The Classical World | History - Empire Building in East | 9th Social Science : History: The Classical World
Chapter: 9th Social Science : History: The Classical World
Empire Building in East
Empire Building in East
Fall of Chin Dynasty
Wang Cheng, popularly
known as Shih Huang Ti (meaning the first emperor), ended
the age of warring states in China. He crushed all local rulers and established
a strong central government. However, uprisings of the peasantry, unlike in
other cultures, occurred again and again in China. Such uprisings led to the
collapse of Chin dynasty.
Han Dynasty and Expansion of Chinese Territories
Han dynasty (206 BC (BCE) - AD (CE) 220, founded by Liu Pang, flourished for 400 years. Their capital was Chang-an. The most popular and powerful ruler was Wu Ti. His generals succeeded in driving away the Huns in the north. Thus the Han Empire once again threw open the silk road for trade. A large export trade, mainly in silk, reached as far as the Roman Empire.
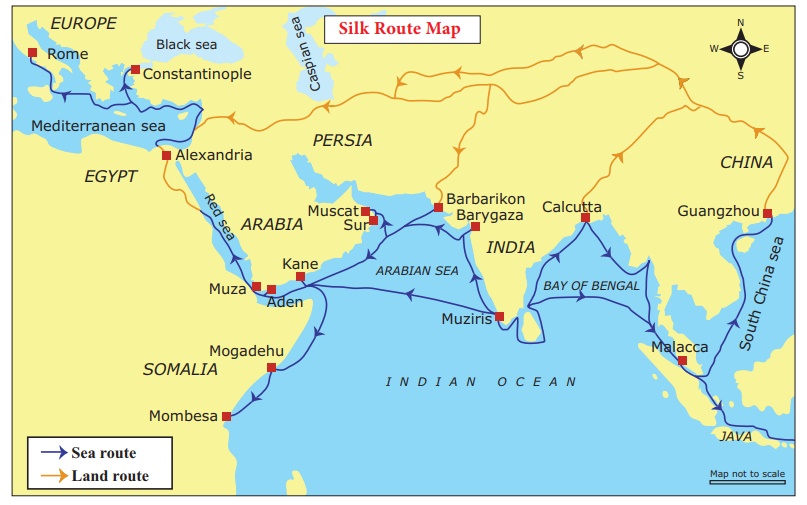
In the north, artisans
and herders of rival “barbarian” dynasties brought in new techniques like the
methods of harnessing horses, use of saddle and stirrup, techniques of building
bridges and mountain roads, and seafaring. Such innovations made Han Empire
prosperous. At the beginning of the Christian Era, the Han Empire rivalled that
of Rome in size and wealth.
Buddhism came to China
from India during the reign of Han dynasty. With Buddhism came the influence of
Indian art to China and from China this spread to Korea and from there to
Japan. Some of the Buddhist art of the time show the impact of Hellenistic
styles.

Han emperors found it
extremely difficult to control the big land owners. So after some decades of
consolidation, China saw the emergence of several rival kingdoms marked by
civil wars in north China. People abandoned their homes and farms, and fled
from there to the Yangtze region and beyond. The period after Han ruled
witnessed political instability across the country.
Related Topics