Chapter: Ophthalmology: Ocular Trauma
Eye Injuries Due to Physical Agents
Injuries Due to Physical Agents
Ultraviolet Keratoconjunctivitis
Etiology:
Injury from ultraviolet radiation can occur from welding
withoutproper eye protection, exposure to high-altitude sunlight with the eyes
open without proper eye protection, or due to sunlight reflected off snow when
skiing at high altitudes on a sunny day. Intense ultraviolet light can lead to
ultraviolet keratoconjunctivitis within a short time (for example just a few
minutes of welding without proper eye protection). Ultraviolet radiation
penetrates only slightly and therefore causes only superficial necrosis in the
corneal epithelium. The exposed areas of the cornea and conjunctiva in the
palpebral fissure become edematous, disintegrate, and are finally cast off.
Ultraviolet keratoconjunctivitis is one of the
most common ocular in-juries.
Symptoms and diagnostic considerations:
Symptoms typically manifestthemselves after a
latency period of six to eight hours. This causes patients to seek the aid of
an ophthalmologist or eye clinic in the middle of the night, complaining of
“acute blindness” accompanied by pain, photophobia, epi-phora, and an
intolerable foreign-body sensation. Often severe blepharo-spasm will be
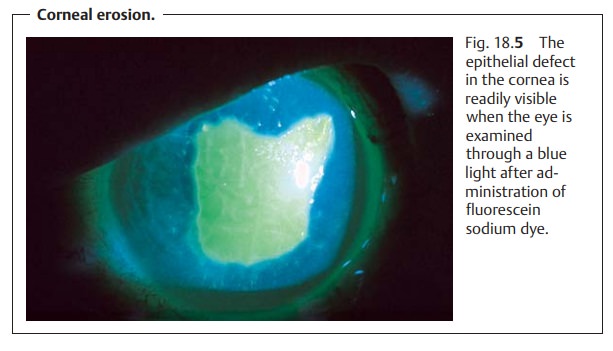
present. Slit-lamp examination will require administration of a topical
anesthetic. This examination will reveal epithelial edema and superfi-cial
punctate keratitis or erosion in the palpebral fissure under fluorescein dye
(see Fig. 18.5).
The topical anesthetic will completely relieve
symptoms within a few seconds and allow the patient to see clearly and open his
or her eyes without pain. Under no circumstances may the patient be allowed
access to this anesthetic without medical supervision. Uncontrolled habitual
use suppresses the pain reflex (eye closing reflex), which could result in
incalculable corneal damage.
Treatment:
The “blinded” patient should be instructed that the symptomswill
resolve completely under treatment with antibiotic ointment within 24 to 48
hours. Ointment is best be applied to both eyes every two or three hours with
the patient at rest in darkened room. The patient should be informed that the
eye ointment will not immediately relieve pain and that eye move-ments should
be avoided.
Burns
Etiology:
Flaring flames such as from a cigarette lighter, hot vapors,
boilingwater, and splatters of hot grease or hot metal cause thermal
coagulation of the corneal and conjunctival surface. Because of the eye closing
reflex, the eyelids often will be affected as well.
Injuries due to explosion or burns from a
starter’s gun also include parti-cles of burned powder (powder burns). Injuries
from a gas pistol will also involve a chemical injury.
Symptoms and diagnostic considerations:
Symptoms are similar to thoseof chemical
injuries (epiphora, blepharospasm, and pain).
A topical anesthetic is administered, and the
eye is examined as in a chemical injury. Immediate
opacification of the cornea will be readily apparent. This is due to
scaling of the epithelium and tissue necrosis, whose depth will vary with the
severity of the burn. In burns from metal splinters, one will often find cooled
metal particles embedded in the cornea.
Treatment:
Initial treatment consists of applying cooling antiseptic
band-ages to relieve pain, after which necrotic areas of the skin, conjunctiva,
and cornea are removed under local anesthesia. Foreign particles such as embedded ash and smoke particles in the
eyelids and face are removed incooperation with a dermatologist by brushing
them out with a sterile toothbrush under general anesthesia. This is done to
prevent them from growing into the skin like a tattoo. Superficial particles in the cornea andconjunctiva are removed
under local anesthesia together with the necrotictissue. The affected areas are
then treated with an antibiotic ointment.
Prognosis:
The clinical course of a burn is usually less severe than that
of achemical injury. This is because burns, like acid injuries, cause
superficial coagulation. Usually they heal well when treated with antibiotic
ointment.
Radiation Injuries (Ionizing Radiation)
Etiology:
Ionizing radiation (neutron, or gamma/x-ray radiation) have
highenergy that can cause ionization and formation of radicals in cellular
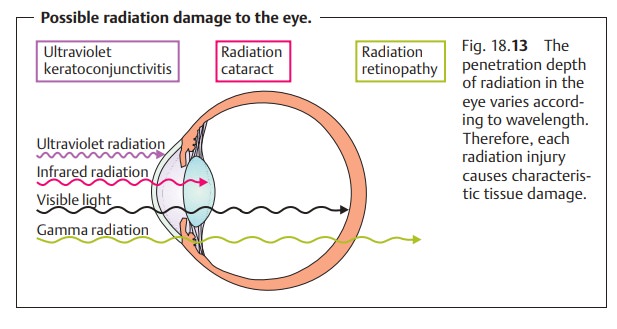
tissue. Penetration depth in the eye varies with the type of radiation, i.e.,
the wavelength, resulting in characteristic types of tissue damage (Fig. 18.13). This tissue damage always
manifests itself after a latency period, often only after a period of years
(see also Symptoms and clinical picture). Common sites include the lens
(radiation cataract) and retina (radiation retinopathy). This tissue damage is
usually the result of tumor irradiation in the eye or nasopharynx. Radiation
disorders have been observed in patients from Hiroshima and Nagasaki and, more
recently, in Chernobyl.
Symptoms and clinical picture:
Loss of the eyelashes and eyelid pigmenta-tion accompanied by blepharitis are typical symptoms. A dry eye is a sign of damage to the conjunctival epithelium (loss of the goblet cells). Loss of visual acuity due to a radiation cataract is usually observed within one or two years of irradiation. Radiation retinopathy in the form of ischemic retinopathy with bleeding, cotton-wool spots, vascular occlusion, and retinal neovasculariza-tion usually occurs within months of irradiation.
Treatment and prophylaxis:
Care should be taken to cover the eyes prior toplanned radiation
therapy in the head and neck. Radiation cataract may be treated surgically.
Radiation retinopathy may be treated with panretinal pho-tocoagulation with an
argon laser.
Related Topics