Employment in India and Tamil Nadu | Economics | Social Science - Answer in detail | 9th Social Science : Economics : Employment in India and Tamil Nadu
Chapter: 9th Social Science : Economics : Employment in India and Tamil Nadu
Answer in detail
Social Science : Economics
EMPLOYMENT IN INDIA
AND TAMILNADU
V. Answer in detail
1. Explain: (a) primary sector,
(b) secondary sector; (c) tertiary sector.
a) Primary sector:
• Primary sector consists of agriculture, animal husbandry,
poultry, fishing etc.
• In developing countries like India, large working force will
be engaged in primary occupation. The primary sector is also known as
agriculture sector.
b) Secondary
sector:
• Secondary sector includes manufacturing, small and large scale
industries and constructional activities.
• In developing countries like India a small proportion is
engaged in secondary sector. The secondary sector is also known as industrial
sector.
c) Tertiary sector:
• Tertiary sector includes transport, insurance, banking, trade,
communication, and non-government services.
• In developing countries like India a small proportion is
engaged in tertiary sector. Tertiary sector is also known as service sector.
2. Explain the employment
structure of India.
• The nature of employment in India is multi-dimensional. Some
get employment through out the year, some others get employment only a few
months in a year.
• The economy is classified into three sectors. They are primary
or agriculture sector, secondary or industrial sector and tertiary or service
sector.
• In developing countries like India a large working force will
be engaged in primary sector.
• Only a small proportion of working force will be in the
secondary and tertiary sectors.
• Employment growth has increased at an average rate of 2%
during the past four decades since 1972-73.
3. Compare the employment
conditions prevailing in the organised and unorganised sectors.
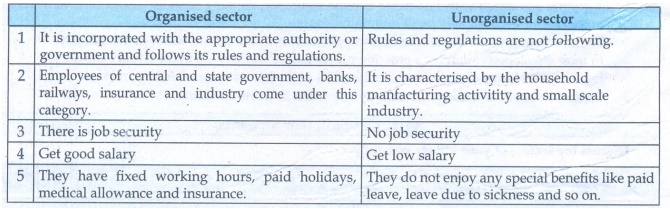
Organised sector
1. It is incorporated with the appropriate authority or
government and follows its rules and regulations.
2. Employees of central and state government, banks, railways,
insurance and industry come under this category.
3. There is job security
4. Get good salary
5. They have fixed working hours, paid holidays, medical
allowance and insurance.
Unorganised sector
1. Rules and regulations are not following.
2. It is characterised by the household manfacturing activitity
and small scale industry.
3. No job security
4. Get low salary
5. They do not enjoy any special benefits like paid leave, leave
due to sickness and so on.
4. Distinguish between Public sector and the Private sector
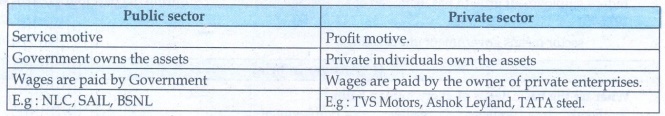
Public sector
• Service motive
• Government owns the assets
• Wages are paid by Government .
• Eg : NI,C, SAIL, BSNL
Private sector
• Profit motive.
• Private individuals own the assets
• Wages are paid by the owner of private enterprises.
• Eg: TVS Motors, Ashok Leyland, TATA steel.
Related Topics