period.
IgM anti-HAV antibody appears during the late incubation period
disappears after 3-4 months. IgG
peaks in 3-4 months and persists much longer for life. ELISA kits for detection
of IgM and IgG antibodies are available.
Does HSV shorten your lifespan?
Becoming infected with the herpes virus seriously complicates your social, emotional and sexual life, but it is
not otherwise a terribly dangerous condition to have. Having genital herpes does make it easier to get HIV (and thus AIDS), but otherwise, the condition is not disabling, and does
not reduce lifespan.
A safe
and effective formalin inactivated, alum
conjugaged vaccine containing HAV grown in human diploid cell culture is
used. Course consists of two intra muscular injections of the
vaccine. Protection begins 4 weeks after injection and lasts for 10 to 20 years. No specific antiviral
drug is available.
Type B Hepatitis (HBV)
HBV is a
42nm DNA virus with an outer
envelope and an inner core 27nm in diameter. Enclosing the viral genome and a DNA
polymerase . It belongs to the family Hepadna Viridae HBV is ‘Hepadna Virus type 1’. Australia
antigen was found to be
associated with serum hepatitis. It was the surface component of HBV, so named
as hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg).
3 types of particles are
visualized, most abundant form is a spherical particle, 22nm in diameter.
The second type of particle is filamentous
or tabular with a diameter of 22nm
both are antigenically identical. Third type of particle are fewer in number,
is a double walled spherical structure
42 nm in diameter. This particle is the complete hepatitis B virus, known as Dane
particle.
The
envelope proteins expressed on the surface contains hepatitis B surface antigen
(HBsAg). HBsAg consists of two
major polypeptides, one of which is glycosylated. The nucleocapsid or core
contains hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg A) (Figure 10.5). Third antigen called the hepatitis B e
antigen (HBeAg) is a soluble non particulate nucleocapsid protein.
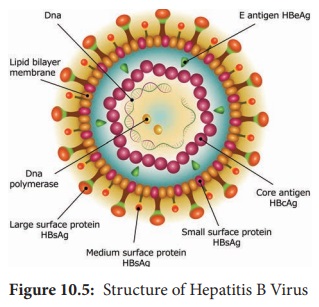
The nucleocapsid encloses the viral genome
consisting of two linear strands of DNA held in a circular
configuration. One of the strands is
incomplete (+ strand) DNA appears
partially double stranded and partially single stranded. Associated with the + strand is a viral DNA polymerase (has
both DNA dependent DNA polymerase
and RNA dependent reverse transcriptase functions). This polymerase can repair the gap in the plus strand and
render the genome fully double stranded.
Natural
infection occurs only in humans. The virus is maintained in
carriers whose blood contains circulating
virus for long periods. Carriers are
of two categories, the highly
infectious super carriers and the simple carriers.
Former have high titre HBsAg along
with HBsAg, DNA polymerase and HBV in ciruculation. Simple carriers have low
infectivity and low titre HBsAg in blood.
HBV is a blood borne virus and the infection is
transmitted by parenteral, sexual and perinatal models. The virus may also be present in other body fluids and excretions such as saliva, breast milk, semen, vaginal secretions, urine bile and feces of these
semen and saliva are known to transmit the infection
very commonly. Transfusion of carrier blood once, the most widely known mode of
infection has largely been eliminated by donor screening that is strictly
enforced. Infection by direct contact with open skin lesions such as pyoderma,
eczema, cuts and scratches is very common among young children in developing countries. Certain groups and occupations
carry a high risk of infection. These include medical and paramedical staff of
blood banks, dialysis units, barbers, sex workers
The
incubation period is long about 1- 6 months. The onset is insidious and fever
is not prominent. Extra hepatic complications like arthralgia, urticaria and
glomerulonephritis may occur. About 90-95% of adults with acute hepatitis infection
recover within 1-2months of onset and eliminate the virus from the body. They
may be Asymptomatic carriers or may progress to recurrent
or chronic liver disease..
Laboratory Diagnosis
Serology
Diagnosis
of hepatitis B depends on the serological
demonstration of the viral markers.
HBsAg is the first marker to appear
in blood after infection, being
detectable. It remains in circulation throughout the symptomatic course of the
disease (2- 6months). Anti HBs is the protective antibody.
HBcAg is not
demonstrable in circulation
because it’s enclosed within the HBsAg coat but its antibody, anti HBc
appears in serum a week or two after the appearance of HBsAg. As anti HBc
remains life long, it serves as a useful indicator of prior infection with HBV.
HBeAg appears in blood concurrently with HBsAg, indicating the high
infectivity. Molecular methods such
as DNA: DNA hybridization and PCR at present used for HBV DNA testing are
highly sensitive and quantitative.
Immunization
Both
passive and active methods of immunization are available. Active immunization is
more effective. The currently
preferred vaccine is genetically engineered by cloning the S gene for HBV in Baker’s yeast. A special vaccine containing all antigenic components of
HBsAg (Pre- S1, Pre-S2 and s) has been developed. No specific antiviral treatment
is available for acute HBV infection.
Related Topics