Chapter: Mechanical : Computer Aided Design : Assembly of Parts
Assembly of Parts
ASSEMBLY OF PARTS
PRE-REQUISITE DISCUSSION
Assembly modeling is a technology
and method used by computer-aided design and product visualization computer
software systems to handle multiple files that represent components within a
product. The components within an assembly are represented as solid or surface
models.
ASSEMBLY MODELING OF PARTS
•
Assembly modeling is a combination of two or more
components using parametric relationships.
•
Typically a designer would start with a base part
•
Add other components to the base part using
merge commands.
Assembly
Tree
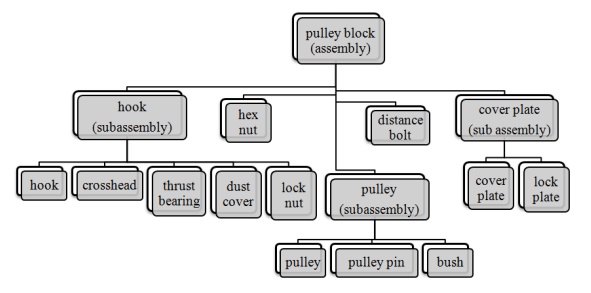
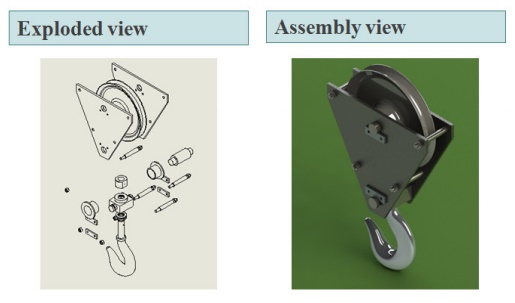
Exploded view
An
exploded view consists of series of steps. One can create steps by selecting
and dragging parts in graphical area.
Example -
Assembly of Pulley block
Bottom-up assembly approach - :
•
Allows the designer to use part drawings that
already exist (off the shelf)
•
Provides the designer w ith more control over
individual parts
•
Multiple copies (instan ces) of parts can be
inserted into the assembly
Top-down assembly approach - :
•
The approach is ideal for large assemblies
consisting of thousands of parts.
•
The approach is used to deal with large designs
including multiple design teams.
•
It lends itself well to t he conceptual design
phase
•
E.g. :
▫
Piping and fittings
▫
Welds
▫
Lock pins
Degrees
of freedom -:
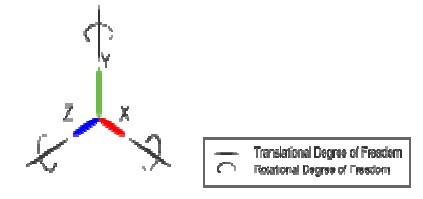
Translation
– movement
along X, Y, and Z axis
•
Rotation – rotate about X, Y, and Z
axis
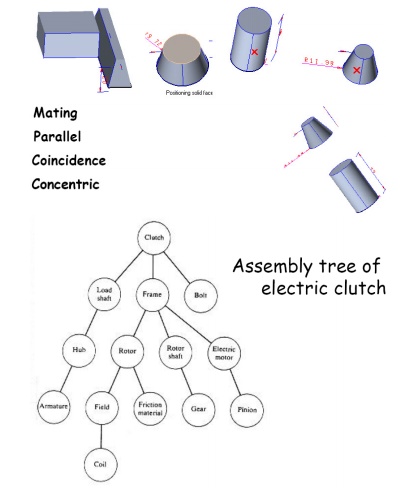
Mating
conditions -:

Assembly Constraints
•
Constraints can be used to create permanent
relationships between parts
•
THEY use the same commands as 2D constraints
•
Typical constraints:
– two faces meet
– axes coincident
– two faces parallel at fixed distance
Assembly sequence affects
• difficulty
of assembly steps
• need for
fixture
• potential
for parts damage during assembly and part mating
• ability
to do in-process testing
• occurrence
of the need for reworking
• time of
assembly
• assembly
skill level
• unit cost
of assembly
Mating condition
• Part
coordinates MCS (modeling coord.)
• Base
part: Datum
• Global CS
• Local CS
• Explicit
position and direction vs mating conditions
• 4 x 4
homogeneous transformation matrix
Mating feature
Types: against, fits, contact, coplanar fits: center
lines are concentric
• Mating
condition = mating type + two faces
• Normal
vector + one point on the face
• against:
two normal vectors are in against directions
• fits:
between two cylinders: center lines are concentric
• Against
and fits allows rotation and translation between parts
Interference fit
• Fits is
clearance fit
• tight
fits is interference fit
• Coplanar:
two normal vectors are parallel
• ‘Coplanar’
complements ‘against’
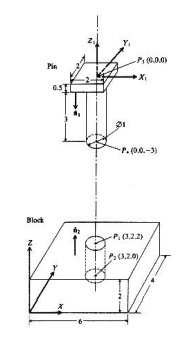
Example
Pin and block
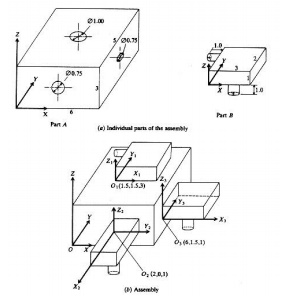
Assembly
from instances
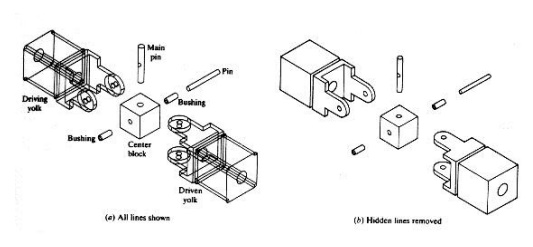
Exploded
view of universal joint
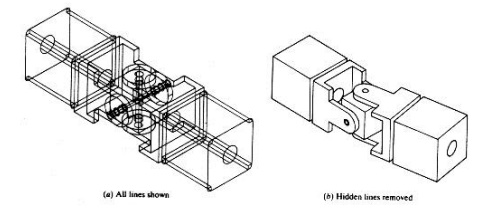
Assembly
view of universal joint
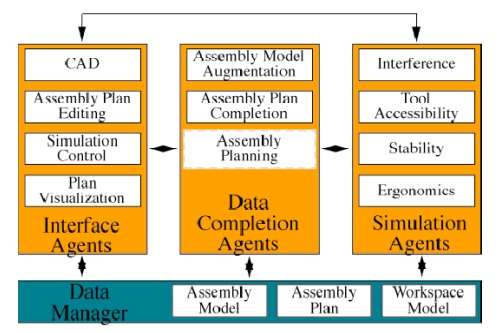
LAYOUT OF INTELLIGENT ASSEMBLY MODELING AND SIMULATION
The goal of IAMS is to avoid this expensive and
time-consuming process by facilitating semblability checking in a virtual,
simulated environment.
In addition to part-part interference checking,
the IAMS tool will check for tool accessibility, stability, and ergonomics.
Intelligent
Assembly Modeling and Simulation
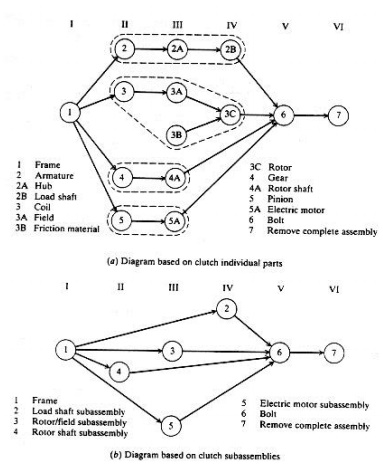
PRECEDENCE DIAGRAM
• Designed
to show all the possible assembly sequences of a product.
• Each
individual assembly operation is assigned a number.
• Diagram
is usually organized into columns
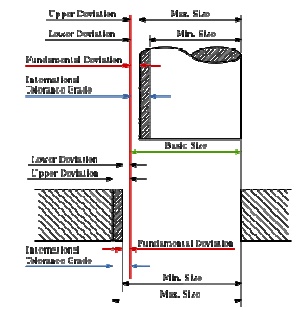
PRODUCTION
DRAWING LIMITS, FITS AND TOLERANCE
Limit
system
There are three terms used in the limit system:
1. Tolerance: Deviation from a basic value
is defined as Tolerance. It can be obtained by taking the difference
between the maximum and minimum permissible limits.
2. Limits: Two extreme permissible sizes
between which the actual size is contained are defined as limits.
3. Deviation: The algebraic difference
between a size and its corresponding basic size. There are two types of
deviations: 1) Upper deviation 2) Lower deviation
The fundamental
deviation is eith er the upper or lower deviation, depending on which is closer
to the basic size.
Tolerances
Due to human erro rs, machine settings, etc., it
is nearly impossib le to manufacture an absolute dimension as specified by the
designer. Deviation in dimensi ons from the basic value always arises. Thi s
deviation of dimensions from the basic v alue is known as Tolerance.
The figure shows mechanical tolerances which
occur during operations.
Fits
The relation
between two mating parts is called fit. Depending upon the actual lim its of the hole or shaft sizes,
fits may be classified as clearance fit, transition fit and interference fit.
Clearance fit
Clearance fit is
defined as a cleara nce between mating parts. In clearance fit, ther e is
always a positive clearance between the hole and shaft.
Transition fit
Transition fit may
result in either an interference or clearance, depending upon th e actual
values of the tolerance of individual parts.
Interference fit
Interference fit is obtained if
the difference between the hole and shaft sizes is negative before assembly. Interference fit generally ranges
from mini mum to maximum interference. The two extr eme cases of interference
are as follows:
Minimum interference
The magnitude of the difference
(negative) between the maximum size of the hole and the minimum size of the shaft in an interference fit before assembly.
Maximum interference
The magnitude of the difference
between the minimum size of the hole and the maximum size of the shaft in an
interference or a transition fit before assembly.
Hole Basis and shaft basis system:
In identifying limit dimensions for the three classes of fit,
two systems are in use:
1. Hole basis system: The size of the
shaft is obtained by subtracting the allowance from the basic size of
the hole. Tolerances are then applied to each part separately. In this system,
the lower deviation of the hole is zero. The letter symbol indication for this
is 'H'.
2. Shaft basis system: The upper deviation of the shaft is zero, and the size of the hole is obtained by adding the allowance to the basic size of the shaft. The letter symbol indication is 'h'.
Related Topics