Chapter: Forensic Medicine: Basic anatomy and physiology
Excretion of waste matter
Excretion of waste matter
The process of removing waste matter from the
blood and from the body is called excretion.
Carbon dioxide is eliminated by the lungs into
the air through breathing. The lungs also give off a considerable quantity of
water as moisture in the breath. The lungs thus serve the dual purpose of
taking up oxygen from the air into the blood, and of eliminating carbon dioxide
from the blood to the air. This is the essential purpose of respiration or
breathing.
Water, along with a small quantity of other
waste substances, is eliminated by the skin in the form of sweat. The kidneys
withdraw from one to one-and-a-half litres of water daily from the blood which
contains dissolved mineral salts and several other important forms of waste
matter (the most important being urea). These form the urine. The urine passes
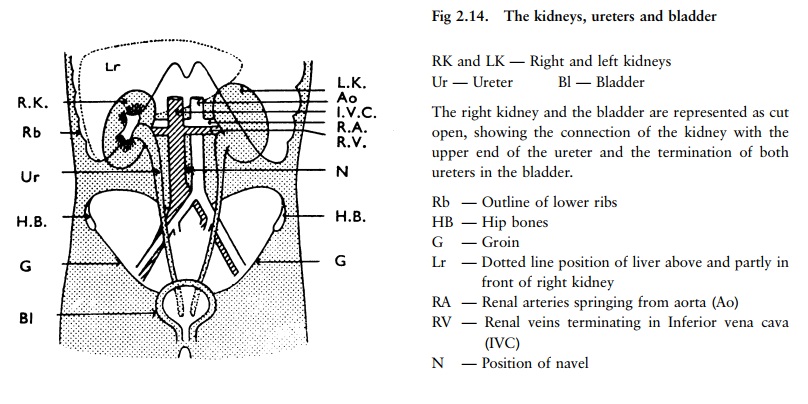
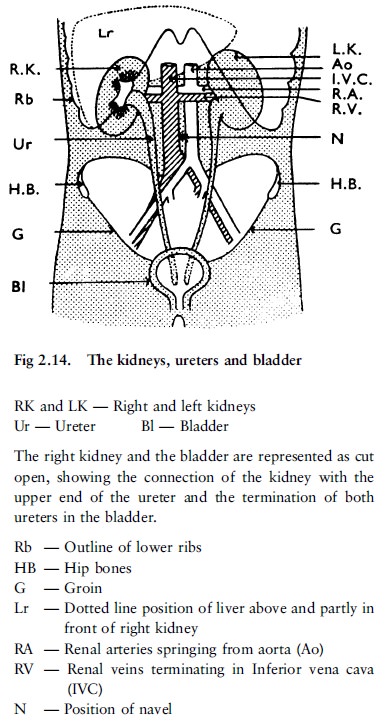
down from the kidneys to the bladder, from where it is expelled (fig 2.14).
Other waste matter is eliminated by the liver in
the bile, and this together with the unabsorbed and undigested portions of the
food is expelled from the body through evacuation of the bowels, as faeces or
stools. The faeces also contain countless numbers of germs or bacteria, as well
as a variety of viruses and yeast.
Related Topics