Chapter: Business Science : Banking Financial Services Management : Mergers, Diversification and Performance Evaluation
Mutual funds and Types of mutual funds
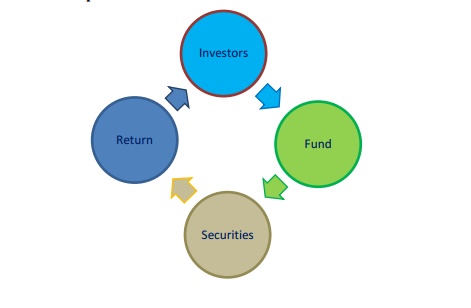
MUTUAL FUND
ü A Mutual Fund is a trust that
pools the savings of a number of investors who share a common financial goal.
The money
thus collected is then invested in capital market instruments such as shares,
debentures and other securities.
The
income earned through these investments and the capital appreciation realised
are shared by its unit holders in proportion to the number of units owned by
them.
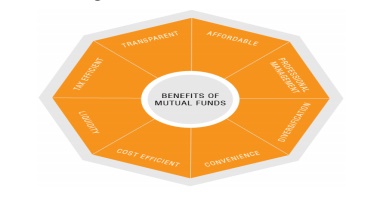
Advantages of Mutual Funds
Disadvantages of mutual fund
No control over costs: The
investor pays investment management fees as long as he remains with the fund, even while the value of
his investments are declining. He also pays for funds distribution charges
which he would not incur in direct investments.
No tailor-made portfolios: The
very high net-worth individuals or large corporate investors may find this to be a constraint as
they will not be able to build their own portfolio of shares, bonds and other
securities.
Managing a portfolio of funds:
Availability of a large number of funds can actually mean too much choice for the investor. So, he may again need advice on
how to select a fund to achieve his objectives.
Delay in redemption: It
takes 3-6 days for redemption of the units and the money to flow back into the investor‘s account.
1 TYPES OF MUTUAL FUNDS
On the basis of Structure
Open
ended Schemes
Closed
ended Schemes.
OPEN ENDED SCHEMES
Open
ended Schemes are schemes which offers unit for sale without specifying any
duration for redemption.
They sell
and repurchase schemes on a continuous basis.
The main
feature of such kind of scheme is liquidity
CLOSED ENDED SCHEMES
These are
the schemes in which redemption period is specified.
Once the
units are sold by mutual funds, then any transaction takes place in secondary
market only i.e stock exchange.
Price is
determined by forces of market.
On the basis of growth objective
GROWTH FUND
The aim
of growth funds is to provide capital appreciation over the medium to long-
term. Such schemes normally invest a major part of their corpus in equities.
Such funds havecomparatively high risks
INCOME FUNDS
Funds that invest in medium to long-term debt
instruments issued by private companies, banks, financial institutions,
governments and other entities belonging to various sectors (like
infrastructure companies etc.) are known as Debt / Income Funds
BALANCED FUND
These
funds provide both growth and regular income as these schemes invest in debt
and equity.The NAV of these schemes is less volatile as compared pure equity
funds.
MONEY MARKET FUNDS
Money
market / liquid funds invest in short-term (maturing within one year) interest
bearing debt instruments. These securities are highly liquid and provide safety
of investment, thus making money market / liquid funds the safest investment
option when compared with other mutual fund types.
On the basis of Special Schemes
INDUSTRY SPECIFIC SCHEMES
Industry
Specific Schemes invest only in the industries specified in the offer document.
The investment of these funds is limited to specific industries like Infotech,
FMCG, Pharmaceuticals etc
INDEX SCHEMES
In this
schemes, the funds collected by mutual funds are invested in shares forming the
Stock Exchange Index.
Example-
Nifty Index Scheme of UTI Mutual Fund and Sensex Index Scheme of Tata Mutual
Fund.
SECTORAL SCHEMES
Sectoral funds are those mutual funds which invest
in a particular sector of the market, e.g. banking, information technology etc.
Sector funds are riskier than equity diversified funds since they invest in
shares belonging to a particular sector which gives them fewer diversification
opportunities
OTHER SCHEMES
Gilt
Security Schemes
Funds of
Funds
Domestic
Funds
Tax
Saving Schemes.
Insurance
business
Related Topics