Zoology - Evolution: Summary | 12th Zoology : Chapter 6 : Evolution
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 6 : Evolution
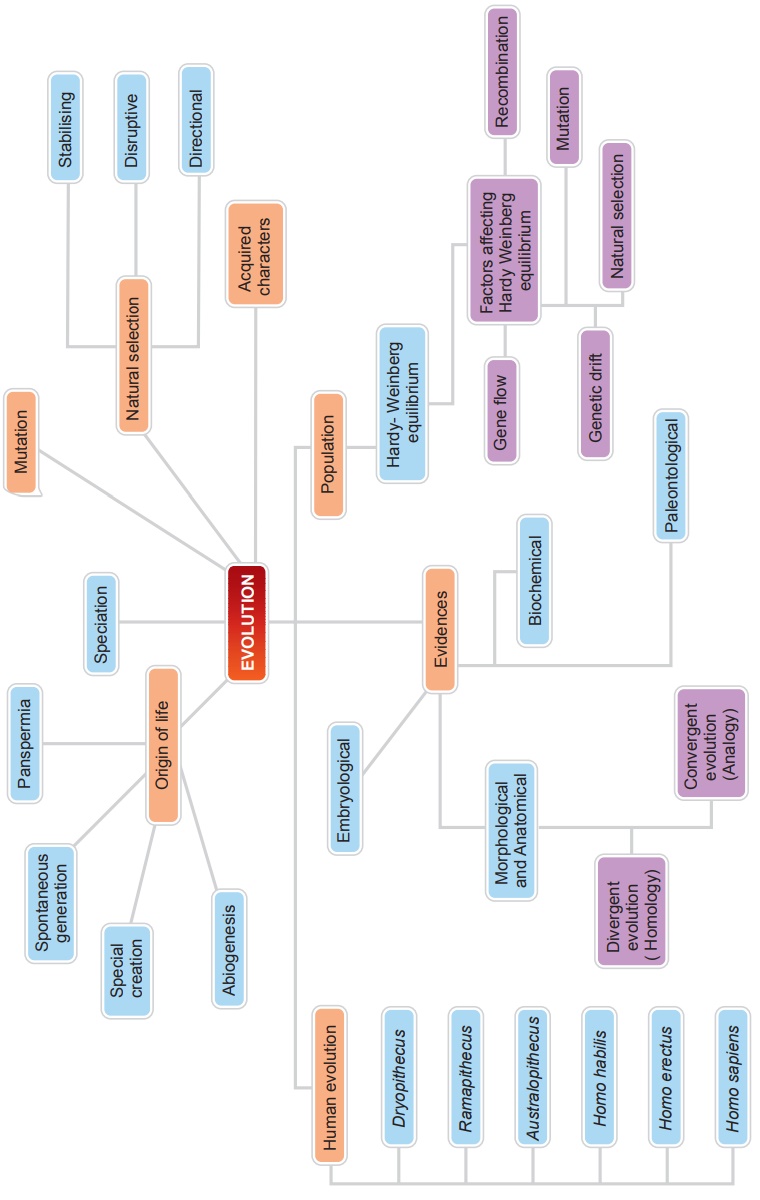
Evolution: Summary
Summary
Evolutionary Biology is
the study of history of life forms on Earth which originated on Earth millions
of years ago.
How Earth originated,
how life originated, what is the place of man in the universe are all general
questions. This chapter deals with several theories to explain the life on
Earth. Evidence from the fossil record and many other areas of biology like
embryology, anatomy and molecular biology indicates a common ancestry.
The theories advanced by
Lamarck, Darwin, Hugo de Vries explained the intricate evolutionary process.
Geological time scale with different eras, periods and epochs gives an idea
about the dominant species in those days. The mathematical distribution of gene
and genotype frequencies remains constant in a small population was contributed
by Hardy and Weinberg in 1608. Natural Selection and gene pool are the
important factors those affect Hardy Weinberg equilibrium.
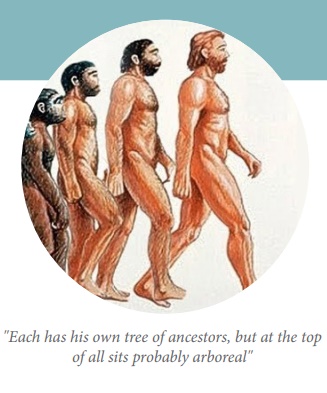
Human evolution states
that humans developed from primates or ape like ancestors. The emergence of
Homo sapiens as a distinct species from apes and placental mammals in brain
size, eating habit and other behavior proves that ‘Ontogeny recapitulates
Phylogeny’.
Separation of a single
population into its subunits preserves the genetic integrity. Types of
isolating mechanism and speciation prevent interbreeding of different species.
Various causes of extinction of animals and the levels of impact are dealt with
in the lesson.
Related Topics