Chapter: 9th Science : Living World of Animals - Diversity in Living Organism - Kingdom Animalia
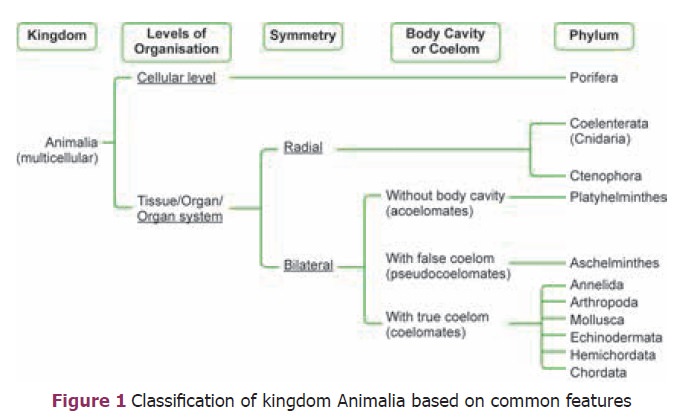
Criteria for Classification of Animal Kingdom
Criteria for Classification of Animal Kingdom
Look at this list of animals: sponge, rotifer, jelly
fish, flatworm, roundworm, snail, earthworm, grasshopper, star fish and
peacock.
Among the above listed animals, sponge does not
have any true tissues. We can divide the animalia into two major
The group of animals that lack true tissues are called as
Porifera.
It is seen that the jelly fish and star fish have
radial symmetry, while if we look at flatworm, roundworm, rotifer, snail,
earthworm, grasshopper and peacock have bilateral symmetry.
1. Grade of organization – Animals are grouped as unicellular or
multicellular based on the number of cells.
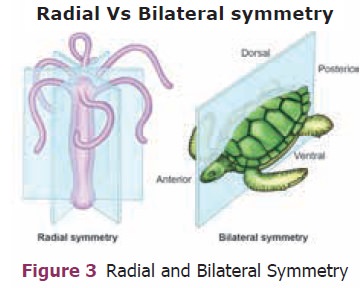
2. Symmetry – It is a plane of arrangement of body parts. Radial
symmetry and bilateral symmetry are the two types of symmetry (Figure 3). In
radial symmetry the body parts are arranged around the central axis, if we cut
through the central axis in any direction, it can be divided into similar
halves. E.g. Hydra, jelly sh and star sh. In bilateral symmetry, the body parts
are arranged along a central axis, if we cut through the central axis, we get
two identical halves E.g. Frog.
3.
Germ
layers – Germ layers are formed during
the development of an embryo. These layers give rise to different organs, as
the embryo becomes an adult. If an organism has two germ layers, the ectoderm
and the endoderm it is said to be diploblastic. If they have three germ layers,
the ectoderm, the mesoderm and the endoderm they are triploblastic animals.
4. Coelom – Coelom refers to a fluid-filled cavity inside the body.
It separates the digestive tract and other organs from the body wall. A true
body cavity or coelom is one that is located within the mesoderm. Based on the
nature of the coelom, animals are divided into 3 groups (Figure 4). Organisms
like the earthworm are called coelomates or eucoelomates because they have true
coelom. Tapeworm is an example of an acoelomate because it does not have a body
cavity. Animals like the roundworm have a body cavity but it is located between
the endoderm and the mesoderm.
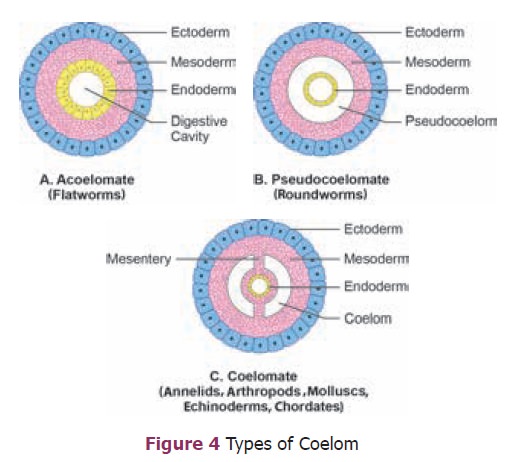
This is considered to be a false coelom and these
organisms are called pseudocoelomates.
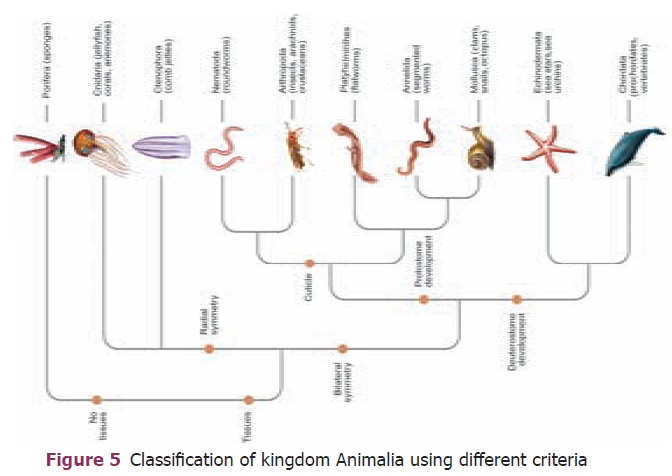
Characters like presence or absence of body cavity
(coelom), segmentation, exoskeleton, jointed legs (appendages), notochord are
used to classify the animalia into ten major Phyla (Figure 5).
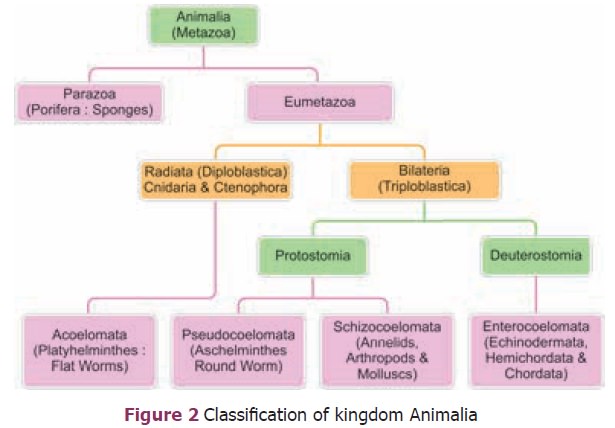
Kingdom Animalia is divided into two groups, based
on the presence or absence of notochord Invertebrata
and Chordata (Prochordata and
Vertebrata). The groups invertebrata is classi ed as follows
Related Topics