Chapter: Basic Concept of Biotechnology : Biomolecules
Classification of Proteins
Classification
of Proteins:
Proteins
are classified on the basis of their chemical composition, shape and solubility
into two major categories as discussed below.
(i)
Simple proteins:
Simple
proteins are those which, on hydrolysis, give only amino acids. According to
their solubility, the simple proteins are further divided into two major
groups’ fibrous and globular proteins.
(a)
Fibrous
Proteins: These are water insoluble animal proteins
eg.collagen (major protein of connective tissues), elastins (protein of
arteries and elastic tissues), keratins (proteins of hair, wool, and nails) are
good examples of fibrous proteins. Molecules of fibrous proteins are generally
long and thread like.
(b)
Globular
Proteins: These proteins are generally soluble in water,acids,
bases or alcohol. Some examples of globular proteins are albumin of eggs,
globulin (present in serum), and haemoglobin. Molecules of globular proteins
are folded into compact units which are spherical in shape.
(ii) Conjugated proteins:
Conjugated proteins are complex proteins which
on hydrolysis yield not only amino acids but also other organic or inorganic
components. The non-amino acid portion of a conjugated protein is called
prosthetic group.
Unlike
simple proteins, conjugated proteins are classified on the basis of the
chemical nature of their prosthetic groups. These are
a)
Nucleoproteins (protein + nucleic acid)
b) Mucoproteins
and glycoprotein’s (protein+ carbohydrates)
c)
Chromo proteins (proteins + a colored
pigment)
d) Lipoproteins
(proteins + lipid)
e)
Metalloproteinase (metal binding
proteins combined with iron, copper or zinc)
f)
Phosphoproteins (proteins attached with
a phosphoric acid group).
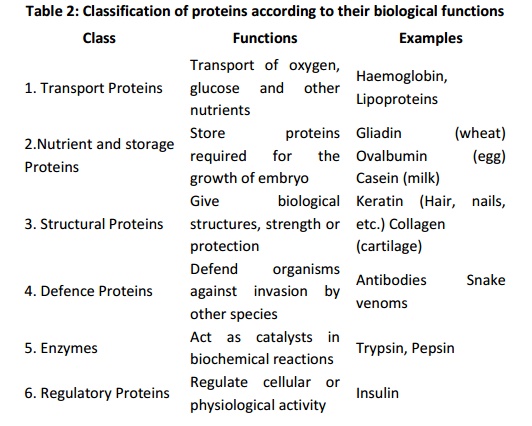
Proteins
can also be classified on the basis of functions they perform, as summarized in
table 2.
Related Topics