Chapter: Maternal and Child Health Nursing : Obstetric Emergencies
Bleeding In Early Pregnancy
Bleeding In Early Pregnancy
This is
bleeding from the genital tract before 24th week of pregnancy.
Approximately, a 20% of pregnant women experience bleeding during the first
trimester. Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy is abnormal. Any report of it should
be viewed seriously by the midwife. When it occurs, the volume of blood loss,
colour and if associated with pain or not should be established.
Causes
·
Abortion
·
Implantation bleeding
·
Cervical lesions.
·
Erosion, mucous polyps and carcinoma of the cervix
·
Hydatidiform mole.
·
Ectopic Pregnancy.
Abortion
This is
bleeding or expulsion of the fetus before 24th week of gestation or
viability or less than 500g of weight (WHO). Abortion may be spontaneous or
induced.
Incidence:
15% of pregnancies abort spontaneously with peak period of 6-10 weeks – This
may not be unconnected with low progesterone secretion (About 65% occurs at
this period) 80% happens in the 1st trimester. Bleeding in the 2nd&
3rd trimester carries a greater risk to the mother & child
because the placenta is already firmly attached.
Causes
Fetal
causes:
·
In about 60% of cases the cause is multiple
resulting from chromosomal abnormalities of the conceptus.
·
Mal-development
·
Defective implantation
Maternal
Causes;
·
Infection – Acute fevers, rubella, syphilis, Chroni
c Nephritis, thyroid dysfunction
·
Environmental factors – Effect of drugs,
cigarette and alcohol,
·
ABO incompatibility, High blood lead, Diabetes,
Hormonal imbalance, High parity, Local disorders of genital tract, retroverted
or Bicornuate uterus, Cervical incompetence, Environmental stress. Local Causes
:
·
Conditions that interfere with embedding and
nutrition of the ovum (anemia), Trauma and Fibroid tumors.
Social
Causes:
Teenage
pregnancy, unmet needs, failed family planning, rape conception.
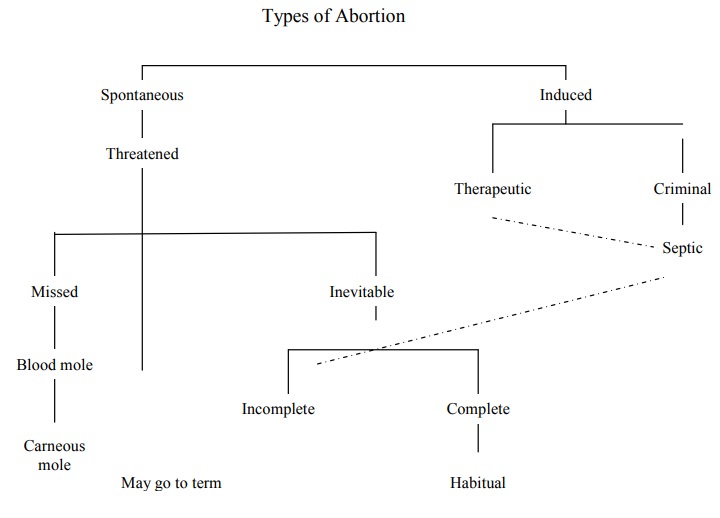
Types of Abortion
Abortion
is classified into the following clinical types
1.
Threatened Abortion
2.
Inevitable Abortion
3.
Incomplete Abortion
4.
Complete Abortion
5.
Missed Abortion
1. Threatened Abortion
Vaginal
bleeding during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy, whether the bleeding is
associated with uterine contraction or not.
It can be
distinguished from implantation bleeding which is usually bright red colour and
stops quickly.
Signs and Symptoms
·
Slight bleeding
·
Os is closed and not effacement
·
Slight uterine contraction
·
Slight abdominal discomfort & cramping with
backache
·
On speculum examinations cervix is closed and
membranes intact
·
Ultrasound scan
Treatment
·
Admission in the hospital
·
Reassure client
·
Assess general condition – history, vital signs etc
.
·
Routine Observation bid or 4hrly
·
No Vaginal Examination and enema
·
Save all discharges – Pads, soiled clothing,
linens etc.
Blood
Test: Grouping and Gross matching, Hb, Rh factor, plasma Human placenta
lactogen level – helps to determine prognosis as low level indicate that
pregnancy will terminate (inevitable abortion)
Drugs
Valium
5mg tds
Amylobarbitone
sodium (sodium Amytal) 200mg nocte Pethidine 50-100mg to relief pain of uterine
contractions, Morphine 15mg.
Speculum
examination to rule out bleeding from local lesion.
Monitor
fetal condition – FH by sonicaid/Dipltone
Do
pregnancy test.
Allow up
and about after bleeding has stopped for 3 days
Nutritious
diet and personal hygiene Prognosis: 70-80% - continue with pregnancy
Prognosis
is better if bleeding becomes brownish from bright red-only about 10% will
abot, while initial brown blood becomes red 66% will abort. If accompanied with
severe uterine contraction there is increased possibility of abortion.
Advice on Discharge
Rest,
less activities, no lifting, or coitus for 2-3 weeks, she should report any
case of bleeding.
2. Inevitable Abortion
Definition:
Abortion is inevitable when bleeding is accompanied with uterine contractions,
bleeding becomes severe and dilatation of the cervix. It is impossible for the
pregnancy to continue. It may end up complete or incomplete.
Signs & Symptoms
·
Slight or severe vaginal bleeding
·
Increase contraction of the uterus – Pain
·
Dilatation of the cervix
·
Membranes may or may not be ruptured, it may bulge
through the Os or in the vagina
·
Shock may be present
·
Product may protrude through the cervical Os or in
the vagina
Treatment
Treat as
threatened abortion until Dr’s arrival. If bleeding is severe, give 0.5mg
ergometrine or 1ml syntometrine ,keep all blood loss for Dr’s inspection.
Give analgesics – Pethidine 100mg or Morphine
15mg .
Oxytocin
drip is given or prostaglandin E2 if it is after 16 weeks.
Evacuate
the uterus under G.A.
Blood
transfusion if necessary.
3. Complete Abortion
When the
entire products of conception are passed, abortion is considered complete. It
occurs usually before the 8th week. Bleeding is reduced to mere
staining.
There are
signs of pregnancy regresses.
4. Incomplete Abortion
The fetus
has been expelled but parts of the placenta and membranes are retained
in-utero. Lochia is heavy, bleeding may be profuse, pain may or may not be
present .Os is partly closed – cervix patulous, there is sub -involution.
Treatment
In the District
Send for
medical Aid
Give
syntometrine 1ml or 0.5mg ergometrine 1m and can be repeated 5-10 minute later
if bleeding is profuse, Pethidine 100mg if there is pain,
Resulscitate
if in shock,
5-10
units of oxytocin in 5% glucose
Accompany
to nearby Hospital and give post abortion care.
In Hospital
Give
syntometrine or ergometrine 0.5mg. Take blood for grouping and cross matching.
Take high vaginal swab, evacuation of the uterus is done.
If in
Shock
Receive
into a warm bed, elevate foot of the bed, give ergometrine- i.v.
Infusion
5% dextrose with Ringers lactate, syntocinon 10unit may be added to drip.
Observe vital signs – pulse every 5 minutes B/P – every 30 minutes.
When
condition improves – evacuate under G.A.
Treat for
anemia if present.
Antibiotic
coverage.
Discharge
on the 5th day.
5. Missed Abortion
This term
is applied when the fetus is dead and is retained with it’s placenta in the
uterus. Death usually occurs before 8 weeks though mother may not know.
Ultrasound may diagnose it even before the woman notices it.
Treatment
·
Some obstetrician will prefer to leave it as
spontaneous expulsion will take place: this may cause anxiety and distress to
the mother.
·
Protaglandin E2 may be given to induce
labour in conjunction with i.v oxytocin
·
Mannual Vacuum aspiration of the content may be
performed
·
Blood coagulation disorder may develop if up to 6-8
weeks
·
Plasma fibrinogen estimate weekly
·
If several weeks have elapsed between death and
expulsion of the conceptus give fresh compatible blood.
6. Habitual Abortion
Abortion
is said to be habitual if it has occurred spontaneously for at least three or
more consecutive occasions. The risk of further abortion with subsequent
pregnancies is high. Occurrence is about 1% of all pregnancies and in the early
weeks of pregnancy if pregnancy continues till mid – trimester there is r isk
of threatened abortion or premature labor.
Causes
Most time
unknown occurs more with incompetent cervix Local causes: fibroid, displacement
of the uterus medical
condition
include diabetes mellitus, nephritis, and tuberculosis.
Treatment
Early
booking ,no coitus, hospitalization may be imperative
Shirodker
stitches – (cervical serclage) at about 1 4th –16 th week complete bed rest - ventolin
tablets 2-4mg bid or daily
7. Septic Abortion
Most
common complication of induced or incomplete abortion. It is due to ascending
infection.
Signs & Symptoms
Anemia,
Signs of Miscarriage, Feeling unwell, lower abdominal pain, headache, vomiting,
Pyrexia, rapid pulse, lochia are profuse and offensive.
May be
localized or as generalized septicemia with peritonitis
Treatment
V.
antibiotic for a start, followed by broad spectrum antibiotic that is effective
against anaerobic infection.
Blood Mole
Occasionally
mixed abortion may progress to blood mole. This is a smooth brownish red mass
which contains the fetus and the placenta and it is completely surrounded by
the capsular deciduas. The mole usually forms before 12th week and
it is retained in the uterus for a period of months. Later the fluid is
extracted from the blood and the fleshy, firm hard mass that is remaining is
known as a Carneous Mole. On histological investigation the fetus may be
found in the centre of the mass.
Treatment
Protaglandin
E2 pessaries will be inserted into the vagina to ripen the cervix
followed by i.v. oxytocin – dosage adjusted according to uterine activities.
Analgesic to relief pains. Observation of the mother.
Extra-uterine Pregnancy
When
fertilized ovum embeds outside the uterine cavity, the pregnancy is said to be
extra uterine. Commonly in the fallopian tube, abdominal cavity, cervix and
rarely ovaian .
Tubal Pregnancy /Ectopic Pregnancy Causes:
Congenital
abnormality of the tube, Previous infection, Surgery on the tube IUCD, Assisted
reproductive techniques
Physiology:
The
blastocyst rapidly erodes the epithelial lining of the fallopian tube and
becomes attached to the muscle layer.
Signs & Symptoms
·
History of amenorrhea
·
Mild lower abdominal discomfort or acute Abdominal
pain
·
Occasional attack of sharp and stabbing pain which
is localized in nature
·
Accompanied by nausea
·
There may be brownish vaginal discharge, dizziness,
shoulder pain – bleeding into the peritoneal cavity
Other signs of pregnancy may be absent
·
Ultrasound may assist diagnosis
·
Shock may be present
Possible outcome:
If occurs
near the distal end of the tube
1.
Tubal abortion may result
2.
Tubal mole
3.
Tubal rupture which may be gradual or sudden
4.
Abdominal pregnancy
Abdominal Pregnancy
This is a
rare condition. The fetus develops outside the uterine cavity following
abortion or rupture. Uterine tube placenta attaches to neighbouring organs.
Majority do not survive. If it occurs in early pregnancy, the product gets
re-absorbed . Infection may occur leading to abscess – peritonitis or septicaem
ia. Rarely proceed to term
Diagnosis:
On
Palpation – lie is abnormal, fetal part is readi ly felt
Management:
Delivery
is by laparatomy
Plaenta
may or may not be removed – later is safer.
Prophylatic antibiotic is given.
Baby:
May have
compression deformities due oligohydramnios
Hydatidiform Mole
Case of
gross malformation of the trophoblast. The chorionic villi proliferate and
become vesicles which looks like a bounch of English grape. Risk is higher in a
woman who has had it before – (1 in 50) and under the age of 20 and above 40
years. There are 2 types:
Complete. No evidence of embryo, cord or
membrane .
Incomplete has evidence of embryo, fetus or
amniotic sac.
Signs & Symptom:
These
vary according to type of mole. Exaggerated pregnancy symptoms by 6 – 8 weeks.
Bleeding or blood stained vaginal discharge after a period of amenorrhea.
·
Slight pink or brownish discharge,
·
Passage of vesicles per vaginam,
·
Anaemia,
·
High chorionic gonadotrophic hormone (CGTH) level,
·
Pre-eclampsia in early pregnancy,
·
On palpation – uterus larger than date, feels dough
y or elastic, no fetal parts, no fetal height can be mapped, no fetal movement.
Diagnosis
Ultrasound,
Increase CGTH,
Treatment
Remove
all the trophoblastic tissues, Terminate pregnancy, Follow up to 2 year until
CGTH is negative, Give psychological support.
Post Abortion Care (PAC)
This is
an approach for reducing morbidity and mortality from incompetent and unsafe
abortion and resulting complications and for improving women’s sexual and reproductive
health lives.
Elements of PAC:
There are
5 elements of PAC which are:
·
Treatment of incomplete and unsafe abortion and
abortion related complications that are potentially life threatening
·
Counseling to identify and respond to women’s
emotional and
·
Physical health needs and other concerns
·
Contraceptives and family planning services to
o
Help women prevent unwanted pregnancy
o
Encourage the practice of birth spacing
o
Reproductive and other health services that are:
Provided on-site
o
Provide via referrals to other facilities in
providers’ networks
·
Community and service provider partnerships to:
o
Prevent unwanted pregnancies and unsafe abortion
o
Mobilize resources for timely care for
complications from abortion
o
Ensures health services reflect and meet community
expectations and needs
Principles that Support Patients’ Rights in PAC Setting
o
Having empathy and respect for patients
o
Maintaining positive interaction and communication
with patients
o
Respecting privacy and confidentiality
Roles of the Midwife in PAC
The
midwife is the general overseer or manager of the totality of Manual vacuum
Aspiration (MVA) services within the facility
o
The midwife has the responsibility of ensuring that
the facilities and the necessary equipments are always available at the MVA
room. Portable water should be made available.
o
She should ensure proper cleaning and setting of
trolley. She must also ensure completeness of the items on both shelves of the
trolley
o
Pre and post procedure care of the patients is an
important responsibility of the midwife.
o
Her role in the actual MVA procedure depends on
whether she is permitted to carry out the procedure or to assist the doctor
during a procedure. In which ever situation, she must have a good grip of the
procedure.
o
She must posses a proper understanding of cleaning
and sterilization/or disinfecting of equipment used during the procedure and
disposal of wastes, aspirates and sharp instruments in order to prevent
infection especially HIV/AIDS
o
She is responsible for keeping record of details of
the procedure.
Manual Vacuum Aspiration (MVA)
This is a
procedure carried out to evacuate uterine contents in incomplete abortion. The
indications are:
o
Threatened or imminent abortion, Inevitable
abortion, Incomplete abortion
o
Infected abortion, Missed abortion, An embryonic
pregnancy, Hydatidiform mole
o
Retained placental products
Advantages
·
Requires only slight dilatation and scrapes gently
·
Lower risk of complications, Lower cost of
services, Can be used in low resource setting, Decreased need for hospitalization,
is a day case.
The
procedure is usually carried out by trained heath personnel. (Refer hand book
for nurses and midwives for details)
Related Topics