Environmental Economics - Environmental Quality | 12th Economics : Chapter 10 : Environmental Economics
Chapter: 12th Economics : Chapter 10 : Environmental Economics
Environmental Quality
Environmental Quality
Environmental quality is a set of properties and characteristics
of the environment either generalized or local, as they impinge on human beings
and other organisms. It is a measure of the condition of an environment
relative to the requirements of one or more species and to any human need.
Environmental quality has been continuously declining due to capitalistic mode
of functioning.
Environment is a pure public good that can be consumed
simultaneously by everyone and from which no one can be excluded. A pure public
good is one for which consumption is non-revival and from which it is
impossible to exclude a consumer. Pure public goods pose a free-rider problem.
As a result, resources are depleted. The contribution of the nature to GDP as
well as depletion of natural resources are not accounted in the present system
of National Income Enumeration.
Externalities and the environment
Introduction
In Environmental Economics, one of the most important
market failures is caused by negative externalities arising from
production and consumption of goods and services. Externalities are third
party effects arising from production and consumption of goods
and services for which no appropriate compensation is paid. Externalities
occur outside of the market i.e. they affect people not directly
involved in the production and consumption of a good or service. They are also
known as spill-over effects.
Meaning of Externalities
Externalities refer to external effects or spillover effects
resulting from the act of production or consumption on the third parties.
Externalities arise due to interdependence between economic units.
Definitions
Externality may be defined as “the cost or benefit imposed by the
consumption and production activities of the individuals on the rest of the
society not directly involved in these activity and towards which no payment is
made”.
The externalities arise from both production and consumption
activities and their impact could be beneficial or adverse. Beneficial
externalities are called “positive externalities” and adverse ones are called
“negative externalities”.
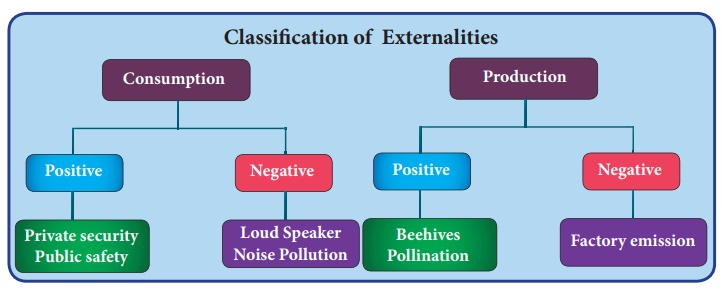
Positive Consumption Externality
When some residents of a locality hire a private security agency
to patrol their area, the other residents of the area also benefit from better
security without bearing cost.
Negative Consumption Externality
A person smoking cigarette gets may gives satisfaction to that
person, but this act causes hardship (dissatisfaction) to the non-smokers who
are driven to passive smoking.
Positive Production Externality
The ideal location for beehives is orchards (first growing
fields). While bees make honey, they also help in the pollination of apple
blossoms. The benefits accrue to both producers (honey as well as apple). This
is called ‘reciprocal untraded interdependency.
Suppose training is given for the workers in a company. If those
trained workers leave the company to join some other company, the later company
gets the benefit of skilled workers without incurring the cost of training.
Negative Production Externality

The emissions and effluents of a factory cause air and water
pollution. Water becomes contaminated and unfit for drinking e.g. Tanneries. The
innocent community bears the external cost for which it is not compensated.
Related Topics