Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
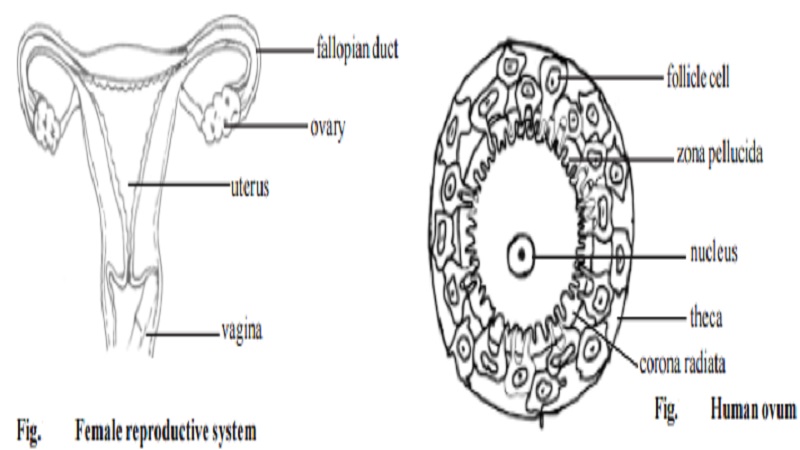
Functioning of female reproductive system
Reproduction
All living organism maintain their populations by reproduction. Most simple organisms such as bacteria reproduce asexually by cell division resulting in offspring's that are genetically identical.
In human beings, reproduction is sexual, involving the fusion of two reproductive cells, namely a sperm (male gamete) and an egg (female ga-mete). If a sperm succeeds in fertilizing an egg, DNA (genetic material) from each parent combines to create a unique individual. Sexual reproduction re-sults in an infinite variety of offsprings.
Functioning of female reproductive system
The central role of the female reproductive system is carried out by the ovaries. They produce sex cells called ova or eggs containing genetic material.
By a process of fertilization an egg derives the potentiality to develop into a foetus. The ovaries also secrete female sex hormones that control sexual development and the menstrual cycle
Endocrine function of Ovary (Female Sex Hormones)
The ovaries produce the female sex hormones oestrogen and progesterone. The secretion of these hormones are controlled by follicle - stimulating hormone and lutenizing hormone which are produced by pituitary gland.Female sex hormones control sexual development at puberty, the menstrual cycle and fertility.
Oestrogens
These are steroidal hormones secreted by the theca interna of the ovum, cells of graffian follicle, corpus luteum and placenta. Oestrogen hormone controls the development of accessory sex organ and secondary sexual characters. It regulates menstrual cycle. Oestrogen promotes growth of ovarian follicles. Further it causes the growth of the breasts and formation of melanin pigments.
Progesterone is the principal hormone secreted by the corpus luteum. It prepares the uterus for implantation of the fertilized ovum.It helps in the formation of placenta and for maintaining pregnancy. Further during preguancy it inhibits contraction of uterus. It also suppresses ovulation and menstruation in pregnancy.
Structure of a mature ovum
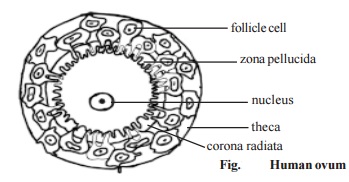
Human ovum is small and contains no yolk (Alecithal egg) It is more than 100mm in diameter At the time of ovulation, the ovum is surrounded by a striated membrane called zona radiata and later it is replaced by an unstriated membrane Zona pellucida(Primary egg membrane).
The growing oocytes are surrounded by follicle cells. Some of the follicular cells of the ovary are found outside the zona pellucida and are termed as Corona radiata (Secondary egg membrane) which is peeled off when the oocyte passes down the oviduct. The follicles and the developing oocyte together constitute Graafian follicle. The whole surface of the graafian follicle is supported by theca interna and theca externa.
Ovulation and fate of the ovum
The shedding of the ovum from the ovary is called ovulation. The ovarian follicle enlarges and reaches the surface of the ovary. The stroma and the theca of the Graffian follicle ruptures and the ovum is shed from the ovary. As it reaches
the fallopian tube it may get fertilized. The fertilized egg reaches the uterus and gets implanted on its wall. If the ovum is not fertilized in the fallopian tube it dies in 12- 24 hours.
Corpus luteum
The corpus luteum is an important structure needed at the time of pregnancy. It is derived from the empty graafian follicle after ovulation. The corpus luteum secretes a hormone called progesterone. It is a steroid hormone, secreted in significant amounts by the corpus luteum and placenta.
Related Topics