Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Virology, Virus: General Properties of Viruses
General Properties of Viruses
General Properties of Viruses
Introduction
The viruses are too small to be seen with a light microscope. Their small size allows them to pass through filters that are used to retain back bacteria in contaminated fluids. Hence, they were first described as filterable agents. Viruses, like other microorganisms (e.g., bacteria, fungi, and parasites), are the infectious agents that are associated with disease in humans. The viruses unlike other infectious agents are obligate intracel-lular parasites, i.e., they absolutely require living host cells in order to multiply. In addition, viruses replicate by assembly of the individual components rather than by binary fission. The viruses show the following features:
1. They are filterable agents.
2. They are obligate intracellular parasites.
3. They contain a single type of nucleic acid, i.e., either DNA or RNA, but not both.
4. The virion of the virus particle consists of a nucleic acid genome packaged into a protein coat (capsid), which itself is sometimes enclosed by an envelope of lipid, proteins, and carbohydrates known as envelope.
5. They multiply inside the living cells by using the synthesiz-ing machinery of the host cell.
6. They replicate by the assembly of the individual com-ponents and do not replicate by division, such as binary fission.
7. They have a few or no enzymes for their own metabo-lism. They always use host cell machinery to produce their components, such as viral messenger RNA (mRNA), protein, and identical copies of the genome.
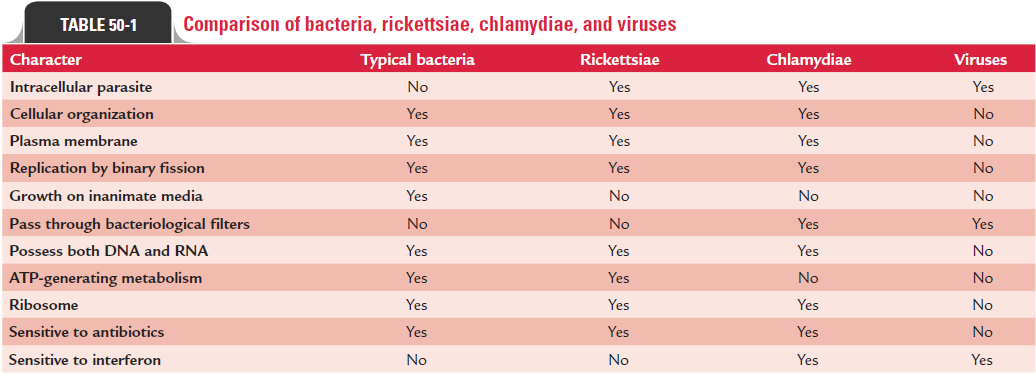
The differences between bacteria and viruses are summarized in Table 50-1. The viruses affect a wide range of hosts. There are viruses that infect invertebrates, vertebrates, plants, protists, fungi, and even bacteria. In medical microbiology, we are concerned mainly with viruses that infect either humans or bacteria. The viruses that infect bacteria are known as bacteriophages or phages.
Related Topics