Chapter: Business Science : Banking Financial Services Management
Evolution , Definition and functions of Banking
OVERVIEW OF INDIAN BANKING SYSTEM
EVOLUTION OF BANKING SECTOR
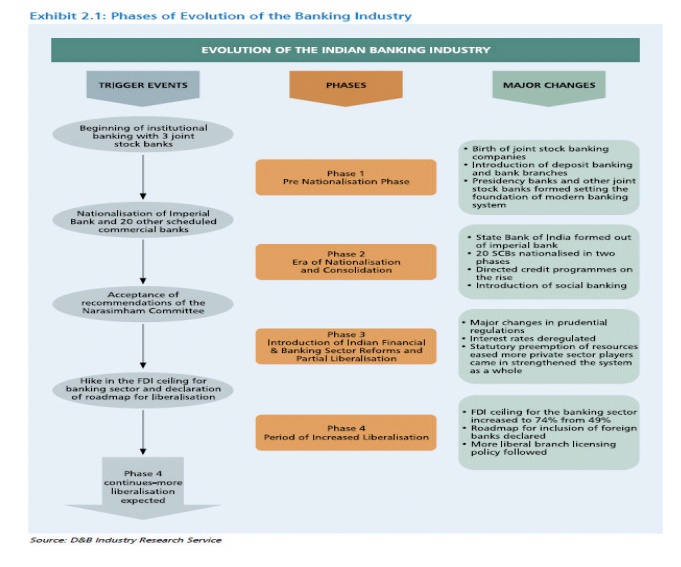
Phase I-
Pre-Nationalisation Phase (prior to 1955)
Phase II-
Era of Nationalisation and Consolidation (1955-1990)
Phase
III- Introduction of Indian Financial & Banking Sector Reforms and Partial
Liberalisation (1990-2004)
Phase IV-
Period of Increased Liberalisation (2004 onwards)
1991-1992
Ø Sub
phases 1) 1991-92 to 1997-1998 2)
1997-98 beyond
Ø Balance of payment problem
Narasimham committee I
There is
no bar to new banks being set up in private sector.
No
treatment between public & private sector sectors.
Asset
reconstruction fund
Recover
bad debts through tribunals
Branch
licensing should be abolished
Narasimham committee II
Rehabitalization
of weak banks
2 or 3
large indian banks should be given an international character.
Formulation
of corporate strategy
Capital
adequacy
Speed up
of computerization &relationship banking
Review
the recruitment procedure
Raghuram Rajan committee(committee
on financial sector reforms-2009)
Macro
economic framework and financial sector development
Broadening
access of finance
Creating
more efficient and liquid market
Creating
a growth friendly & regulatory framework
Creating
a robust infrastructure for credit.
Definition of Banking
According to the Indian Banking Companies Act , ―Banking Company is one which
transacts the business of banking which means the accepting for the purpose of
lending or investment of deposits money from the public repayable on demand or
otherwise and withdrawable by cheque, draft, order or otherwise‖.
FUNCTIONS OF BANKS
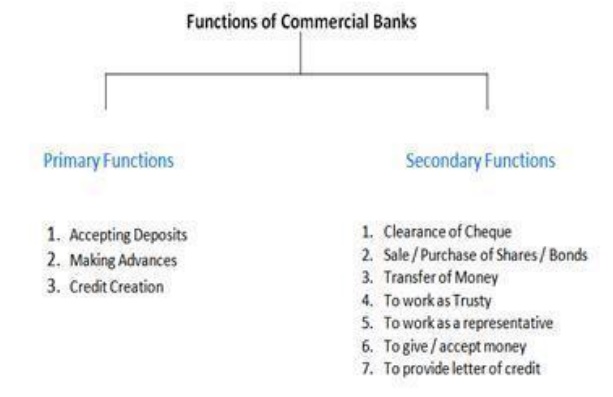
The
functions of a bank may broadly be divided into two parts.
Basic or
primary functions.
Secondary
functions.
Bank
offers to deposit money in any of the following accounts:
Current or
Demand Account(one where
the amount can
be withdrawn at
any time by
the
depositor.)
Saving Account (helps in
mobilization of the saving of low income people)
Fixed Deposit Account or Term
Deposit Account:(which amounts are deposited for a certain fixed period of time. The deposits
cannot be withdrawn before the expiry of this fixed period)
Foreign Currency Account(foreign
currency saving account or foreign currency term deposit
account)
Advancing Loans:
Banks
grant loan in any of the following forms:
Overdraft
is a short-term loan granted by commercial banks to their account holders.
Under this type of loan, the customers are allowed to draw more than what they
have in their current account up to a certain limit. The excess amount
overdrawn is called overdraft.
Cash Credit:
Cash
credit is a very common form of loan granted by commercial banks to businessmen
and industrial units against the security of goods. The loan granted under this
head is credited to current account opened in the name of borrower. The
borrower can withdraw money through cheques according to his requirement. The
interest is charged on the amount actually withdrawn by the borrower.
Loans:
Commercial
banks grant loans for short and medium-term to individuals and traders against
the security of movable and immovable property. The amount of loan is credited
to the borrower's account. Interest is charged on the entire loan sanctioned.
Agency functions
General
utility functions
Miscellaneous
functions
Agency
Functions:
The banks
render important services as agent on behalf of their customers in return for a
small commission. When banks act as agent, law of agency applies. The agency
functions or services of bank are as follows:
Collection of Cheques:
Ø The commercial banks collect
dividends, interest on investment, pension and rent of property due to the
customers. When any income is collected by the bank, a credit voucher is sent
to the customer for information.
Acts as trustee:
Ø The banks act as trustee to
manage trust property as per instructions of property owners. Banks are
required to follow the terms and conditions of trust deed.
Acts as an agent:
Ø Commercial bank sometimes acts
as an agent on behalf of its customers at home or abroad in dealing with other
banks or financial institutions.
Obeys standing instructions:
Ø Sometimes, customer may order
his bank to do something on his behalf regarding the conduct of his account.
This written order is called standing instruction. The bank being the agent of
its customer obeys the standing instructions.
Acts as tax consultant:
Commercial
bank acts as tax consultant to its client. The commercial bank prepares general
sales tax return, income tax return, etc. Tiles the same with tax authorities.
General
Utility Functions:
Provides
lockers facilities:
Issue of
traveler's cheque(customers for traveling in and outside the country.)
Foreign
exchange:exchange of their home currency
Transfer
of money:provide facilities for the transfer of money to any place within and
outside the country
Finances
foreign trade:accepting foreign bills of exchange.
Trade
information:provide trade information and tender advice to its customers
Modaraba
Company:The commercial banks act as Modaraba and leasing companies under the
provisions of Modaraba Companies Ordinance, 1980.
Purchase PTCs:
Ø Commercial banks underwrite or
purchase Participation Term Certificate (PTCs), Term Finance Certificates
(TFCs) and Modaraba Certificates. This helps the companies to raise their
capital.
Financial standing:
Commercial
banks answer reference letters regarding the financial standing and business
reputation of customers. Banks provide this information with great care and
utmost secrecy.
Commercial
banks provide facilities for the collection of utility bills from general
public on behalf of government bodies. This facilitates the public to pay
utility bills in time.
Zakat Collection:
Ø Commercial banks collect Zakat
from their account holders and deposit the same into Central
Zakat
Fund, according to Zakat and Usher ordinance - 1980.
Hajj services:
Ø The commercial banks provide
free Hajj sendees to the intending pilgrims. Banks receive Hajj applications.
Banks also facilitate to form Hajj groups. Banks make necessary arrangements
for the training of intending pilgrims,
Qarz-e-Hasna:
Ø The commercial banks provide
Qarz-e-Hasna to deserving patients for medical treatment and to students for
higher studies within the country and abroad. The Qarz-e-Hasna is refund Ale in
easy installments,
Electronic banking and E-banking:
Electronic
banking is offering improved services to the customers as fellows:
ATM Cards
Credit
Cards
Electronic
transfer of money
Related Topics