Chapter: Obstetrics and Gynecology: Intrapartum Care
Control of Pain in Normal Labor And Delivery
Control of Pain
Management of discomfort and pain
during labor is an essential part of good obstetric practice. Some patients
tolerate pain by using techniques learned in childbirth preparation programs.
It is important that bedside staff be knowledgeable about these pain management
techniques and be supportive of the patient’s decisions. Unless
con-traindicated, pharmacologic analgesics to ameliorate pain of contractions
should be made available on request to women in labor.
During the first stage of labor,
pain results from the contraction of the uterus and dilation of the cervix. This
pain travels along the visceral afferents, which accompany sympathetic nerves
entering the spinal cord at T-10, T-11, T-12, and L-1. As the fetal head
descends, there is also dis-tension of the lower birth canal and perineum. This
pain is transmitted along somatic afferents that comprise por-tions of the
pudendal nerves that enter the spinal cord at S-2, S-3, and S-4. To provide
relief from obstetric pain, the following methods of anesthesia and analgesia
are used.
· Epidural block: infusion
of local anesthetics or narcoticsthrough a catheter into the epidural space.
The most effective form of intrapartum pain relief in the United States, it can
be used in either vaginal or abdominal deliv-eries and in postpartum procedures
such as tubal ligation.
· Spinal anesthesia: a single
injection of anesthetic
· Combined spinal–epidural: combination
of the abovetwo techniques
· Local block: local
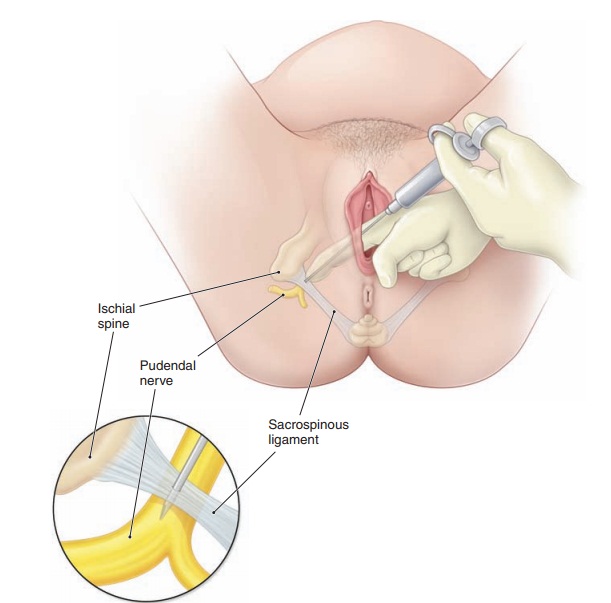
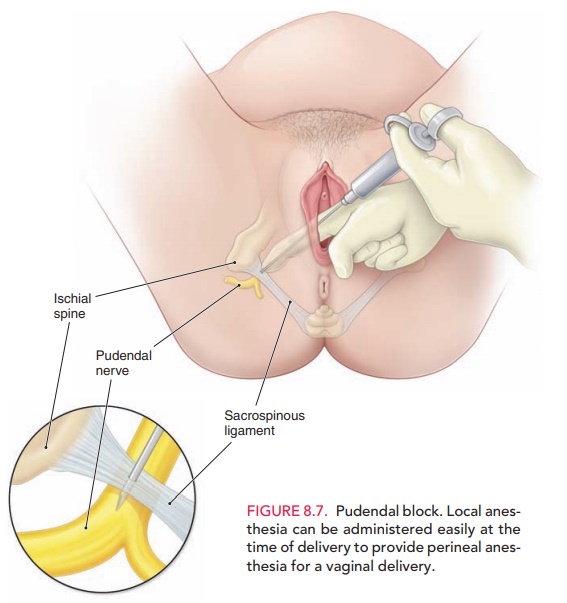
injection of anesthetic into theperineum or vagina. A pudendal block is a local block (Fig. 8.7).
· General anesthesia: inhaled
or intravenous administra-tion of anesthetic agents that results in a loss of
mater-nal consciousness. This technique is reserved only for cesarean
deliveries in selected cases.
To determine which method of
obstetric pain control should be used, the positive and negative aspects of
each should be considered. Of the regional modes of analgesia, epidural
anesthesia is superior to spinal anesthesia in that it can be left as a
continuous source of analgesia and anesthe-sia during both the labor and delivery
process. The advan-tage of this technique is its ability to provide analgesia
during labor as well as excellent anesthesia for delivery, yet main-tain the
patient’s sense of touch, facilitating participation in the birth process.
Spinal anesthesia provides good pain relief for procedures of limited duration,
such as cesarean delivery or vaginal delivery when labor is rapidly
progressing. Combined spinal–epidural anesthesia has advantages: the epidural
catheter to titrate medications throughout labor and the rapid onset associated
with spinal techniques. All of these types of regional anesthesia may be
associated with a postdural puncture headache. However, combined
spinal–epidural anesthesia avoids the risk of spinal headache in the mother and
reduces the risk of sympathetic blockade, which could lead to hypotension.
There is also less motor blockade than with spinal anesthesia. Local block may
pro-vide anesthesia for episiotomy and repair of vaginal and per-ineal
lacerations; however, paracervical block may result in fetal bradycardia.
General anesthesia is associated with complications such as maternal aspiration
and neonatal depression. If properly administered, it is effective for most
cesarean deliveries, but regional anesthesia is preferable.
Related Topics