Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Bacteriology: Staphylococcus
Cell Wall Components and Antigenic Structure - Staphylococcus aureus
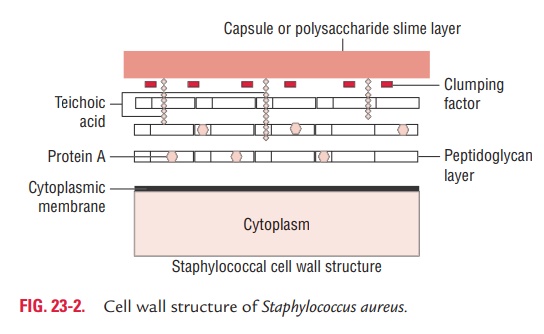
Cell Wall Components and Antigenic Structure
Cell wall associated proteins and polymers include the following (Fig. 23-2):
◗ Cell wall peptidoglycan
S. aureus cell wall is rich in peptidoglycans. Peptidoglycan isa polymer of the polysaccharide, which provides rigidity to the cell wall of the bacteria. It has the characteristic penta glycine bridges that link tetrapeptides to the muramic acid residues.
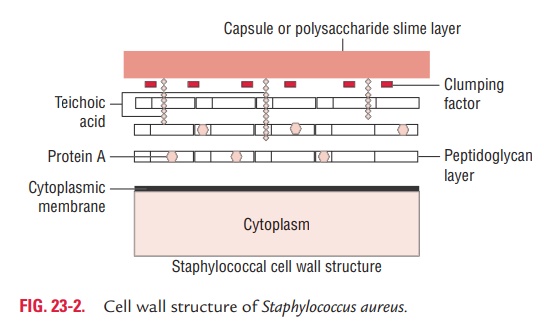
◗ Teichoic acid
Teichoic acid is the major antigenic determinant of the cell wall of S. aureus. It is a polymer of ribitol phosphate. Antibodies to teichoic acids develop in endocarditis and in certain other staphylococcal infections.
◗ Protein A
It is the major protein in the cell wall and has a molecular weight of 13,000 Da. It is present in large quantities in the cell wall of certain strains of S. aureus, such as the Cowan’s strain of S. aureus (SAPA). This is a group specific antigen. The anti-gen is present in more than 90% strains of S. aureus. Protein A is absent in both the coagulase-negative staphylococci (CONS) and micrococci.
Related Topics