Chapter: BIOLOGY (ZOOLOGY) Standard XI first year 11th text book Assignment topics question and answer Explanation Definition
Genetics : Sex - linked Inheritance
Genetics : Sex - linked Inheritance
Most of the inheritable characters are controlled by genes located in autosomes. The inheritance of traits related to autosomes normally follows Mendel's laws. Mendelian ratios are not obtained for those characters for which genes are exclusively located either in X or Y chromosome. The genes that occur only on X chromosomes are called as X - linked genes. Similarly, that the genes occur exclusively on Y chromosomes are called the holandric genes. The inheritance of X or Y linked genes is called as sex linked inher-itance. Thus the sex linked inheritance may be X- linked, Y- linked or XY linked.
X - Linked inheritance
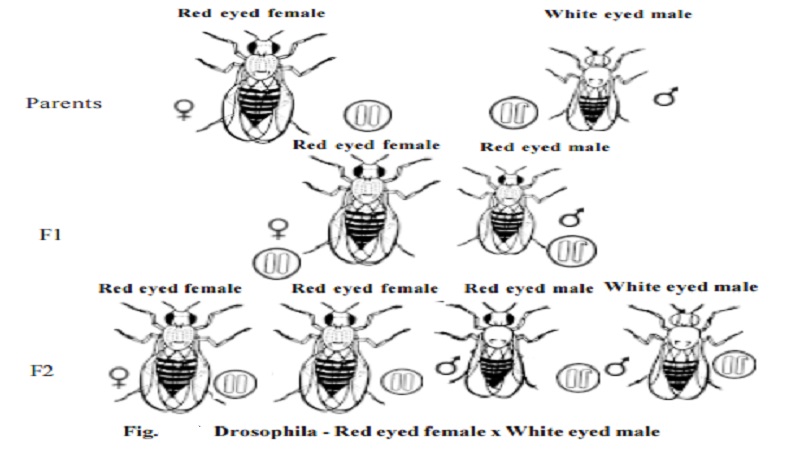
T. H. Morgan (1910) in his studies on inheritance of genes in Droso-phila discovered that the pattern of inheritance of certain traits were found to vary with the sex of the parent and offspring. He found that the gene for white eye colour is X - linked. Further it was found to be recessive to another X - linked, dominant gene for red eye colour.
Red eyed female x white eyed male
When a wild red eyed female Drosophila is crossed with a mutant white eyed male, all the F1 individuals (males and females) have red eyes. When the red eyed male and red eyed female of the F1 were intercrossed, in the F2 generation all the female flies were found to be red eyed. Among the males 50 % had red eyes and another 50 % had white eyes.
White eyed female x Red eyed male
When a white eyed female Drosophila is crossed with a red eyed male, all the female individuals in the F1 generation are red eyed and all the males are white eyed. When these red eyed female individuals and white
eyed male individuals of F1 are intercrossed the F2 generation possessed 50 % red eyed and 50 % white eyed females. Similarly the male population of F2 included 50 % red eyed and 50 % white eyed flies.
Sex linked inheritance in Humans
Most of the sex linked characters in humans are X - linked. There are 150 confimed X- linked traits known. Most of them are recessives.
Colour blindness :
The human vision is basically due to cells called rods and cones found on the retina of the eye. The cone cells are sensitive to red, green and violet light. The formation of colour sensitive cones is controlled by a dominant X-linked gene.
The recessive form of this gene is incapable of producing colour sensitive cones. Hence homozygous recessive females (XCXC) and Hemizygous recessive males (XCY) are unable to differentiate between red and green colour. The frequency of colour blind women is less than colour blind men.
Colour - blind man x normal visioned woman
When a colour-blind man marries a normal woman in their F1 progeny all children would be normal. However the female will be a carrier for the recessive gene. If that female gets married to a normal male in the F2 genera-tion normal and colour-blind nature will occur in 3 : 1 ratio.
Related Topics