Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 10 : Medical Virology
Cultivation of Viruses
Cultivation of Viruses
Viruses
are obligate intracellular
parasites; they cannot be grown on any inanimate culture medium. Three methods are employed for the
cultivation of viruses – inoculation
into animals, embryonated eggs and tissue culture or cell culture.
i. Animal Inoculation
The
earliest method for the cultivation of viruses causing human diseases was
inoculation into human volunteers. Monkeys were used for the isolation of the
polio virus by Landsteiner and Popper
(1909). The embryonated hen’s egg
was first used for cultivation of
viruses by Good pasture (1931). The
embryonated egg offers several sites
for the cultivation of viruses. Non human primates provide the only method for
virus cultivation. Mice are most widely employed animals in Virology.
ii. Embryonated Eggs
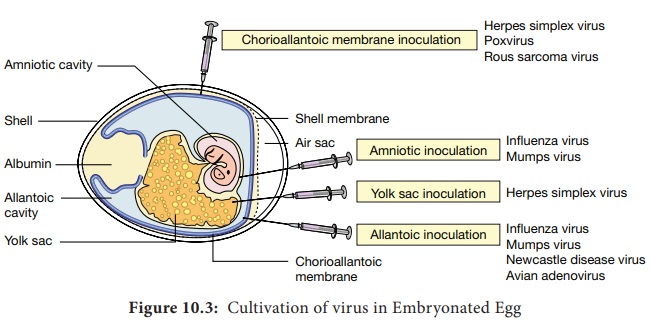
a. Chorioallantonic Membrane (CAM)
Inoculation
on the chorioallantonic membrane produces visible lesions (pocks). Different viruses have
different pock morphology. Example: variola or vaccinia
b. Allantonic Cavity
Inoculation
on the allantonic cavity provides a
rich yield of influenza and some paramyxo viruses.
c. Amniotic Sac
Inoculation
into the amniotic sac is for the
primary isolation of the influenza virus
d. Yolk Sac
Inoculation
into the yolk sac is for the
cultivation of some viruses like Chlamydiae and Rickettsiae.
Allantonic
inoculation is employed for growing influenza virus for vaccine production
(Figure 10.3).
iii. Tissue Culture
First
tissue culture in Virology was maintained by Steinhardt and colleagues (1913)
for the vaccinia virus in fragments of
rabbit cornea. Bacterial contamination was the major limitation. Different
types of culture used are:
a. Organ culture
Small bits of organs can be
maintained, used for the isolation
of some viruses. Example: Corona virus (respiratory pathogen) cultured on
tracheal ring organ culture
b. Explant culture
Fragments of minced tissue are grown as ‘explants’. This is also known as
tissue culture. Example: Adeno virus cultured on Adenoid tissue explants.
iv. Cell Culture
Tissues
are dissociated into the component cells by the action of enzymes (trypsin) or by mechanical process and are
suspended in a growth medium (amino acids, vitamins, salts, glucose) supplemented with fetal calf serum of
antibiotics and indicator (Phenol
red). This media is dispensed in
bottles, tubes or petridishes. The cells adhere to the glass surface and on
incubation divides to form a confluent monolayer sheet of cells covering the
surface within about a week. The cell culture is classified into three types.
a Primary cell cultures.
In this
culture, normal cells are taken from
the body and cultured. They are capable of only limited growth in culture.
Example: Monkey kidney, Human embryonic kidney, Chick embryo cell culture.
b. Diploid cell strains
These are
cells of a single type that retain
the original diploid chromosome number
and serotype during serial sub cultivation for limited number of times.
Example: Human fibroblast.
c. Continuous cell lines
These are single type, derived from cancer cells that are capable of continuous serial cultivation. Example: Cells derived from cancers, such as Hela, Hep-2 and KB cell lines.
Related Topics