Chapter: 11th Food Service Management : Chapter 5 : Bakery
Baking Ingredients
Baking
Ingredients
1.
Wheat
flour / Maida
2.
Leavening
agents
3.
Yeast
4.
Baking
powder
5.
Eggs
6.
Shortenings
7.
Sugar
1. Wheat Flour / Maida
·
Wheat is
used principally for baking.
·
Wheat
contains 6–18 per cent protein.
·
Wheat
flour contains glutelin and gli-adin as proteins which are commonly known as
gluten (functional protein).
·
The
strength of the wheat flour is based on the quality of gluten used.
·
The
quality of baking is related to the strength of wheat.
·
Maida is
the refined wheat flour which is commonly used.
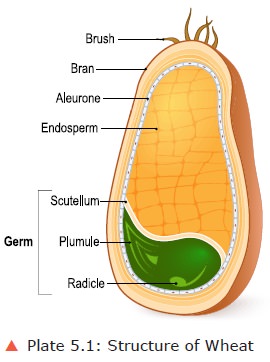
Structure
of Wheat: Wheat grains are composed of outer bran coats, a germ and
starchy endosperm.
a. Bran
·
Bran is
the outer layer of the kernel and constitutes 5 percent of the kernel.
·
During
milling the bran is discarded.
·
Bran is
rich in fibre, minerals, thia-mine and riboflavin.
b. Aleurone Layer
·
This is
located just under the bran.
·
It is rich in protein, phosphorous, thi-amine and
also contains moderate amount of fat.
·
The aleurone layer makes up about 8 percent of the
whole kernel and is lost in the milling process along with bran.
c. Endosperm
·
This is
the large central part of the ker-nel and constitutes 84-85 percent of the
kernel.
·
The
endosperm consists mainly of starch and protein. But low in mineral matter,
fibre, fat and vitamins.
d. Germ
·
This is a small structure at the lower end of the
kernel and is separated from the endosperm by the scutellum.
·
It makes up 2-3 percent of the whole kernel.
·
It is rich in protein, fat, vitamins and minerals.
·
Germ serves as a store of nutrients for the seed
during germination. During milling some of the germ is lost along with the bran
and aleurone layer.
II. Types of Wheat
a. Hard
Wheat: Hardness is related to the degree of adhesion between starch and
protein. Hard wheat yields coarse flour and is a good source of gluten. It is
used to make bread flour.
b. Soft
Wheat: Soft wheat gives very fine flour and contains less amount of good
quality protein. It is used for making cakes, cookies and pastries.
c. Strong Wheat: Strong wheat is used to make good quality bread because it
produces large loaf volume, good crumb structure and product with good keeping
qualities. It has a high protein content.
d. Weak
Wheat: Low protein content in weak wheat produces only a small loaf with
coarse crumb structure. The flour of weak wheat is good for biscuits and cakes.
![]()
III. Types of Wheat Flour
Some of the types of flours used
for bak-ing are as follows:
a. Bread Flour:
·
It is
milled from blends of hard wheat.
·
The
moisture content, protein content, and starch quality can be controlled.
·
It is
used mainly for making products leavened with yeast.
b. Soft
Flour: It is used for making all types of high quality cakes and sponge cakes.
c. Self-Raising Flour:
·
A mixture of wheat flour and sodium carbonate is
known as self-raising flour.
·
This
flour is used for making pud-dings, cakes, pastries etc.
d. All-Purpose Flour:
·
It is made from blend of hard and soft wheat and
has a moderate protein content.
·
It is
suitable for use in the yeast and quick breads, biscuits, pastries and cakes.
e. Biscuit Flour
·
Biscuit flour is made from weak wheat of low protein
content.
·
The flour should make a dough hav-ing more
extensibility, but less spring (resistance) than bread dough.
·
The extensibility of biscuit flour dough may be
increased by the addition of sodium metabisulphite to the dough.
·
Dough pieces should retain the size and shape after
being stamped out.
f. Cake Flour
·
Cake flour is a medium strength flour ground from
soft low protein wheat of fine structure.
·
This
flour allows the aerated structure to be retained after the cake has been built
up.
g. Pastry
Flour: Pastry flour is made of soft wheat which is fairly low in protein.
2. Leavening Agents:
Leavening agents are substances
that cause expansion of dough and batters by releasing gases. It produces
porous struc-ture in the baked products. The important leavening agents are as
follows:
a.
Yeast
b.
Baking
powder
c.
Steam
obtained from heating of the dough in the oven
d.
Air in a
dough or batter expands in the oven while heated
e.
Carbon-di-oxide
from fermentation.
3. Yeast
Yeast: Two forms of
yeast used in
baking are
·
moist compressed yeast
·
active
dry yeast
In the bread making process yeast ferments simple sugars and produces
car-bon-di-oxide and alcohol. The increase in fermentation rate with time is
due to two conditions in a dough.
a.
Yeast cells are multiplying and the enzymes are
becoming more active while the dough is prepared and held.
b.
Sugar for fermentation is gradually being liberated
from starch in the dough by the action of natural flour enzymes.
4. Baking Powder
Baking
Powder: Baking powders are related foods that contain particles of
sodium-bi-carbonate. Baking powders are of three kinds:
·
Fast
acting
·
Slow
acting and
·
Double
acting powders (contain both fast and slow acting in combination with sodium
bi-carbonate).
5. Egg:
· Egg acts as principle structure builder.
·
It adds flavour, colour and increases the nutritive
value of the baked product.
·
Egg white contains protein. When whipped it forms
films and entraps air. On heating it coagulates to produce rigidity.
6. Shortenings:
·
Shortenings
are fats and oils.
·
Butter,
margarine and hydrogenated oils are the most common shortenings used in baking.
·
It acts
as tenderizers.
·
It melts
and releases air bubbles which will help in the leavening action of baking
powder and expanding steam.
7. Sugar:
·
Sugar is a tenderizer in baked foods.
·
It is necessary for yeast growth and indirectly
aids the fermentation process.
·
Brown colour of the crust is due to the Maillard
reaction between the protein and sugar which occurs during baking.
·
It influences the tenderness and the volume of
baked products. Honey and glucose are also used in baked products.
8. Other Ingredients:
Milk powder and skimmed milk are used in bread and bun making. It
increases the nutritive value of bread. It improves fla-vour and gives a brown
crust.
Oxidising agents like potassium bromate, potassium iodate and calcium
peroxide are used to improve the handling characteristics of the dough and
spe-cific volume and texture of the finished products.
Salt has a retarding effect on yeast fermentation. Salt is used as a
taste enhancer and as a preservative.
Water is important for gluten formation. It dissolves sugar and salt
and serves as a dispersion media for yeast cell.
Related Topics