Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Infectious Diseases
Epstein Barr Virus - Herpes Viruses
Epstein Barr Virus
·
DNA virus
·
One of Herpes Group
· Spread by respiratory secretions (e.g. sneeze, kiss)
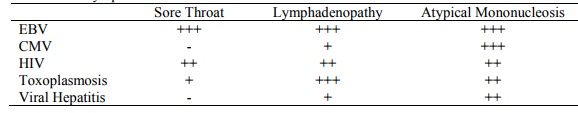
· Pre-schoolers an important reservoir: usually just a non-specific URT infection. In later life (e.g. adolescent) get it more acutely plus hepatitis. 1 – 5% present as hepatitis
·
Associated with Burkett‟s
lymphoma & nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Clinical
·
Highly variable course. Often asymptomatic if < 5 years
·
Sore throat (often exudative)
·
Fever
· Lymph nodes up
·
Tender liver (liver involvement ® ¯appetite
and feeling unwell), maybe big spleen
·
Rash in 10%
·
Doesn‟t resolve (especially after
antibiotics)
·
Will be tired for weeks/months
·
Incubation 30 – 50 days
·
Association with symptoms:
Investigations
· Throat swab
·
FBC: may be atypical
mononuclear lymphocytes
·
EBV serology
Treatment
·
Symptomatic
·
Don’t give penicillin if risk of EBV:
leads to rash that can be interpreted as penicillin allergy. (E.g. amoxycillin, rash in 80 – 90%)
·
Infectious for months. No isolation required
·
Steroids if upper airway
obstruction in kids
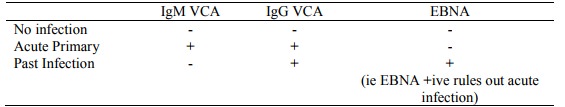
Antibodies to EBV
·
IgM Anti-VCA (Virus capsid
antigen) and IgG Anti-VCA
o Usually appear in blood 7 days after symptoms develop in acute primary
EBV infection
o IgM: usually persists for 2 – 4 months
o IgG: usually persists for life
·
Anti EBNA (Epstein-Barr nuclear
antigen): Appears 2 months after primary infection and persists for life
·
Profiles:
·
Paul-Bunell now largely
obsolete. Negative in 10 – 15 % of cases
Associated diseases
·
Burkett‟s lymphoma
·
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
·
Hodgkin‟s disease (EBV in 40 –
60% of cases)
·
Chronic EBV may occur but is very
uncommon (recurrent sore throat, cervical lymphadenopathy)
Related Topics