Nuclear Physics | Science - Book Back Questions with Answers | 10th Science : Chapter 6 : Nuclear Physics
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 6 : Nuclear Physics
Book Back Questions with Answers
Nuclear Physics (Science)
I. Choose the correct answer
1. Man-made radioactivity is also known as _____________
a. Induced radioactivity
b. Spontaneous radioactivity
c. Artificial radioactivity
d. a & c
2. Unit of radioactivity is _____________
a. roentgen
b. curie
c. becquerel
d. all the above
3. Artificial radioactivity was discovered by ___________
a. Bequerel
b. Irene Curie
c. Roentgen
d. Neils Bohr
4. In which of the following, no change in mass number of the daughter nuclei takes place
i) α decay ii) β decay iii) γ decay iv) neutron decay
a. (i) is correct
b. (ii) and (iii) are correct
c. (i) & ( iv) are correct
d. (ii) & (iv) are correct
5. ____________ isotope is used for the treatment of cancer.
a. Radio Iodine
b. Radio Cobalt
c. Radio Carbon
d. Radio Nickel
6. Gamma radiations are dangerous because
a. it affects eyes & bones
b. it affects tissues
c. it produces genetic disorder
d. it produces enormous amount of heat
7. _____________ aprons are used to protect us from gamma radiations
a. Lead oxide
b. Iron
c. Lead
d. Aluminium
8. Which of the following statements is/are correct?
i. α particles are photons
ii. Penetrating power of γ radiation is very low
iii. Ionization power is maximum for α rays
iv. Penetrating power of γ radiation is very high
a. (i) & (ii) are correct
b. (ii) & (iii) are correct
c. (iv) only correct
d. (iii) & (iv) are correct
9. Proton - Proton chain reaction is an example of __________________
a. Nuclear fission
b. α - decay
c. Nuclear fusion
d. β - decay
10. In the nuclear reaction 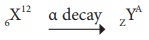 , the value of A & Z.
, the value of A & Z.
a. 8, 6
b. 8, 4
c. 4, 8
d. cannot be determined with the given data
11. Kamini reactor is located at __________
a. Kalpakkam
b. Koodankulam
c. Mumbai
d. Rajasthan
12. Which of the following is/are correct?
i. Chain reaction takes place in a nuclear reactor and an atomic bomb.
ii. The chain reaction in a nuclear reactor is controlled
iii. The chain reaction in a nuclear reactor is not controlled
iv. No chain reaction takes place in an atom bomb
a. (i) only correct
b. (i) & (ii) are correct
c. (iv) only correct
d. (iii) & (iv) are correct
II. Fill in the blanks
1. One roentgen is equal to 3.7 x 1010 disintegrations per second
2. Positron is an antiparticle of electron.
3. Anemia can be cured by Radio iron isotope
4. Abbreviation of ICRP
5. Dosi meter is used to measure exposure rate of radiation in humans.
6. Gamma rays has the greatest penetration power.
7. ZYA → Z+1YA + X ; Then, X is
8. ZXA → ZYA This reaction is possible in Gamma decay.
9. The average energy released in each fusion reaction is about 3.84x10 12 J.
10. Nuclear fusion is possible only at an extremely high temperature of the order of 107 to 109 K K.
11. The radio isotope of phosphorous helps to increase the productivity of crops.
12. If the radiation exposure is 100 R, it may cause leukemia.
III. State whether the following statements are true or false: If false, correct the statement
1. Plutonium -239 is a fissionable material. - True
2. Elements having atomic number greater than 83 can undergo nuclear fusion. - False
Elements having atomic number greater than 83 can undergo nuclear fusion not fusion.
3. Nuclear fusion is more dangerous than nuclear fission.
4. Natural uranium U-238 is the core fuel used in a nuclear reactor.
Natural uranium U-235 is the core fuel used in a nuclear reactor.
5. If a moderator is not present, then a nuclear reactor will behave as an atom bomb.
If a moderator is not present, then a nuclear reactor will not behave as an atom bomb.
6. During one nuclear fission on an average, 2 to 3 neutrons are produced.
7. Einstein’s theory of mass energy equivalence is used in nuclear fission and fusion.
IV. Match the following
Match: I
a. BARC - Kalpakkam
b. India’s first atomic power station - Apsara
c. IGCAR - Mumbai
d. First nuclear reactor in India - Tarapur
Answer:
(a) BARC - Mumbai
(b) India's first atomic power station - Tarapur
(c) IGCAR - Kalpakkam
(d) First nuclear reactor in India - Apsara
Match: II
a. Fuel - lead
b. Moderator - heavy water
c. Coolant - cadmium rods
d. Shield - uranium
Answer:
(a) Fuel - uranium
(b) Moderator - cadmium rods
(c) Coolant - heavy water
(d) Shield - lead
Match: III
a. Soddy Fajan - Natural radioactivity
b. Irene Curie - Displacement law
c. Henry Bequerel - Mass energy equivalence
d. Albert Einstein - Artificial Radioactivity
Answer:
(a) Soddy and Fajan - Displacement law
(b) Irene Curie - Artificial Radio activity
(c) Henry Becquerel - Natural radio activity
(d) Albert Einstein - Mass energy equivalence
Match: IV
a. Uncontrolled fission reaction - Hydrogen Bomb
b. Fertile material - Nuclear Reactor
c. Controlled fission reaction - Breeder reactor
d. Fusion reaction - Atom bomb
Answer:
(a) Uncontrolled fission reaction - Atom bomb
(b) Fertile Material - Breeder reactor
(c) Controlled fission reaction - Nuclear Reactor
(d) Fusion reaction - Hydrogen Bomb
Match: V
a. Co - 60 - Age of fossil
b. I - 131 - Function of Heart
c. Na - 24 - Leukemia
d. C - 14 - Thyroid disease
Answer:
(a) Co-60 - Leukemia
(b) I - 131 - Thyroid disease
(c) Na-24 - Function of Heart
(d) C- 14 - Age of fossil
V. Arrange the following in the correct sequence:
1. Arrange in descending order, on the basis of their penetration power
Alpha rays, beta rays, gamma rays, cosmic rays
(i) gamma rays
(ii) beta rays
(iii) Alpha rays
(iv) cosmic rays
2. Arrange the following in the chronological order of discovery
Nuclear reactor, radioactivity, artificial radioactivity, discovery of radium.
(i) radioactivity .
(ii) discovery of radium
(iii) artificial radio activity
(iv) Nuclear reactor
VI. Use the analogy to fill in the blank
1. Spontaneous process : Natural Radioactivity, Induced process :
2. Nuclear Fusion : Extreme temperature, Nuclear Fission :
3. Increasing crops : Radio phosphorous, Effective functioning of heart :
4. Deflected by electric field : α ray, Null Deflection :
VII. Numerical problems:
1. 88Ra226 experiences three α - decay. Find the number of neutrons in the daughter element.
α - decay:
ZXA → z-2YA-4 + 2He4
3α - decay:
2XA → Z-6YA-12 + 3(2He4)
88Ra226 → 82Pb214 + 32He4 (or)
88Ra226 → 82X214 + 32He4
2. A cobalt specimen emits induced radiation of 75.6 millicurie per second. Convert this disintegration in to becquerel (one curie = 3.7 × 1010 Bq)
1 Curie = 3.7 x 1010
Becquerel disintegrations per second
75.6 millicurie = 75.6 x 10-3 x 1 Curie.
75.6 x 10-3 x 3.7 x 1010 = 279.7 x 107Bq
VIII. Assertion and reason type questions:
Mark the correct choice as
(a) If both the assertion and the reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both the assertion and the reason are true, but the reason is not the correct ex-planation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
1. Assertion: A neutron impinging on U235, splits it to produce Barium and Krypton.
Reason: U - 235 is a fissile material.
Answer: (b) If both the assertion and the reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
2. Assertion: In a β - decay, the neutron num-ber decreases by one.
Reason: In β - decay atomic number in-creases by one.
Answer: (d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
3. Assertion: Extreme temperature is neces-sary to execute nuclear fusion.
Reason: In a nuclear fusion, the nuclei of the reactants combine releasing high energy.
Answer: (c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
4. Assertion: Control rods are known as 'neu-tron seeking rods'
Reason: Control rods are used to perform sustained nuclear fission reaction
Answer: (d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
IX. Answer in one or two word (VSA)
1. Who discovered natural radioactivity?
Henri Becquerel.
2. Which radioactive material is present in the ore of pitchblende?
Uranium.
3. Write any two elements which are used for inducing radioactivity?
Alpha particle & neutro.
4. Write the name of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted during a natural radioactivity.
Gamma ray.
5. If A is a radioactive element which emits an α - particle and produces 104Rf 259. Write the atomic number and mass number of the element A.
106A263 → 104Rf259 + 2He4.
Atomic number: 106
Mass number: 263
6. What is the average energy released from a single fission process?
3.2 x 10-11J.
7. Which hazardous radiation is the cause for the genetic disease?
Gamma.
8. What is the amount of radiation that may cause death of a person when exposed to it?
600R.
9. When and where was the first nuclear reactor built?
1942, Chicago, USA.
10. Give the SI unit of radioactivity.
Becquerel (Bq).
11. Which material protects us from radiation?
Lead.
X. Answer the following questions in few sentences.
1. Write any three features of natural and artificial radioactivity.
Natural radioactivity
1. Emission of radiation by self¬disintegration of nucleus
2. Alpha, beta and gamma radiations are emitted.
3. It is a spontaneous process.
Artificial radioactivity
1. Emission of radiation by disintegration of nucleus through induced process.
2. Mostly elementary particles such as neutron, positron, etc. are emitted.
3. It is an induced process.
2. Define critical mass.
The minimum mass of fissile material necessary to sustain chain reaction is called "critical mass(mc)". It depends on the nature, density and the size of fissile material.
3. Define one roentgen.
One Roentgen is defined as the quantity of radioactivity substance which produces a charge of 2.58 x 10-4 coulomb in 1 kg of air under standard conditions of pressure, temperature and humidity.
4. State Soddy and Fajan’s displacement law.
Soddy and Fajan’s displacement laws :
(i) When a radioactive element emits an alpha particle, a daughter nucleus is formed whose mass number is less by 4 units and the atomic number is less by 2 units, than the mass number and atomic number of the parent nucleus.
(ii) When a radioactive element emits a beta particle, a daughter nucleus is formed whose mass number is the same and the atomic number is more by 1 unit, than the atomic number of the parent nucleus.
5. Give the function of control rods in a nuclear reactor.
Control rod : Control rods are used to control the number of neutrons in order to have sustained chain reaction. Mostly boron or cadmium rods are used as control rods.
6. In Japan, some of the new born children are having congenital diseases. Why?
In Japan two atom bombs were exploded in 1945. This explosion emitted hazardous radiation like γ rays, which adversely affects new born children with congenital diseases.
7. Mr. Ramu is working as an X - ray technician in a hospital. But, he does not wear the lead aprons. What suggestion will you give to Mr. Ramu?
Ramu can use a pocket Dosimeter that measures exposure to ionizing radiation.
8. What is stellar energy?
Fusion reaction that takes place in the cores of sun and other stars results in an enormous amount of energy which is called as "stellar energy".
9. Give any two uses of radio isotopes in the field of agriculture?
(i) To kill the insects and parasites and prevent the wastage of agricultural products.
(ii) To keep fresh beyond their normal life enhancing the storage time prevent sprouting and spoilage of onions, potatoes and gram.
XI. Answer the following questions in detail.
1. Explain the process of controlled and uncontrolled chain reactions.
Answer:
(a) Controlled chain reaction : In the
controlled chain reaction the number of neutrons released is maintained to be
one. This is achieved by absorbing the extra neutrons with a neutron absorber
leaving only one neutron to produce further fission. Thus, the reaction is
sustained in a controlled manner. The energy released due to controlled chain
reaction can be utilized for constructive purpose. Controlled chain reaction is
used in a nuclear reactor to produce energy in a sustained and controlled
manner.
(b) Uncontrolled chain reaction : In the
uncontrolled chain reaction the number of neutrons multiplies indefinitely and
cause fission in a large amount of fissile material. This results in the
release of huge amount of energy within a fraction of second. This kind of
chain reaction is used in atom bombs to produce explosion.
2. Compare the properties of alpha, beta and gamma radiations.
Answer:
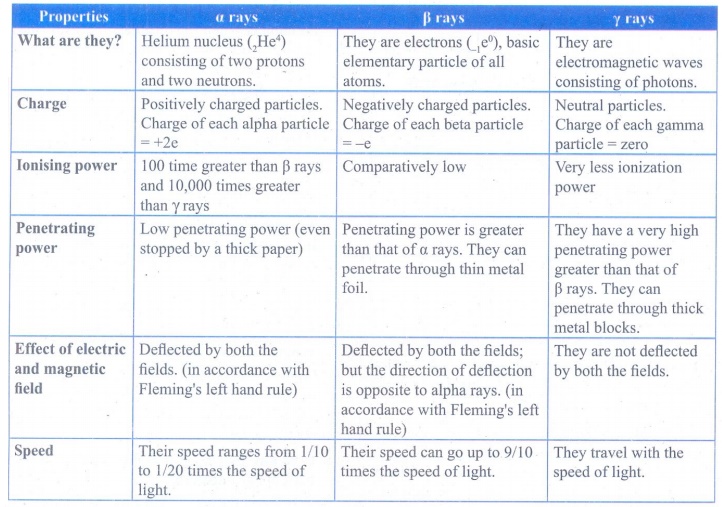
What
are they?
α rays: Helium nucleus (2He4)
consisting of two protons and two neutrons.
β rays: They are electrons (1e0),
basic elementary particle of all atoms.
γ rays: They are electromagnetic waves consisting of
photons.
Charge
α rays: Positively charged particles. Charge of each
alpha particle +2e
β rays: Negatively charged particles. Charge of each
beta particle = -e
γ rays: Neutral particles. Charge of each gamma
particle = zero
Ionising
power
α rays: 100 time greater than β rays and 10,000 times
greater than γ rays
β rays: Comparatively low
γ rays: Very less ionization power
Penetrating
power
α rays: Low penetrating power (even stopped by a
thick paper)
β rays: Penetrating power is greater than that of α
rays. They can penetrate through thin metal foil.
γ rays: They have a very high penetrating power
greater than that of β rays. They can penetrate through thick metal blocks.
Effect
of electric and magnetic field
α rays: Deflected by both the fields. (in accordance
with Fleming's left hand rule)
β rays: Deflected by both the fields; but the
direction of deflection is opposite to alpha rays. (in accordance with
Fleming's left hand rule)
γ rays: They are not deflected by both the fields.
Speed
α rays: Their speed ranges from 1/10 to 1/20 times
the speed of light
β rays: Their speed can go up to 9/10 times the speed
of light.
γ rays:They travel with the speed of light.
3. What is a nuclear reactor? Explain its essential parts with their functions.
Answer:
A
Nuclear reactor is a device in which the nuclear fission reaction takes place
in a self - sustained and controlled manner to produce electricity.
The
essential components of a nuclear reactor are (i) fuel, (ii) moderator, (iii)
control rod, (iv) coolant and (v) protection wall.
(i) Fuel: A fissile material is used as fuel. The
commonly used fuel material is uranium.
(ii) Moderator:
A moderator is used to slow down the high energy neutrons to get slow neutrons.
Graphite and heavy water are the commonly used moderators.
(iii) Control rod: Control rods are used to control
the number of neutrons in order to have sustained chain reaction. Mostly boron
or cadmium rods are used as control rods.
(iv) Coolant: A coolant is used to remove the heat produced in the reactor core to produce steam. This steam is used to run a turbine to produce electricity Water, air and helium are some of the coolant materials
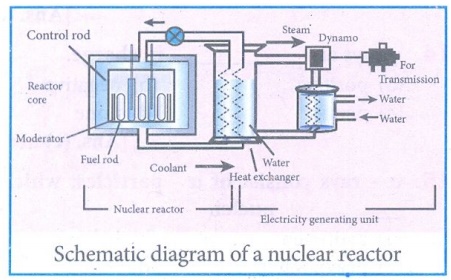
(v) Protection wall: A thick concrete lead wall is
built around the nuclear reactor in order to prevent the harmful radiations
from escaping into the environment
XII. HOT Questions:
1. Mass number of a radioactive element is 232 and its atomic number is 90. When this element undergoes certain nuclear reactions, it transforms into an isotope of lead with a mass number 208 and an atomic number 82. Determine the number of alpha and beta decay that can occur.
90X232 → 82Y208 + 6 2He4 + 4 -1e0
6 – Alpha : 90
4 – Beta : 12
90 - 12 = 78
2. 'X – rays should not be taken often'. Give the reason.
X- rays are radiations that can penetrate deep into your body. Over exposure of X-ray may lead to the damage of some sensitive organs present inside our body. It is better to wear lead aprons while taking X-ray films.
3. Cell phone towers should be placed far away from the residential area – why?
Cellphone towers emit high frequency radio waves or microwaves which are dangerous to humans. These electro magnetic radiations can cause health problems like Cancer, Birth defects, low sperm count, memory loss etc. So it is better to place cell phone towers far away from residential areas.
Related Topics