Chapter: Medical Physiology: Pituitary Hormones and Their Control by the Hypothalamus
Growth Hormone Promotes Growth of Many Body Tissues
Growth Hormone Promotes Growth of Many Body Tissues
Growth hormone, also called somatotropic hormone or somatotropin, is a small protein molecule that contains 191 amino acids in a single chain and has a molecular weight of 22,005. It causes growth of almost all tissues of the body that are capable of growing. It promotes increased sizes of the cells and increased mitosis, with development of greater numbers of cells and specific differentiation of certain types of cells such as bone growth cells and early muscle cells.
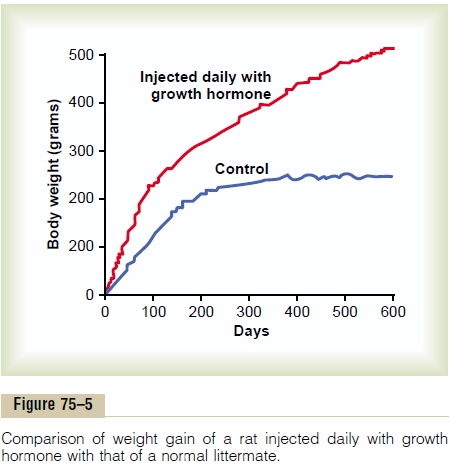
Figure 75–5 shows typical weight charts of two growing littermate rats, one of which received daily injections of growth hormone and the other of which did not receive growth hormone. This figure shows marked enhancement of growth in the rat given growth hormone—in the early days of life and even after the two rats reached adulthood. In the early stages of development, all organs of the treated rat increased proportionately in size; after adulthood was reached, most of the bones stopped lengthening, but many of the soft tissues continued to grow. This results from the fact that once the epiphyses of the long bones have united with the shafts, further lengthening of bone cannot occur, even though most other tissues of the body can continue to grow throughout life.
Related Topics