Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Bacteria : Introduction, Occurrence, Size
Bacteria Introduction
In 1676 Anton Van Leeuwenhoek discovered the microbial world by his simple microscope. It was only after the invention of compound microscope by Hooke in 1820, that bacteria came to lime light. These very minute creatures were designated as 'small microscopic species' or ' Infusorial animalcules'. Louis pasteur(1822-95 ) made a detailed study of bacteria and proposed germ theory of disease. Robert Koch, a german microbiologist, was the first scientist to prove the cause and effect relationship between microbes and animal diseases. Ehrenberg(1829) was the first to use the term bacterium. The branch of study that deals with bacteria is called Bacteriology. Bacteria are unicellular organisms and they are prokaryotic. i.e they do not have a membrane bound nucleus and membrane bound organelles .
Occurrence
Bacteria are omnipresent. They are found in all environments, where organic matter is present. They are found in air, water, soil and also in or on the bodies of plants and animals. Some of the bacteria live as commensals (eg. Escherichia coli in the human intestine) and some live as symbionts (eg. Rhizobium) in the root nodules of leguminous plants. Several of them cause diseases in plants, animals and human beings.
Size
Bacteria are very small, most being approximately 0.5 to 1 micron in diameter and about 3 to 5 microns in length.
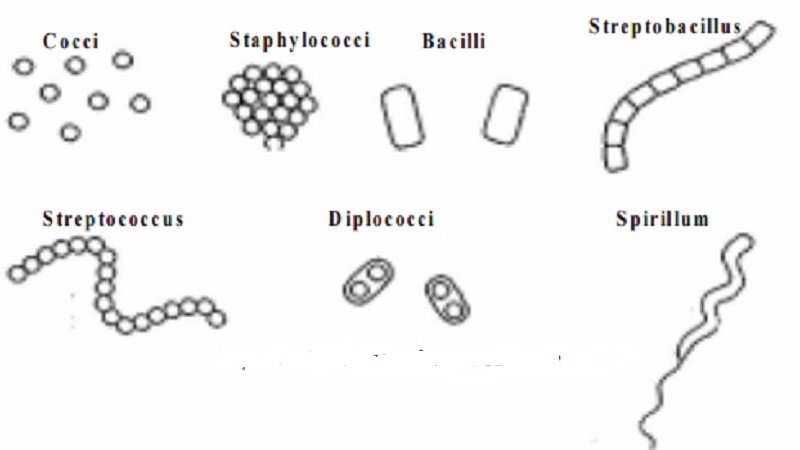
Classification of bacteria based on the shape and arrangement
The rigid bacterial cell wall determines the shape of a cell. Typical bacterial cells are spherical (Cocci), straight rods (Bacilli) or rods that are helically curved (spirilla), some bacterial cells are pleomorphic ie they can exhibit a variety of shapes eg. Arthrobacter
Cocci bacteria appear in several characteristic arrangements depending on their plane of division.
Related Topics