Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Cloning : Differentiation, Cloning of Sheep (Mechanism), Ethical Issues, Merits and Demerits of cloning
Cloning
Cloning is an experimental technique wherein, a group of genetically identical organisms is produced. Cloning of various animals was has become possible due to knowledge gained in the field of developmental biology and developmental genetics. It helped a lot, to understand the genetic control over differentiation of cells and the development of multicellular organisms.
Differentiation : In the development of multicellular animals the zygote represents the progenitor cell of the future embryo. Multitudes of cells arise from mitotic divisions of the fertilized egg cell. These cells later become distinct cell types differing in form and function. This process is called differentiation.
In the 1950s two embryologists R.Briggs and T.King developed a technique called nuclear transplantation. The nuclei from frog egg cells are taken out with a micropipette (enucleation) and replaced with nuclei taken from the cells of an embryo the same animal. The recipient cells developed into normal tadpoles and frogs with all the different cell types. The investigators, with the above technique produced a number of genetically identical individuals. Cells of early embryo which are capable of complete development and producing the whole organisms are said to be totipotent.
However, experiments by J. Gurdon revealed that nuclei from older embryos and tadpoles when transplanted to the enucleated egg cells affected the developmental potential. The older the individual from which the nuclei were taken, less the recipient egg cell was able to develop normally. His experiments also revealed that cells from different parts of the embryo differed in the degree of successful development attained after nuclear transplantation. It is learnt that cells of embryos at a later stage of development switch over from totipotent state to pluripotent state. The later gives rise to development of specific tissues or organs.
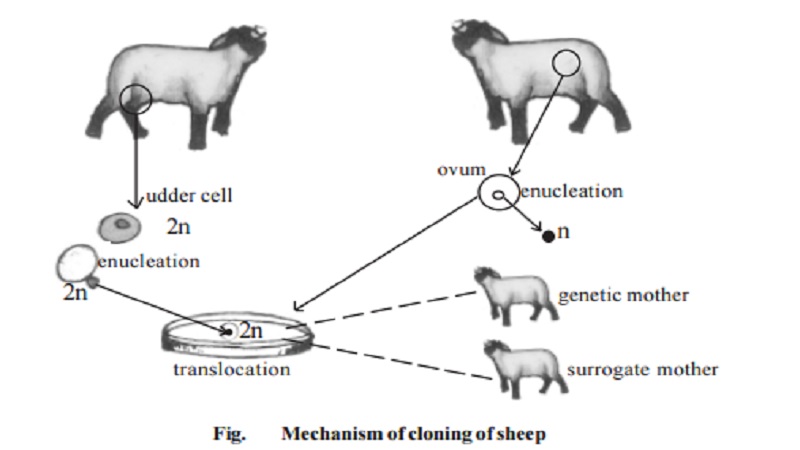
Cloning of Sheep (Mechanism) :
Dr. Ian Wilmut has produced a cloned sheep called Dolly by nuclear transplantation method. To produce cloned sheep he took the udder cell which is a somatic cell with diploid number of chromosomes. An egg cell was also removed from a donor sheep. The egg cell cannot grow into a new sheep on its own because it only has half a set of chromosomes(n). The body cell cannot grow into a new sheep on its own because it is not a reproductive cell. So udder cell nucleus(2n) was removed. Similarly the egg cell nucleus (n) was also removed. The nucleus of the somatic cell (Udder) was injected into the enucleated egg. The egg after the nuclear
transplantation comes to possess full set of chromosomes viz. the 2n diploid. The egg was then transplanted back into the uterus of the sheep from which it was removed. The egg also can be transplanted to a new surrogate mother for development. The egg cell grew and developed into a sheep (Dolly). This cloned sheep is genetically identical to the donor sheep, which donated the diploid nucleus of its somatic cell and not the sheep which donated the egg cell.
Ethical Issues, Merits and Demerits of cloning :-
1. Cloning of animals is considered as an unethical and unnatural technique by some people.
2. It is feared that attempts to clone human may lead to the birth/production of wrong persons.
3. Cloning cannot produce children like the children born to genetic mothers. Variations in traits are bound to appear.
4. When organisms are created by cloning from somatic cells of the adult, the longevity of the new born, disease tolerance capacity are some criteria to be considered. Cloned animals have also developed diseases like arthritis.
5. Cloning also leads to wastage of egg cells. In the cloning of Cat, 200 egg cells were used and 57 were implanted. Out of that only one cloned cat survived to birth.
6. Cloned animals may have health problems. They may die at a much earlier age than the rest of the species . So cloned animals from somatic cells of adult, may have short life span.
7. Among the benefits of cloning, special mention should be made regarding its role in biodiversity. Cloning will help to maintain biodiversity. It can bring back even the animals which have become extinct recently and safe guard all endangered species facing extinction.
8 . Though human cloning has its own ethical problems, the principle could be used to grow new organs from the cloned stem cells. Such organ culture may solve transplantation problems, such as tissue incompatibility, tissue rejection, harmful immune reactions etc. Many human lives could be saved.
Related Topics