Chapter: Ophthalmology: Ocular Trauma
Blunt Ocular Trauma (Ocular Contusion)
Blunt Ocular Trauma (Ocular Contusion)
Epidemiology and etiology:
Ocular contusions resulting from blunt
traumasuch as a fist, ball, champagne cork, stone, falling on the eye, or a
cow’s horn are very common. Significant deformation of the globe can result
where the diameter of the blunt object is less than that of the bony structures
of the orbit.
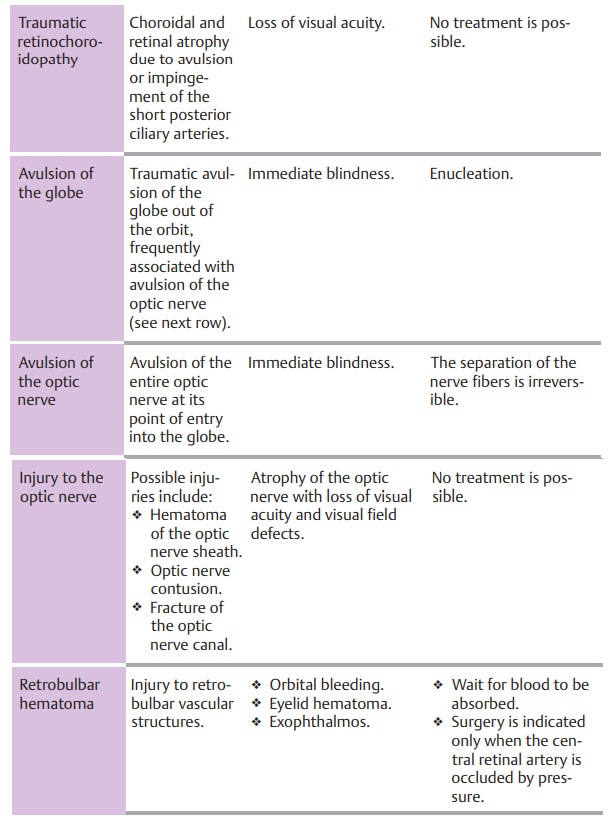
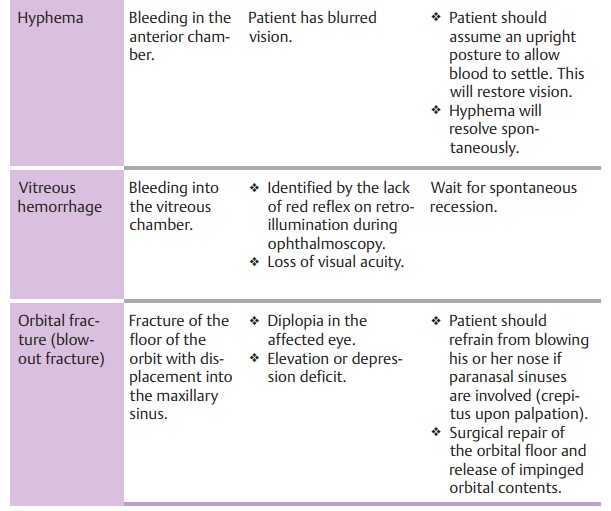
Clinical picture and diagnostic considerations:
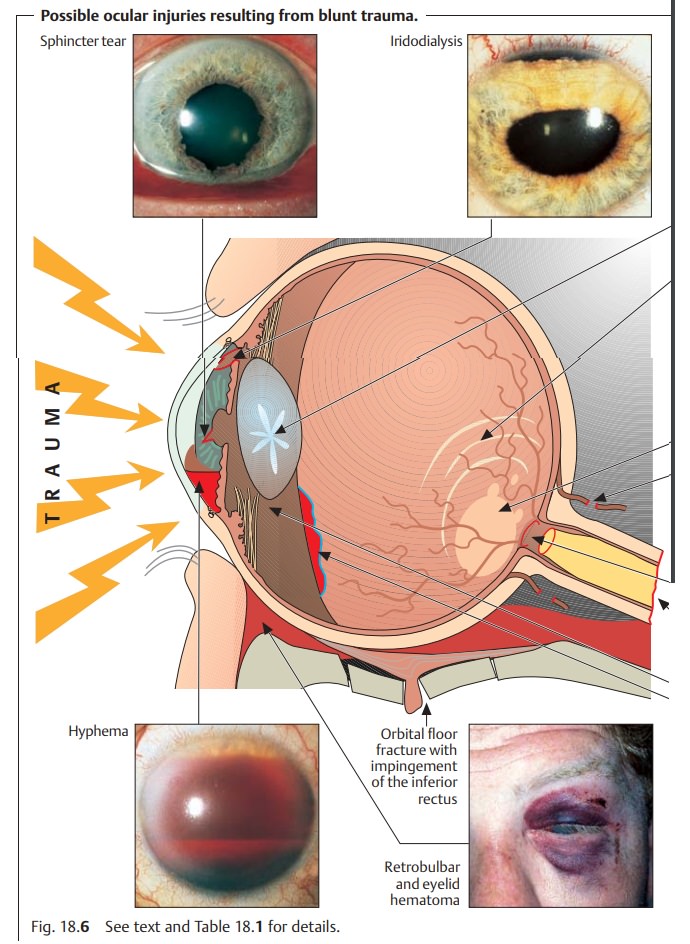
Deformation exerts signifi-cant traction on intraocular structures and can cause them to tear. Often there will be blood in the anterior chamber, which will initially prevent the examiner from evaluating the more posterior intraocular structures.
Do not administer medications that act on the
pupil as there is a risk of irreversible mydriasis from a sphincter tear, and
pupillary movements increase the risk of subsequent bleeding. The posterior
intraocular structures should only be thoroughly examined in mydriasis to
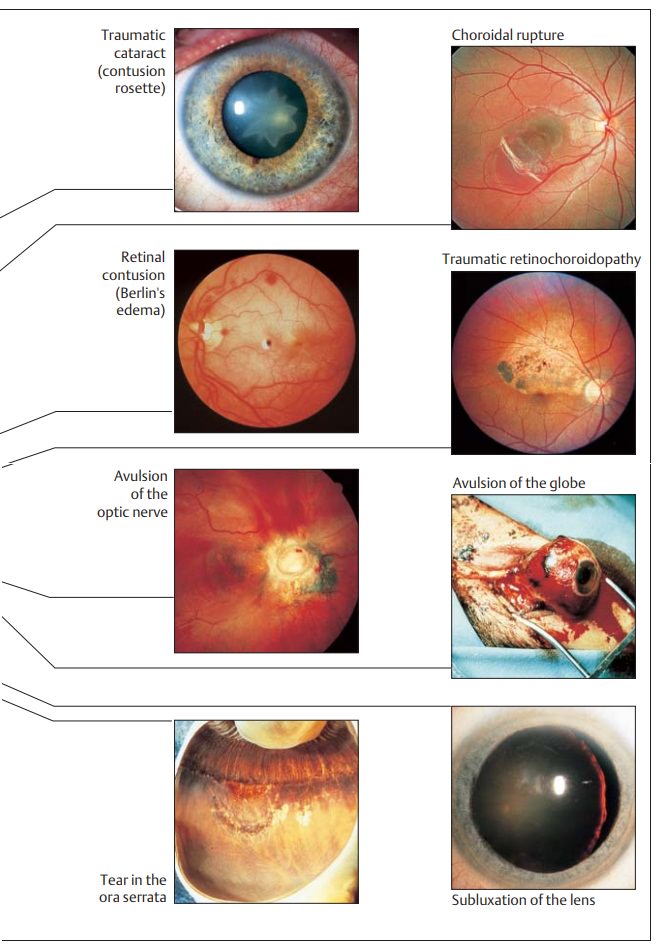
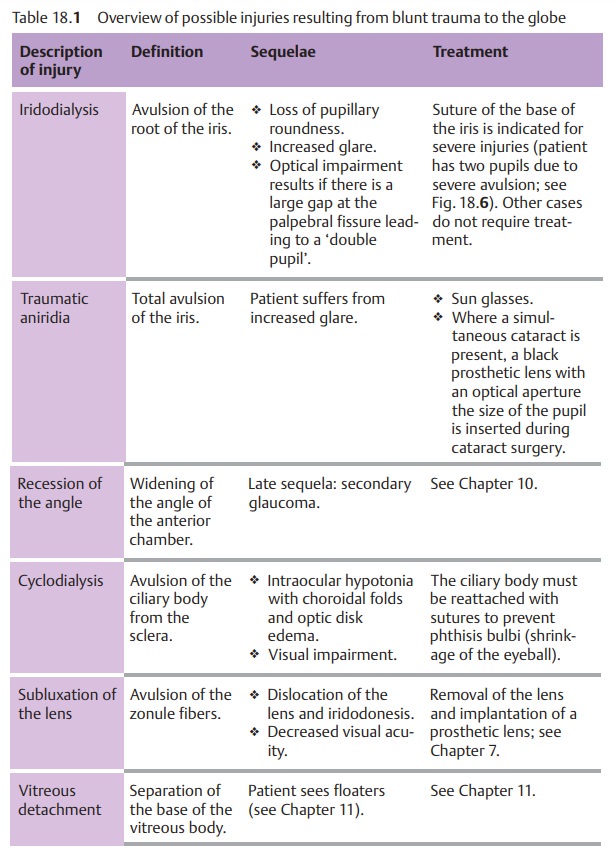
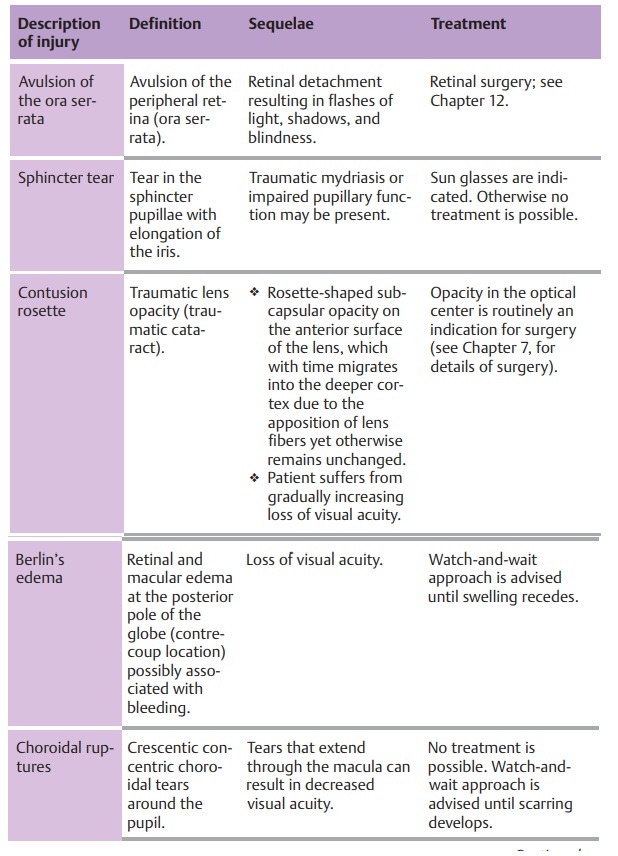
deter-mine the extent of injury after a week to ten days.Common injuries are
listed in Table 18.1 and Fig. 18.6.
Late sequelae of blunt ocular trauma include:
âť– Secondary glaucoma.âť– Retinal detachment.âť– Cataract.
Late sequelae of blunt ocular trauma may occur
years after the injury.
Treatment:
This involves immobilizing the eye initially,
to allow intraocularblood to settle. See Table 18.1 for details.
Subsequent bleeding three or four days after
the injury is common.
Related Topics