Political Science - Functions of Political Parties | 11th Political Science : Chapter 9 : Public Opinion and Party System
Chapter: 11th Political Science : Chapter 9 : Public Opinion and Party System
Functions of Political Parties
Functions of Political Parties
In a democracy, political parties serve as an
integral link through which government and the public can interact. Political
Parties act as a foundation that orients the people towards political
initiatives and public experience. Political Parties work to influence
political thought and opinion with the intention of mobilizing votes. They
provide a platform for political, economic and social activism that serves as a
training ground for future regional and national leadership. In the long run
they hold leaders accountable for their actions through rigorous debate and
queries both within the party as well as through opposition parties. Thus the
people are presented with a diverse choice of candidates, ideologies and
approaches to various issues governing the nation. Their confidence in
democracy is thus reinforced in the knowledge that they can bring about change
and transformation should a majority of the population desire a transformation
in the way they are governed.
The Party System
The party system helps to operate and stabilize
governments and they are particularly relevant for the effective functioning of
democracies. The party system provides a system of checks and balances against
the government’s policies. By soliciting popular support among the masses and
providing a structure for leadership and dialogue within the party according to
specific party objectives and agenda, it helps sustain good governance.
Types of Party Systems
Different types of party system have evolved in
various parts of the globe depending on the particular elements of democracy
practiced. By and large the quality of a democracy is determined by how the
government is representative of its people, how accountable the government is
to its people, how human rights and equality of status and opportunity is
guaranteed to all citizens and the level of political participation exercised
by the people. The various types of party system address these issues in
different ways, thereby determining the quality of democracy practiced.
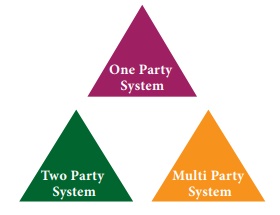
A. One Party System
In a one party system, a single political party
exercises its right to form the government, which is often derived from a
written or unwritten constitution. In most cases under a one party system,
there is less participation and weaker accountability. Examples: Communist Party of China, (CPC) the Peoples` Action Party
(PAP)in Singapore, Korean Workers Party, (KWP) North Korea, Communist Party of
Vietnam (CPV) Vietnam, Communist Party of Cuba (CPC) Cuba. The single party
system does not provide adequate space for democratic expressions and not
provide scope for alternative. For example in the 1920s fascist movements
advocating nationalistic militarism, captured power in Germany under Hitler, in
Italy under Mussolini and in Spain under General Franco. They prevented other
political parties to emerge.
B. Two Party System
In the two party system, two political parties,
with distinctly different interests have equal opportunity to attain a majority
and form the government. The majority party is the governing party and the
minority party forms the opposition party in two-party systems. The Two-Party
system has far greater accountability by the political leaders and greater
political participation. The threat of being voted out by the opposition hangs
as a ‘Damocles sword’ on the incumbent thereby guaranteeing a higher degree of
responsible conduct and action. However since the political atmosphere is
heavily polarized, drastic changes can happen once a party loses power which
may prove detrimental to national interests. Examples of the two-party system
include USA –Democrats and Republicans and UK Conservatives and Liberals.
However, in either country there is no
constitutional restriction on number of parties. The constitutional procedures
and peoples’ political maturity led to the emergence of two party system.
C. Multi-Party system
In the Multi- party system, multiple political
parties are capable of garnering popular support and forming a government,
either as a majority party or in coalition with many non-majority parties with
similar political objectives. In this system, the political leaders are
constantly observed and checked by checks and balances by their coalition
partners. They are also subject to rigorous accountability to the people. The
multi-party system offers the electorate the multiple avenues of political
participation and the ability to bring about political change for greater
national development.
The proportional representation system in France
and Italy results in multi-party systems and coalition cabi-nets.
Examples of countries with multi-party systems
include Canada, France, Germany, India and Sweden.
Topic for Pair 2:Why do we need at least two parties
in a democratic system?
Topic for Pair 3: If all the decision of a political party
are made by a single family and all other members are neglected, then what
challenge is being faced by that party?
Topic for Pair 4: Do you think that dynasty (family)
politics is confined to only a few states or parties?
Related Topics