Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: The Urinary System
Functions of the Kidneys
OTHER FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEYS
In addition to the functions described thus far, the kid-neys have other functions, some of which are not directly related to the formation of urine. These func-tions are secretion of renin (which does influence urine formation), production of erythropoietin, and activation of vitamin D.
Secretion of renin—When blood pressure de-creases, the juxtaglomerular ( juxta means “next to”) cells in the walls of the afferent arterioles secrete the enzyme renin. Renin then initiates the renin-angiotensin mechanism to raise blood pres-sure. The sequence of events is presented in Table 18–2. The end product of this mechanism is angiotensin II, which causes vasoconstriction and increases the secretion of aldosterone, both of which help raise blood pressure.
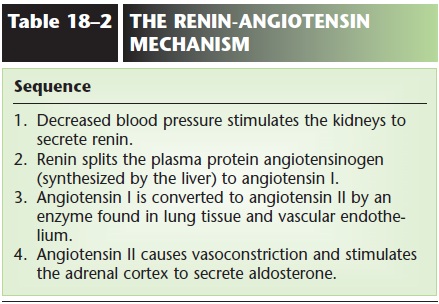
A normal blood pressure is essential to normal body functioning. Perhaps the most serious change is a sudden, drastic decrease in blood pressure, such as would follow a severe hemorrhage. In response to such a decrease, the kidneys will decrease filtration and urinary output and will initiate the formation of angiotensin II. In these ways the kidneys help ensure that the heart has enough blood to pump to maintain cardiac output and blood pressure.
Secretion of erythropoietin—This hormone is secreted whenever the blood oxygen level decreases (a state of hypoxia). Erythropoietin stimulates the red bone marrow to increase the rate of RBC production. With more RBCs in circulation, the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood is greater, and the hypoxic state may be corrected.
Activation of vitamin D—This vitamin exists in several structural forms that are converted to cal citriol (D2) by the kidneys. Calcitriol is the most active form of vitamin D, which increases the absorption of calcium and phosphate in the small intestine
Related Topics